📚 Literature and Arts: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
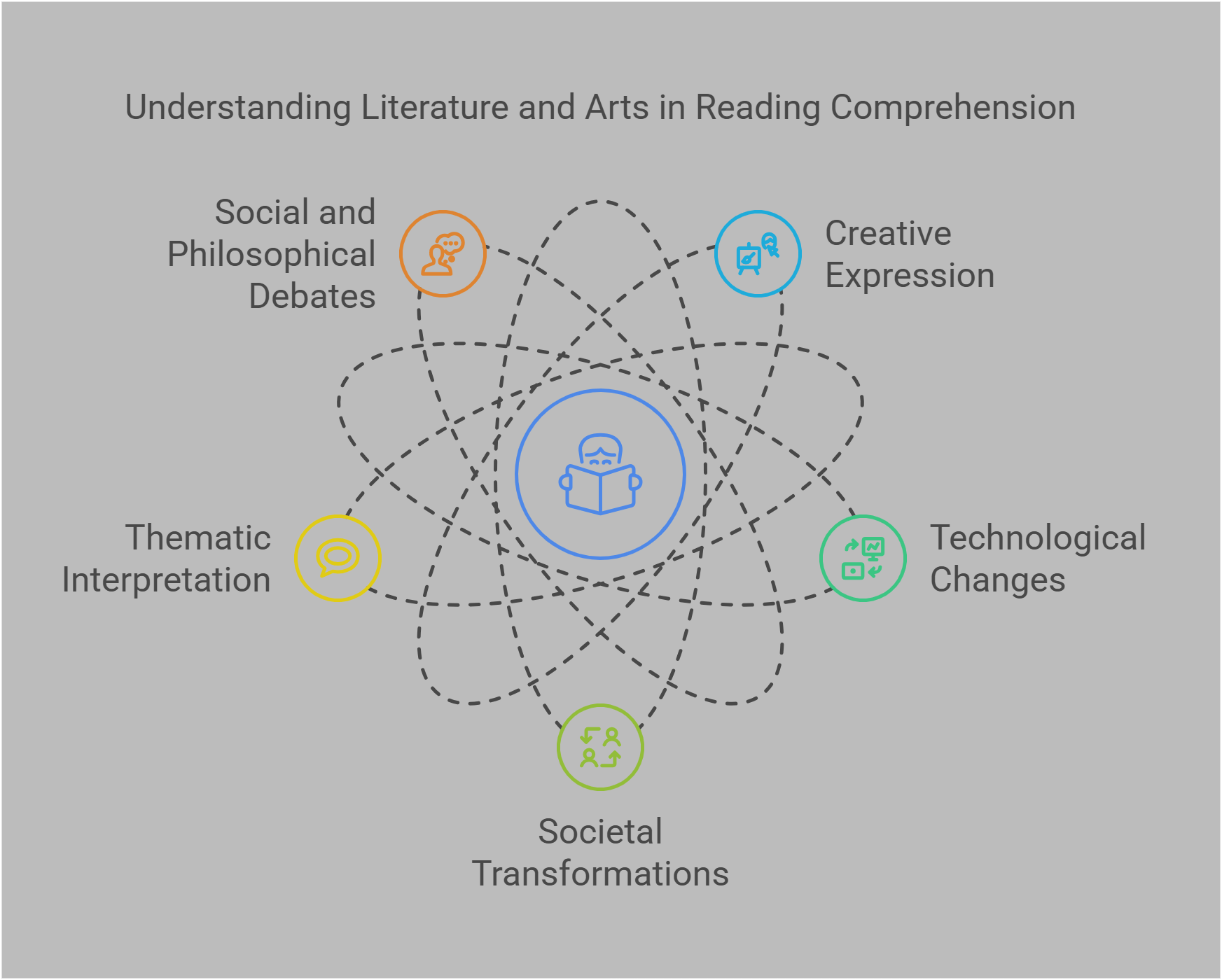
Literature and arts topics in reading comprehension passages delve into how creative expression evolves amidst technological changes and societal transformations. Understanding these concepts enhances one’s ability to interpret arguments, appreciate thematic underpinnings, and engage with complex artistic narratives in RC passages. These themes are often intertwined with critical social or philosophical debates, offering rich material for analysis and interpretation.
📝 Overview
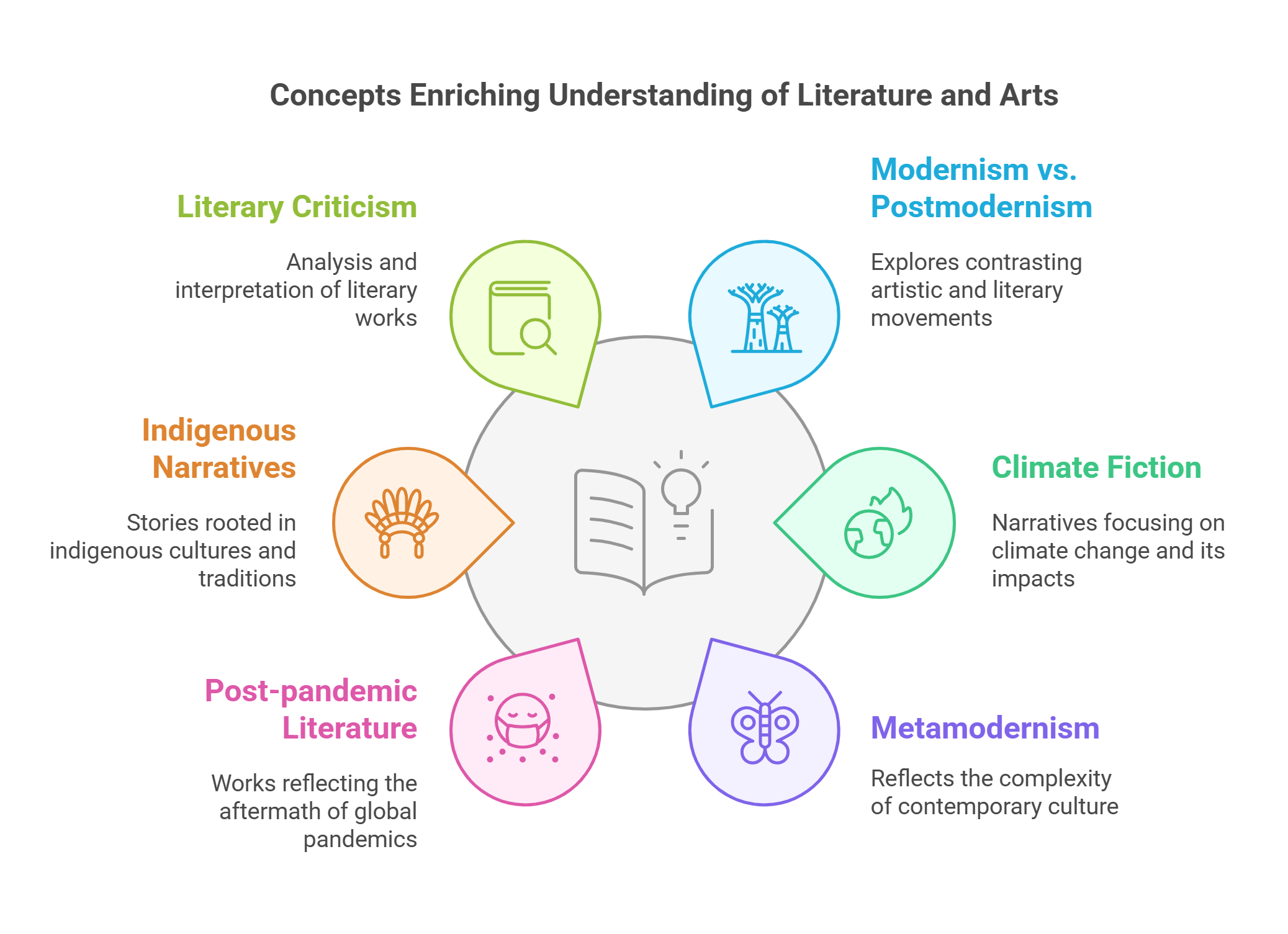
In this guide, we explore ten essential concepts related to literature and the arts:
- Modernism vs. Postmodernism
- Climate Fiction (Cli-Fi)
- Metamodernism
- Post-pandemic Literature
- Indigenous Narratives
- Literary Criticism
- Art Movements
- Visual Arts
- Performing Arts
- Cultural Heritage
🔍 Detailed Explanations
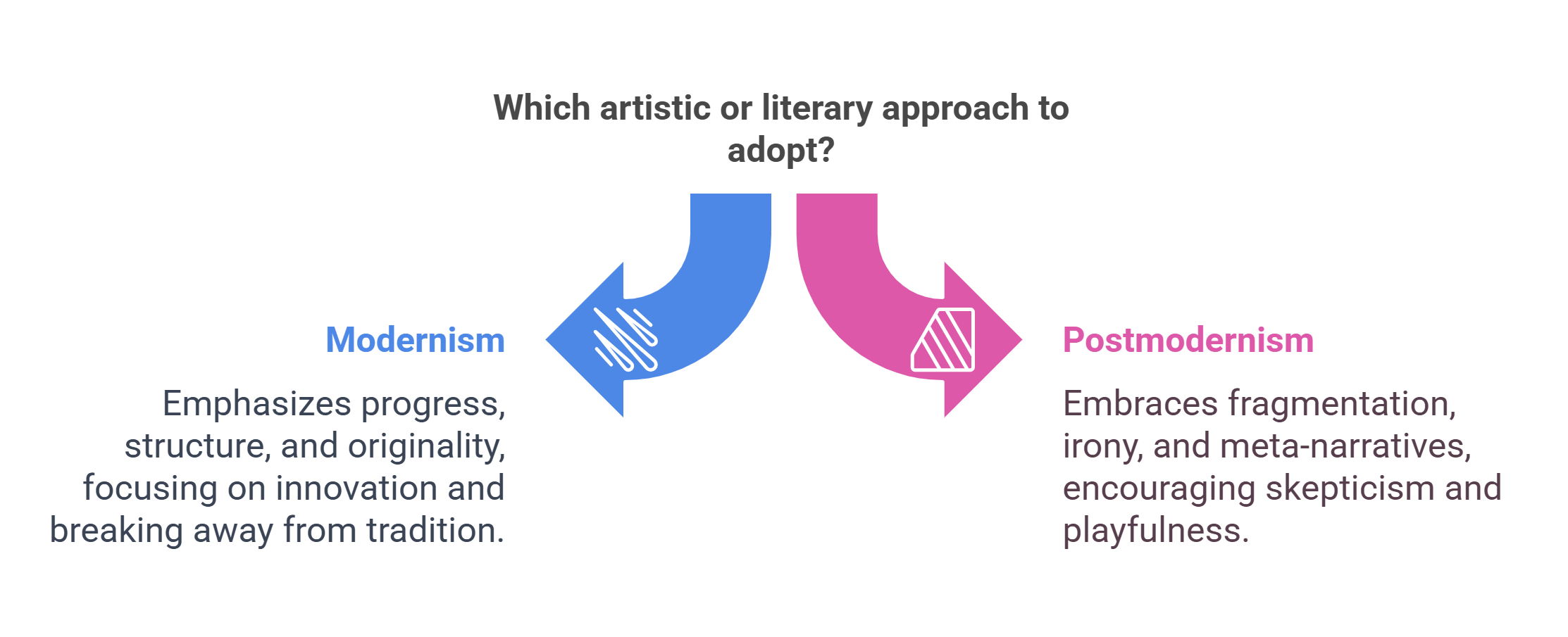
1. Modernism vs. Postmodernism
Modernism focuses on breaking away from traditional forms and embracing innovation, individuality, and the idea of progress. In contrast, postmodernism often critiques modernism’s grand narratives, embracing skepticism, fragmentation, and playfulness in artistic and literary expression.
- Modernism: Emphasizes progress, structure, and originality.
- Postmodernism: Highlights fragmentation, irony, and meta-narratives.
- Both reflect responses to social and cultural changes.
- Applications in understanding evolving art and literature.
Explained Simply: Imagine building a Lego city with all perfect blocks (Modernism), and then deciding it’s fun to mix colors, leave gaps, and add random toys to the city to make it surprising (Postmodernism).
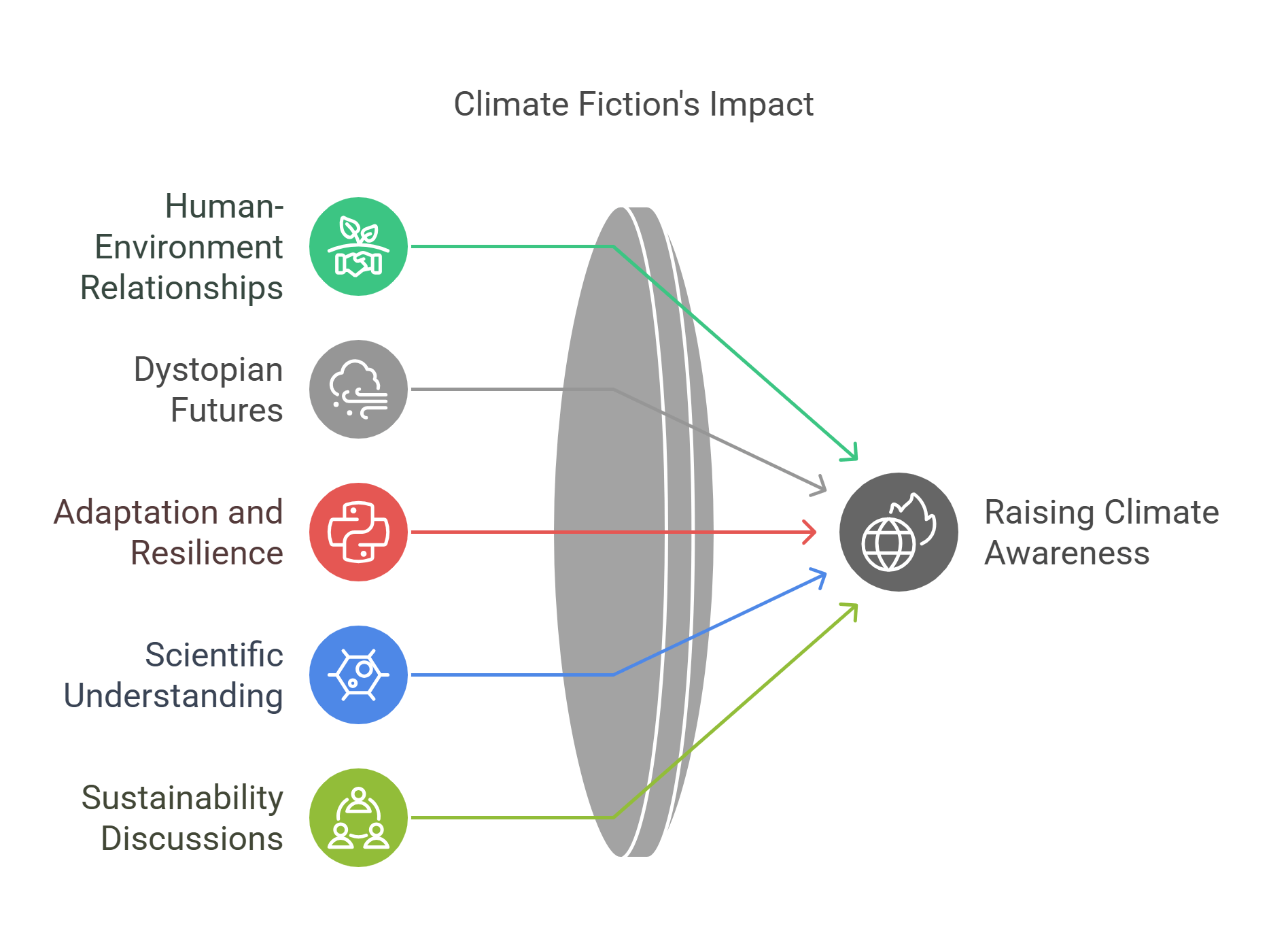
2. Climate Fiction (Cli-Fi)
Climate Fiction (Cli-Fi) explores the impacts of climate change through imaginative storytelling. This genre often integrates ecological themes with speculative or dystopian settings, making abstract environmental challenges relatable and urgent.
- Explores human-environment relationships.
- Often set in dystopian or speculative futures.
- Highlights themes like adaptation and resilience.
- Combines scientific understanding with narrative art.
- Sparks discussions on sustainability and ethics.
Explained Simply: Imagine a story where superheroes fight to save the world, not from villains, but from storms, fires, and melting ice! That’s what Climate Fiction does—it makes nature the big story.
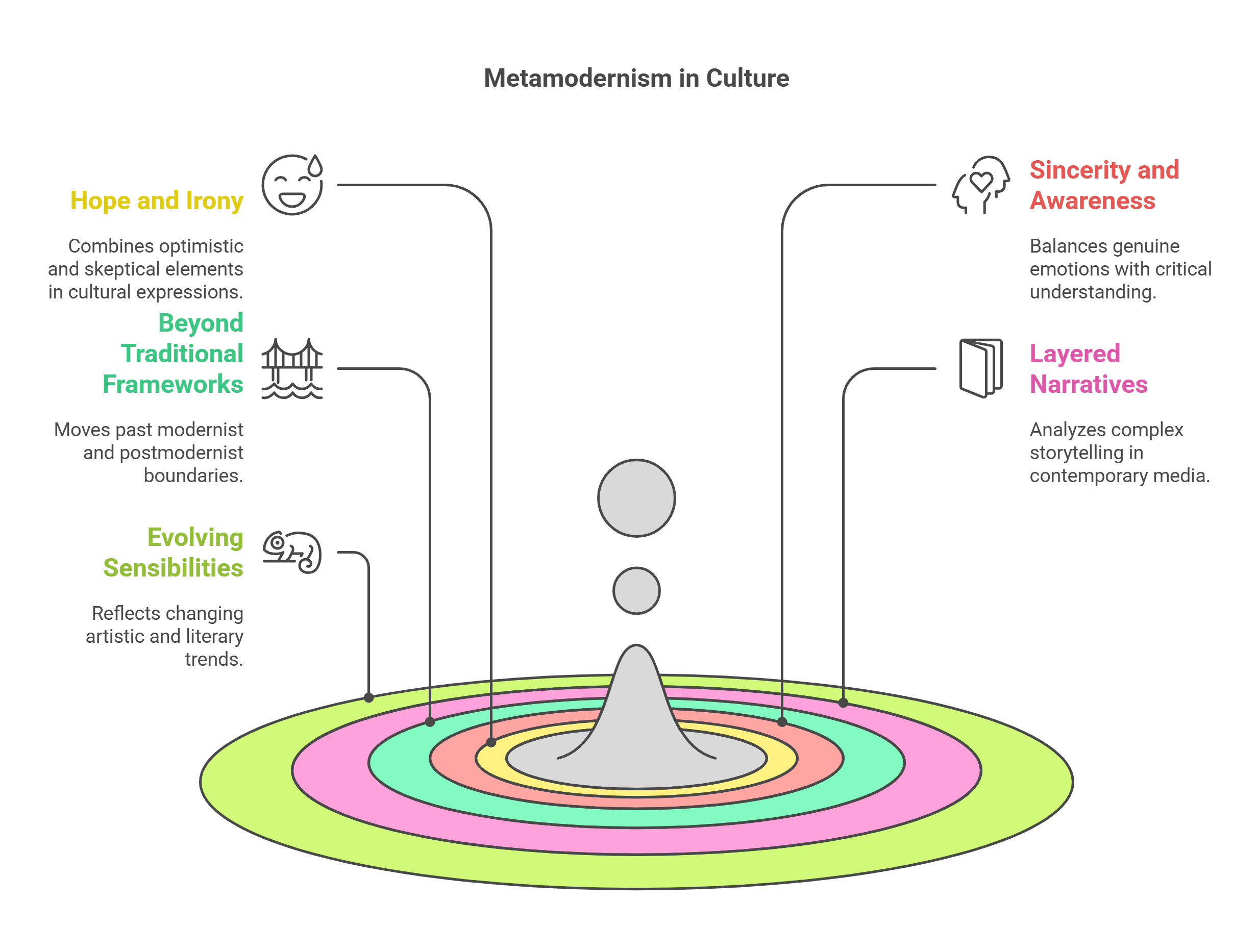
3. Metamodernism
Metamodernism oscillates between the structured innovation of Modernism and the ironic skepticism of Postmodernism. It represents a cultural synthesis that combines sincerity, hope, and self-awareness. This movement reflects contemporary society’s blend of optimism and doubt, often evident in modern storytelling and art.
- Combines hope and irony in cultural expression.
- Balances emotional sincerity with critical awareness.
- Moves beyond strict modernist or postmodernist frameworks.
- Relevant in analyzing layered narratives.
- Reflects evolving artistic and literary sensibilities.
Explained Simply: Think about a movie where characters laugh, cry, and joke all at once—like balancing funny and serious feelings together. That’s the magic of metamodernism!
4. Post-pandemic Literature
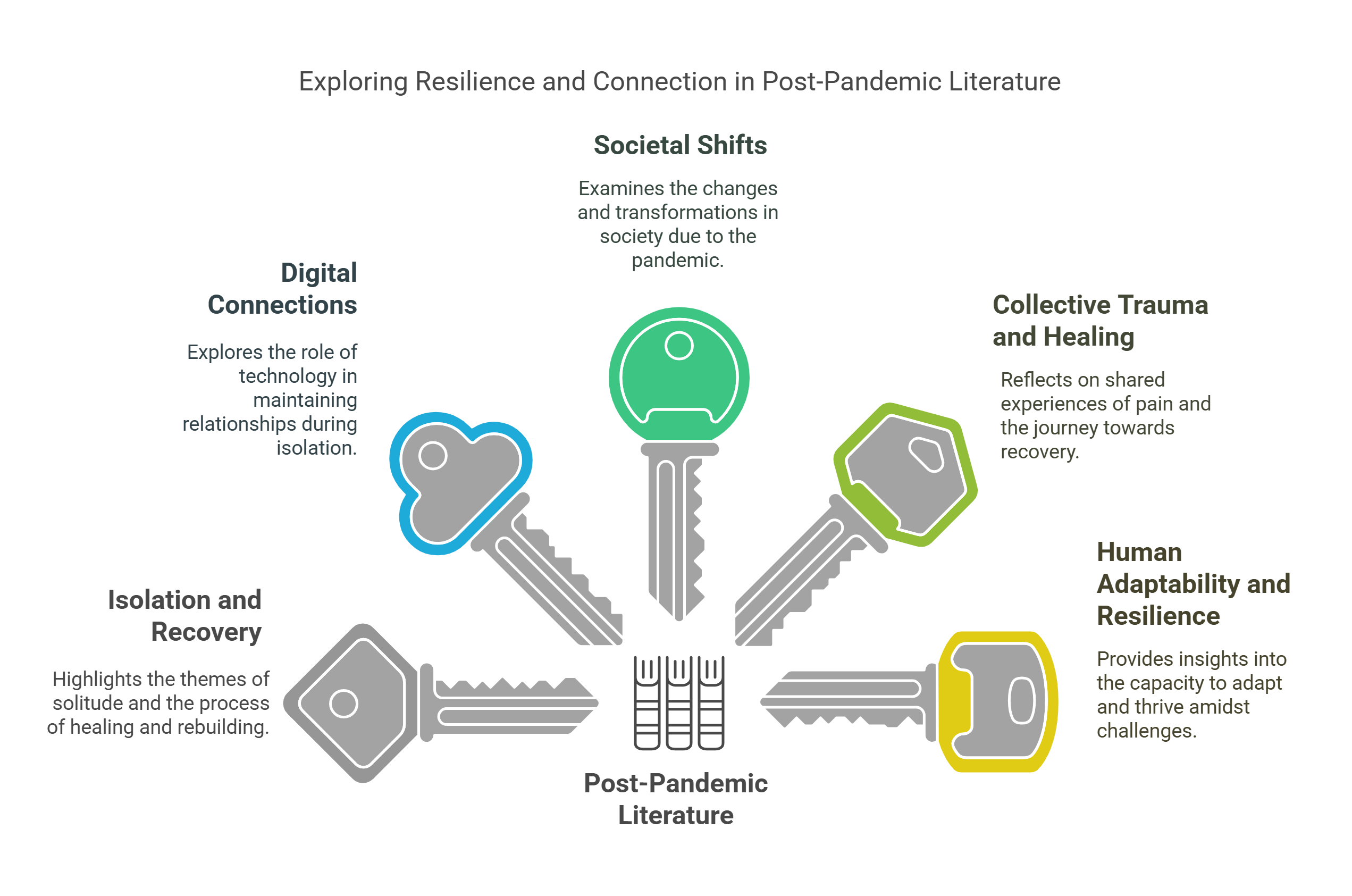
Post-pandemic literature captures themes of isolation, resilience, and societal transformation prompted by global health crises. It often reflects on the fragility of human connection, the role of technology in sustaining relationships, and collective efforts to overcome adversity.
- Focuses on themes of isolation and recovery.
- Explores digital connections and societal shifts.
- Reflects on collective trauma and healing.
- Provides insights into human adaptability and resilience.
- Relevant in analyzing contemporary narratives.
Explained Simply: Imagine stories about people finding new ways to play, talk, and stay friends even when they’re stuck at home—that’s what post-pandemic literature is about!
5. Indigenous Narratives
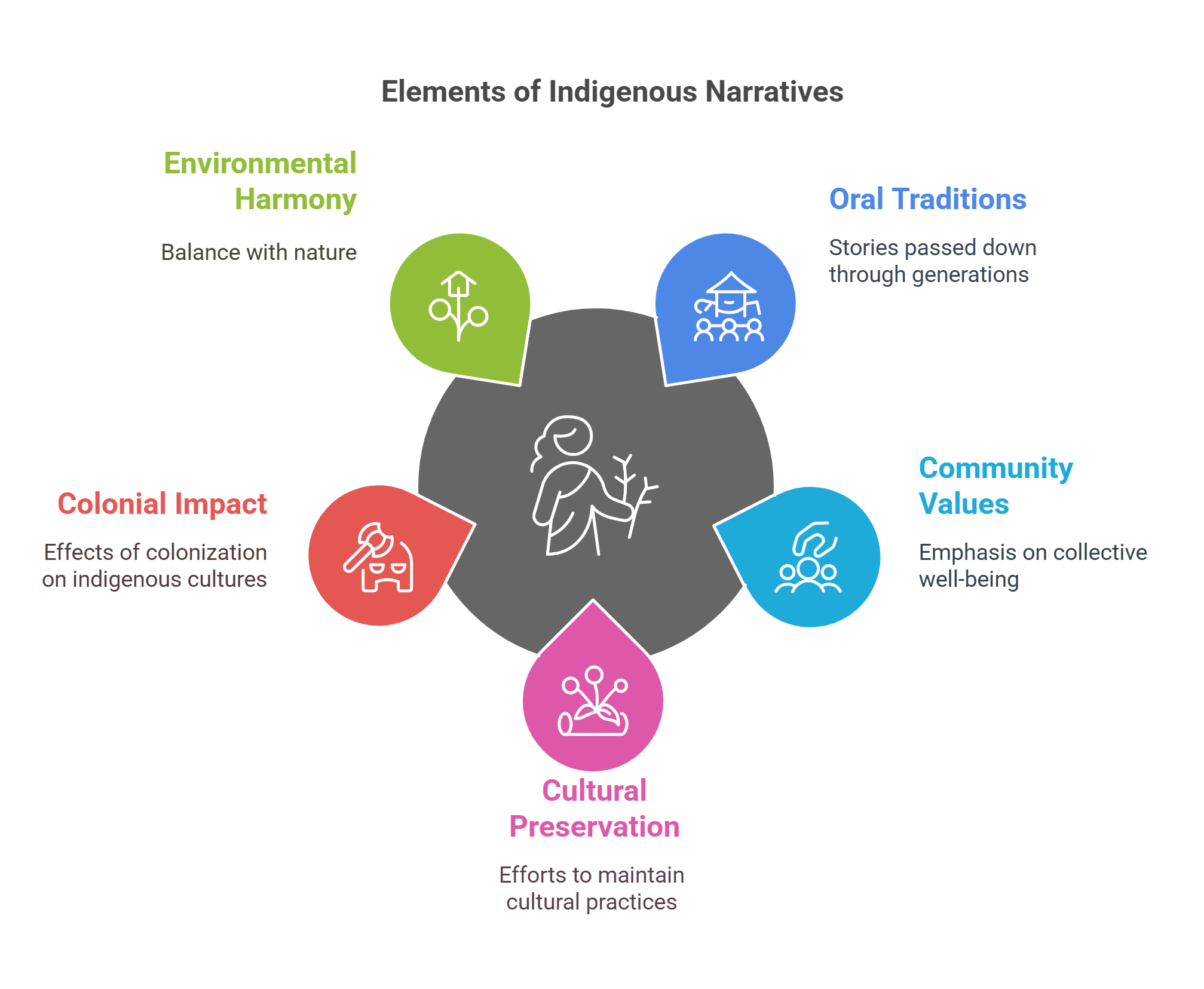
Indigenous Narratives preserve cultural traditions while addressing modern issues. Rooted in oral storytelling, these narratives emphasize community, harmony with nature, and resilience. They are often interwoven with themes of identity, colonial impact, and cultural reclamation.
- Rooted in oral traditions and communal values.
- Highlight cultural preservation and identity.
- Address the impacts of colonization.
- Combine traditional and contemporary storytelling methods.
- Emphasize environmental harmony and spiritual connection.
Explained Simply: It’s like the oldest bedtime stories, passed down from grandparents, showing how to care for the earth and each other while telling magical tales.
6. Literary Criticism
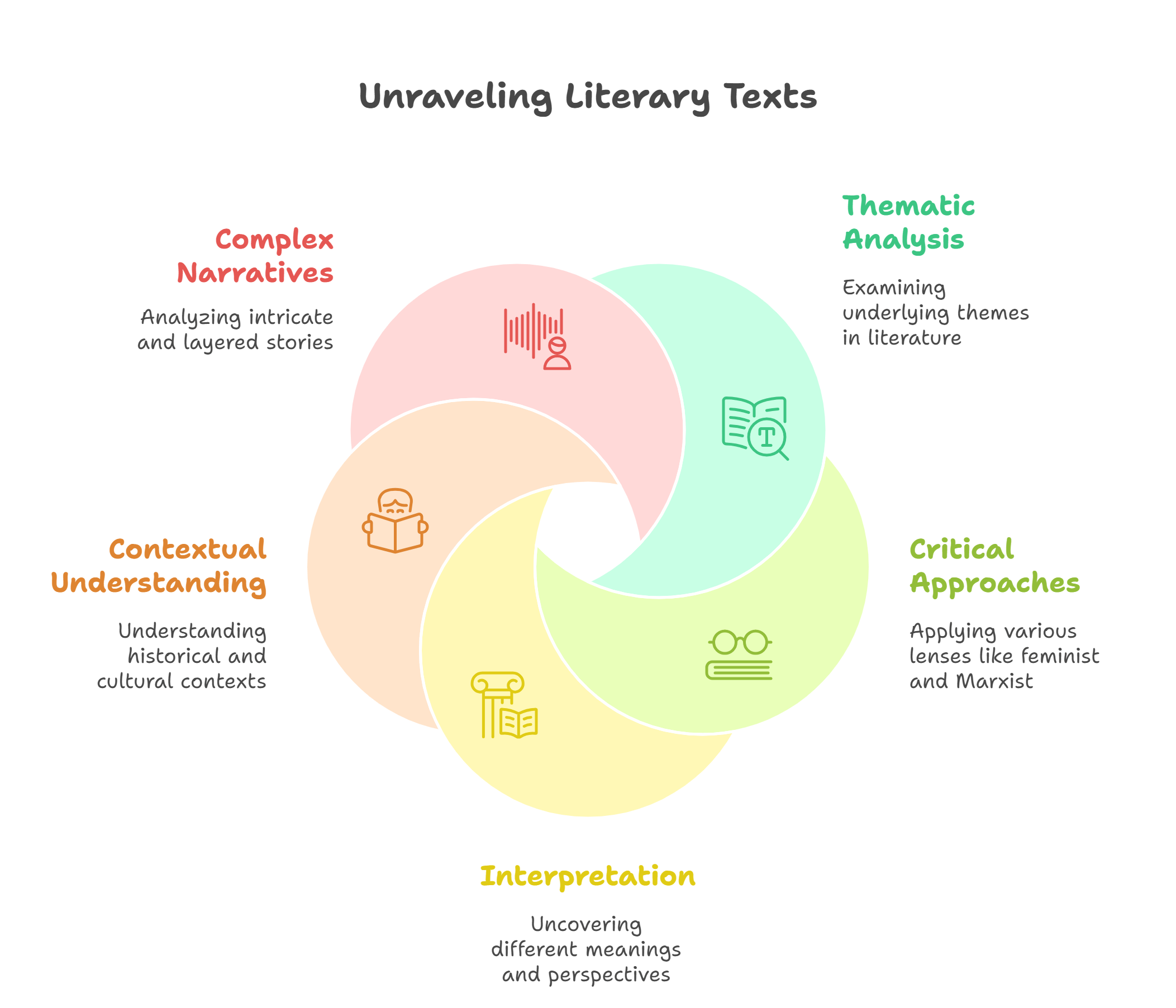
Literary criticism involves analyzing texts to understand their deeper meanings, themes, and historical contexts. It includes various approaches, like feminist, Marxist, and psychoanalytic critiques, each offering unique lenses for interpreting literature.
- Examines themes, structure, and context in literature.
- Includes various critical approaches (e.g., feminist, cultural).
- Helps uncover hidden meanings in texts.
- Essential for analyzing complex narratives.
- Encourages diverse interpretations of literature.
Explained Simply: Imagine solving a mystery where the clues are hidden in a book! Literary criticism helps find those clues and figure out what the story really means.
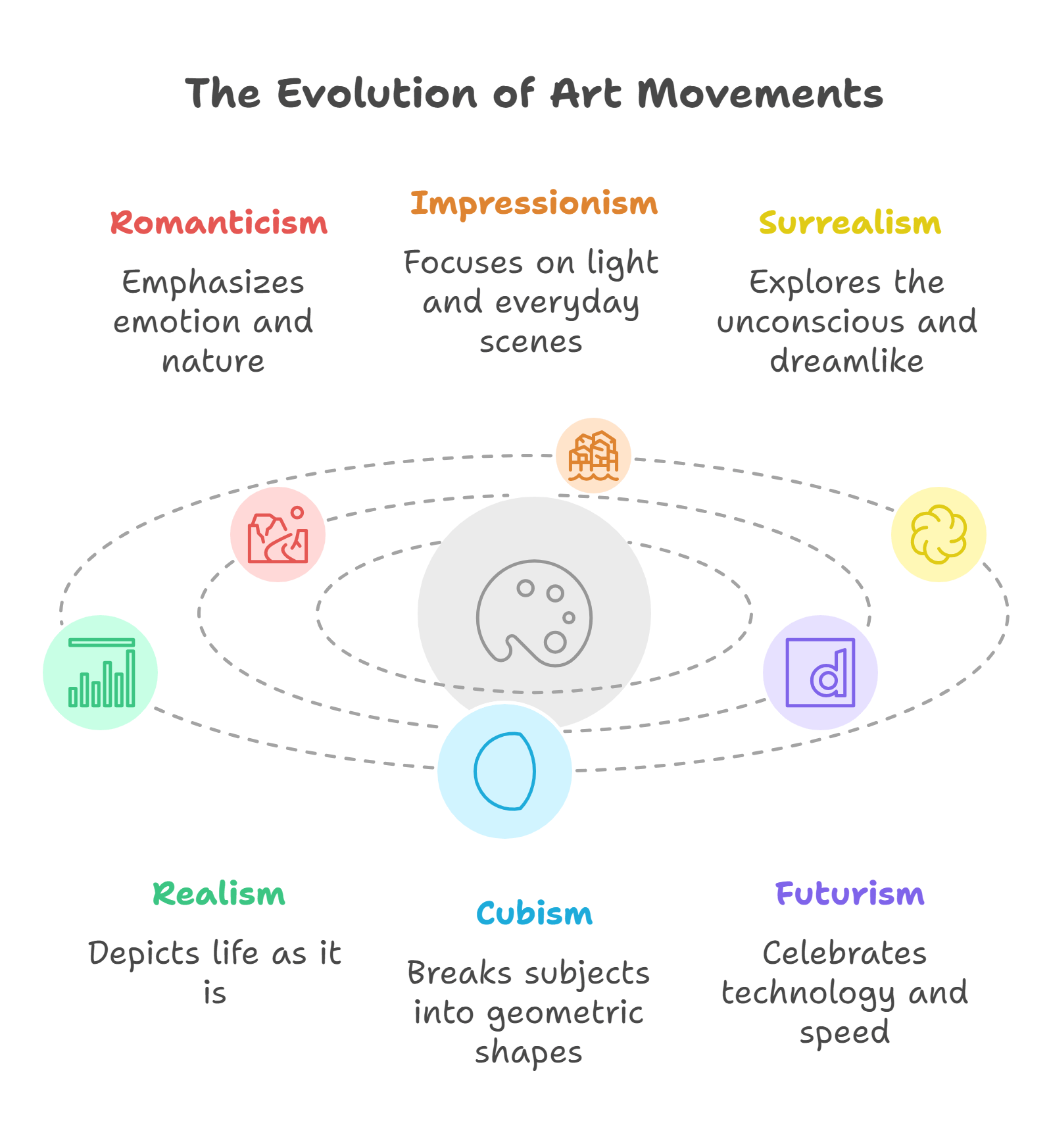
7. Art Movements
Art movements like Romanticism, Impressionism, and Surrealism reflect changing cultural, political, and philosophical ideas. Understanding these movements provides insight into the evolution of artistic expression and its societal impact.
- Showcases the evolution of artistic styles.
- Reflects historical and cultural shifts.
- Includes movements like Realism, Cubism, and Futurism.
- Provides context for analyzing visual and written art.
- Relevant for interpreting culturally significant works.
Explained Simply: It’s like fashion for paintings! Just like clothes change styles, art does too, with cool names like “Impressionism” or “Surrealism.”
8. Visual Arts
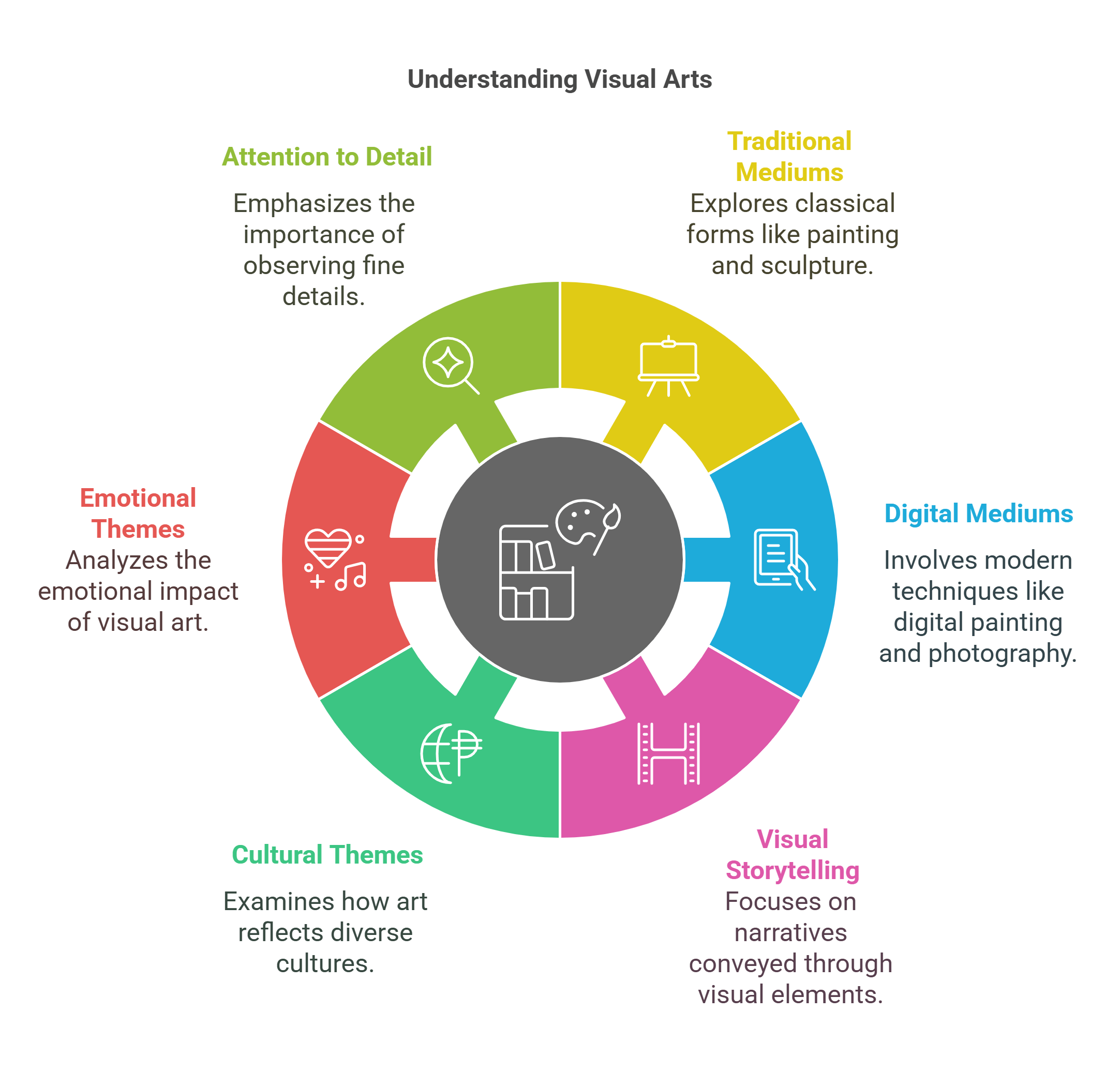
Visual arts encompass paintings, sculptures, photography, and digital media. They use color, form, and texture to convey ideas, emotions, and cultural narratives. Understanding visual arts enhances one’s ability to analyze non-verbal communication in RC passages.
- Includes traditional and digital mediums.
- Focuses on visual storytelling and symbolism.
- Explores cultural and emotional themes.
- Requires attention to detail and context.
- Relevant for interpreting artistic descriptions in passages.
Explained Simply: It’s like drawing a picture that talks without words—it tells you a story through shapes and colors!
9. Performing Arts
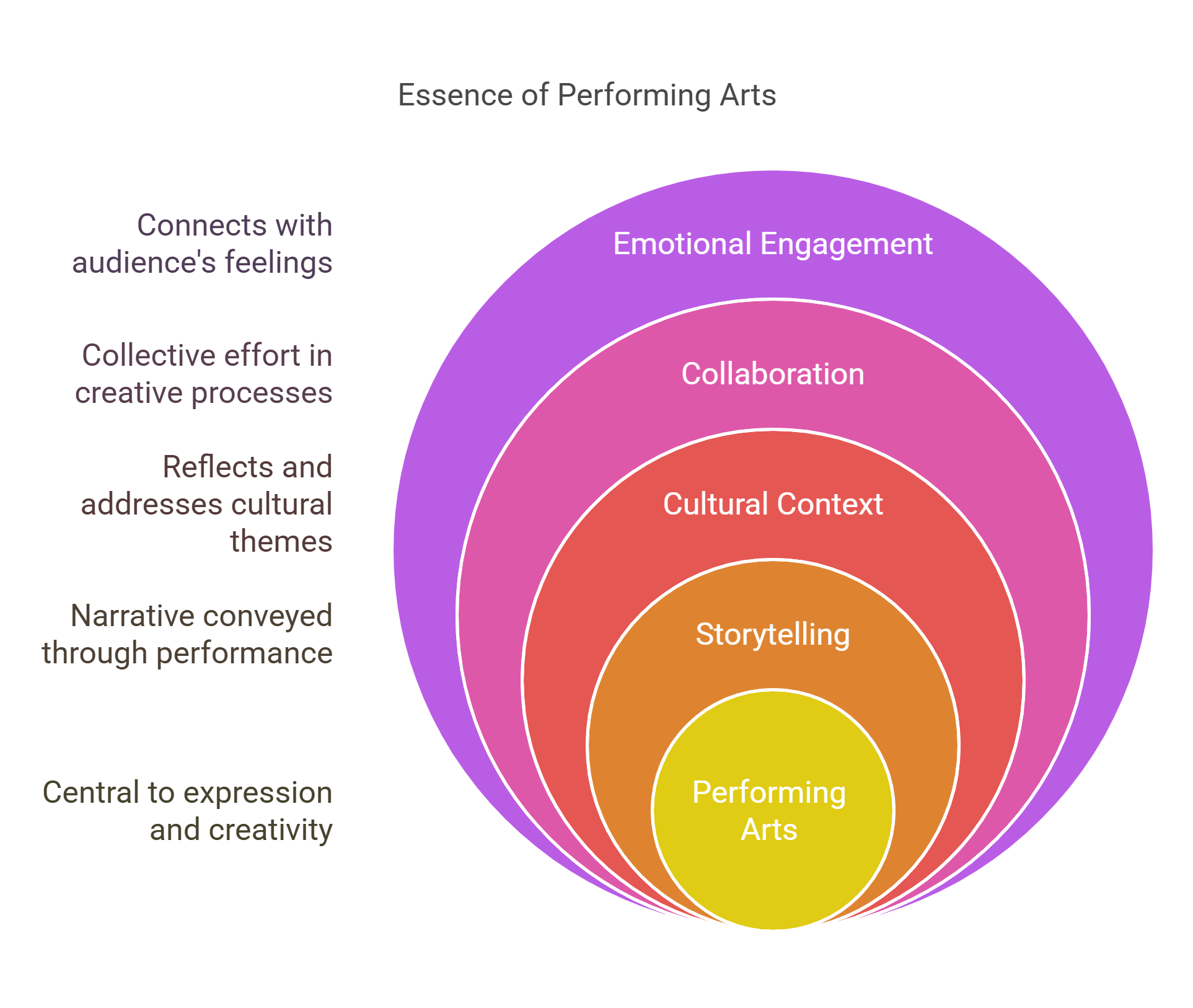
Performing arts include theater, dance, and music, showcasing stories through movement, sound, and performance. They emphasize the collaborative nature of creative expression and often address cultural or historical themes.
- Encompasses music, theater, and dance.
- Highlights storytelling through performance.
- Reflects cultural and historical contexts.
- Demonstrates collaboration in creativity.
- Provides emotional and sensory engagement.
Explained Simply: Think of a play or dance where people tell a story by moving or singing—it’s like acting out a bedtime story on a stage!
10. Cultural Heritage
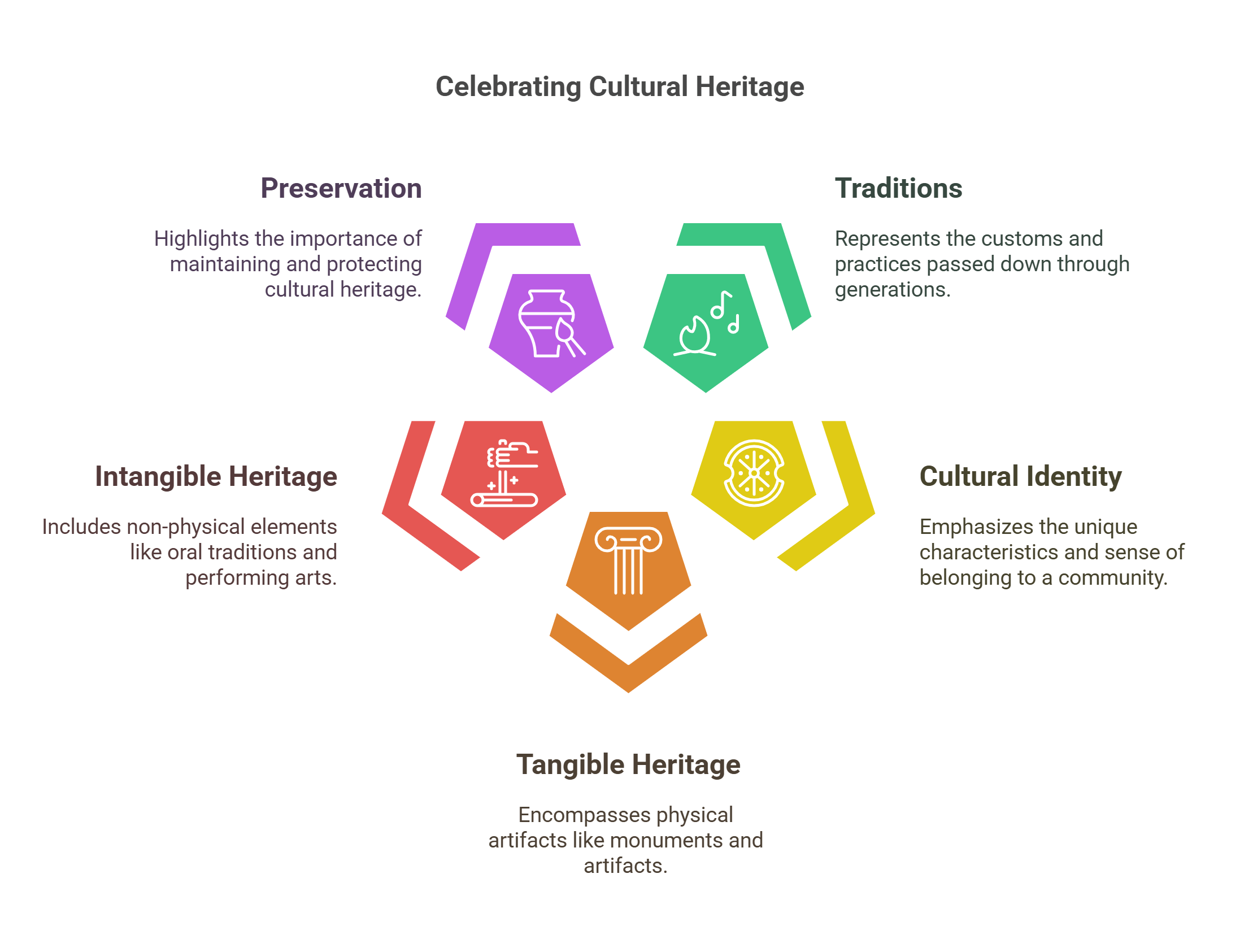
Cultural heritage preserves the traditions, artifacts, and stories of communities. It connects past and present, offering insights into identity and shared history. Understanding cultural heritage enriches comprehension of texts that explore legacy and identity.
- Preserves traditions and historical narratives.
- Emphasizes cultural identity and continuity.
- Includes tangible and intangible heritage.
- Highlights the importance of preservation.
- Relevant for analyzing passages about identity and legacy.
Explained Simply: It’s like a treasure box of old stories, clothes, and songs that show where we came from and who we are!
✨ Conclusion
Literature and arts concepts enrich your ability to decode complex RC passages by providing the tools to engage with diverse themes, cultural dialogues, and creative expressions. Mastering these ideas enhances both comprehension and critical thinking, preparing you for the nuanced analysis required in GMAT RC sections.











