Definition & Meaning: Word Root -Cracy
The word root ‘-Cracy’ derives from the Greek ‘-kratia’, meaning ‘power’ or ‘rule’. It predominantly describes various forms of governance or rule. For example, ‘plutocracy’ denotes a government controlled by the wealthy, a composition of:
- Pluto/Plut: Wealth
- Cracy: Rule
Thus, Pluto + Cracy = Government/rule by the wealthy.
This root is primarily utilized within political science to categorize different governmental systems.
Example sentence:
“In the past, the country experienced years of political turmoil, transitioning from a neocracy to a kleptocracy.”
Enhanced Introduction
The exploration of political systems and their classifications offers a window into understanding how societies are structured and governed. The root ‘-Cracy’ is instrumental in this examination, providing the linguistic framework to dissect the myriad ways power can be wielded and distributed. From ancient oligarchies to contemporary democracies, ‘-Cracy’ encapsulates the essence of governance, reflecting the diversity of political ideologies and practices.
Words Based on the Root -Cracy
Commonly Used Words
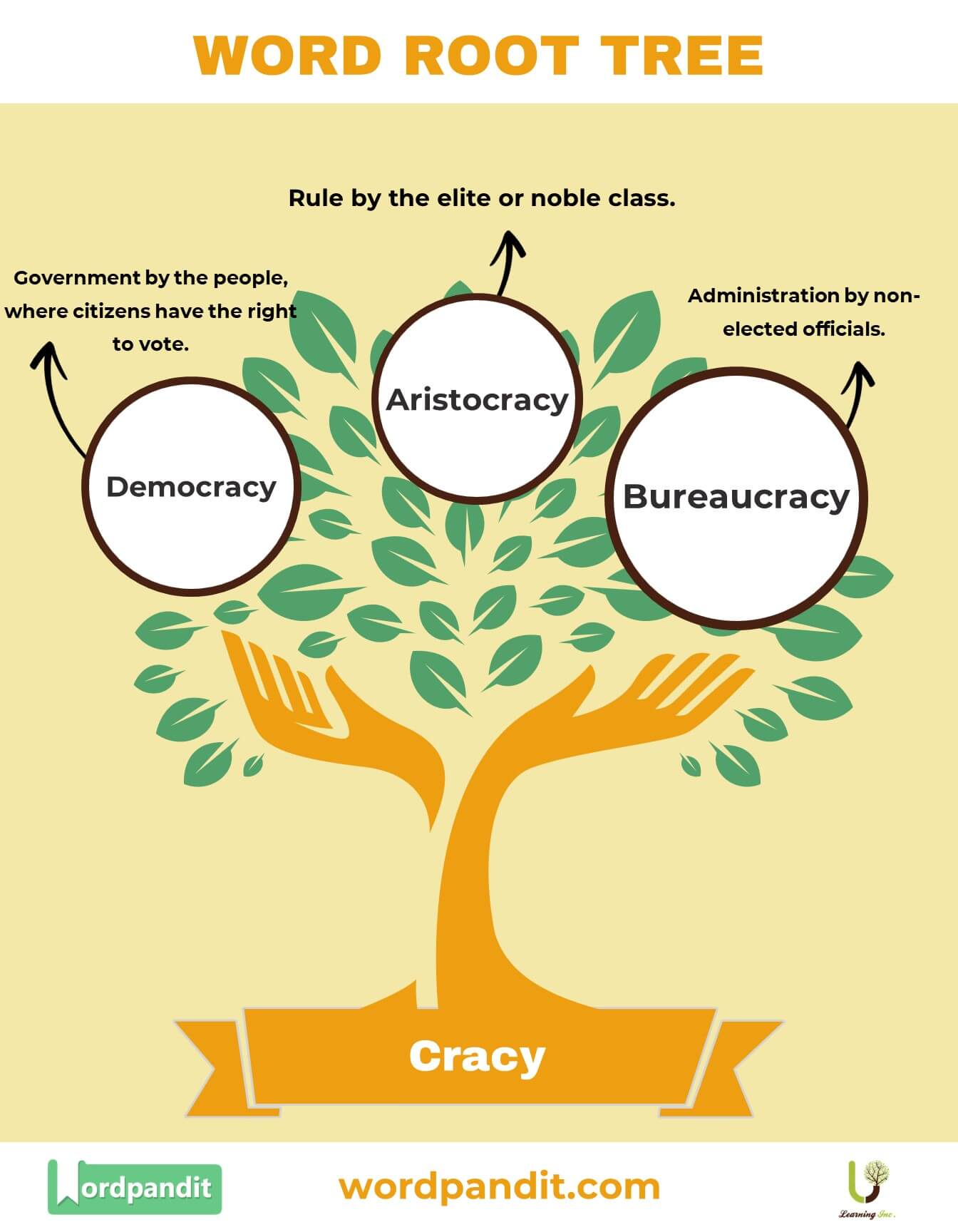
- Democracy: Government by the people, where citizens have the right to vote.
- Aristocracy: Rule by the elite or noble class.
- Bureaucracy: Administration by non-elected officials.
- Autocracy: Rule by a single individual with absolute power.
Archaic Words
- Timocracy: A system where only property owners may participate in government.
- Stratocracy: Rule by military chiefs.
- Diabolocracy: Hypothetical rule by a devil, used more in a metaphorical sense.
Technical Words/Jargon
- Kakistocracy: Governance by the least qualified or most unprincipled citizens.
- Ochlocracy: Rule by the mob or a mass of people.
- Gerontocracy: Governance by the elderly.
Related Word Roots
-Archy (Rule)
- Monarchy: Rule by a single sovereign, typically a king or queen.
- Oligarchy: Rule by a small, elite group.
- Anarchy: A state of society without government or law.
-Nomos (Law)
- Economy: The management of the resources of a community, country, etc.
- Autonomy: The right or condition of self-government.
- Astronomy: Originally, laws governing the celestial bodies, now the science that deals with the material universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere.
By examining ‘-Cracy’ and its associated terms, we embark on a temporal journey that extends beyond the mere measurement of time. It encompasses the human endeavour to comprehend our place in history, the rhythm of the natural world, and the unfolding of events. This exploration not only broadens our linguistic repertoire but also connects us more deeply with the universal experience of time itself, underscoring the power of language to bridge epochs and cultures.