Hepat: The Root of Liver and Its Vital Significance
Discover the rich meaning and applications of the root "hepat," derived from Greek, meaning "liver." From the vital hepatic system to diseases like hepatitis, this root highlights the liver’s essential role in health and medicine.
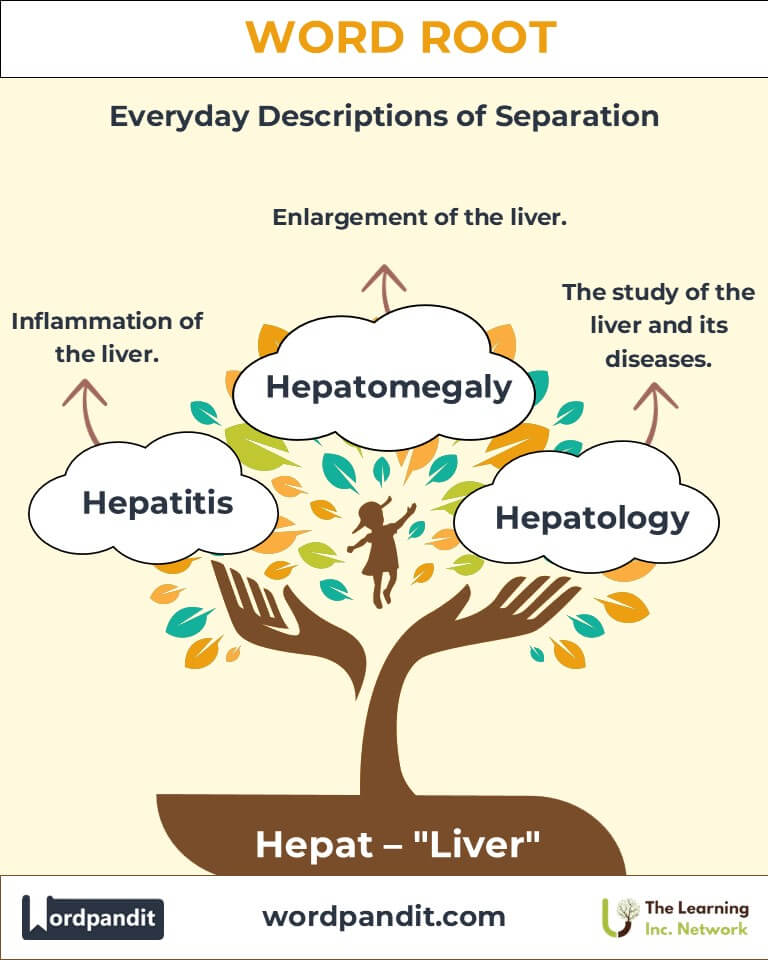
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Vitality of "Hepat"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Hepat"
- Common "Hepat"-Related Terms
- "Hepat" Through Time
- "Hepat" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Hepat" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Hepat" Root
- The "Hepat" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Hepat" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Hepat" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Legacy of "Hepat"
Introduction: The Vitality of "Hepat"
The root "hepat," pronounced hep-at, originates from the Greek word hēpar, meaning liver. As a cornerstone of medical terminology, it underscores the liver's vital role in detoxification, metabolism, and overall health. From the hepatic artery to hepatitis, the root "hepat" permeates the language of medicine and biology, symbolizing the centrality of the liver to life.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "hepat" traces its origins to the Greek word hēpar, used to describe the liver as the seat of vital energy and blood purification. In ancient Greece and Rome, physicians emphasized the liver's role in maintaining balance within the body. As medical science advanced, "hepat" became integral to describing liver anatomy, diseases, and treatments, influencing terms in Latin, Arabic, and modern languages.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Hepat"
To remember "hepat," imagine a bustling detox center labeled "HEPAT," symbolizing the liver cleansing the bloodstream and supporting bodily functions.
Mnemonic Device: "Hepat is the healer, cleaning toxins and fueling the body with life!"
Common "Hepat"-Related Terms
- Hepatic (hep-at-ik): Relating to the liver.
Example: "The hepatic vein carries blood away from the liver to the heart." - Hepatitis (hep-uh-tai-tis): Inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections.
Example: "Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination." - Hepatology (hep-uh-tol-uh-jee): The study of the liver, its functions, and diseases.
Example: "Advances in hepatology have improved liver transplant outcomes." - Hepatomegaly (hep-uh-toh-meg-uh-lee): Enlargement of the liver, often indicating disease.
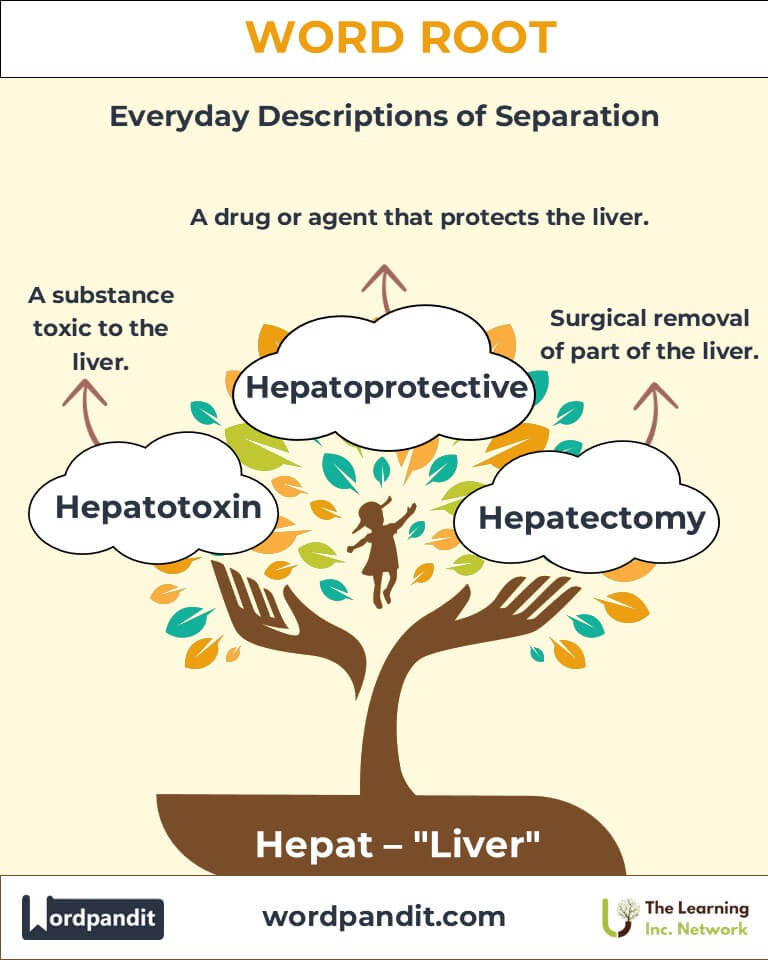
Example: "Hepatomegaly was detected during the physical examination." - Hepatotoxin (hep-uh-tox-in): A substance toxic to the liver.
Example: "Alcohol is a common hepatotoxin that can cause liver damage."
"Hepat" Through Time
- Ancient Beliefs: The liver was considered the seat of life and emotions in early Greek medicine.
- Renaissance Science: During the Renaissance, the term "hepat" appeared in anatomy texts, solidifying its role in describing liver-related functions.
- Modern Medicine: Terms like hepatitis gained prominence with the discovery of viral hepatitis in the 20th century, reflecting the liver's vulnerability to infections and toxins.
"Hepat" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Hepatology focuses on liver diseases like cirrhosis and hepatitis. Hepatocellular carcinoma refers to primary liver cancer. - Pharmacology:
Hepatoprotective drugs are medications that protect the liver from toxins. - Toxicology:
Hepatotoxicity studies assess the impact of drugs and chemicals on liver health. - Surgery:
Hepatectomy involves surgical removal of part of the liver, often for cancer treatment.
Illustrative Story: "Hepat" in Action
Dr. Saira, a hepatologist, worked tirelessly to treat a patient with hepatitis C. With advancements in antiviral medications, she helped the patient achieve a full recovery. Inspired by her success, she initiated a community program to raise awareness about liver health, emphasizing the importance of vaccination and avoiding hepatotoxins like alcohol. Her work highlighted the life-saving potential of understanding "hepat" and its applications.
Cultural Significance of the "Hepat" Root
Across cultures, the liver has symbolized vitality and resilience. Traditional Chinese medicine views the liver as the organ of balance and detoxification. In ancient Mesopotamia, hepatoscopy—examining the liver of sacrificed animals—was a divination practice to predict the future. The "hepat" root thus connects science and culture in its representation of life’s essence.

The "Hepat" Family Tree
- Chole- (bile):
Examples: Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), Cholestasis (reduced bile flow). - Hemo- (blood):
Examples: Hematology (study of blood), Hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells). - Gastro- (stomach):
Examples: Gastroenterology (study of the digestive system).
FAQs About the Hemi Word Root
Q: What does "hemi" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Hemi" means "half" and originates from the Greek word "hemi." It is often used to describe something that is divided into two equal parts or pertains to one half of a whole. This root appears frequently in scientific, architectural, and medical terminologies.
Q: How is "hemi" different from "semi"?
A: While both mean "half," "hemi" is rooted in Greek and often refers to physical or spatial divisions, such as "hemisphere" (half of a sphere). In contrast, "semi," derived from Latin, is used more broadly, including abstract or figurative contexts like "semifinal" (a stage preceding the final) or "semicircle" (half of a circle).
Q: What is a hemisphere, and why is it significant?
A: A hemisphere is half of a sphere. In geography, it divides the Earth into Northern and Southern Hemispheres (by the equator) or Eastern and Western Hemispheres (by the prime meridian). This concept is vital in understanding global climates, time zones, and navigation.
Q: What is hemiplegia, and what causes it?
A: Hemiplegia refers to paralysis on one side of the body, typically caused by damage to the brain or spinal cord. Common causes include strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or neurological diseases. It highlights the root "hemi" by affecting only one half of the body.
Q: What is a hemicycle, and where is it used?
A: A hemicycle is a semicircular structure or arrangement often found in amphitheaters, auditoriums, or legislative chambers. Its design enhances acoustics and visibility, making it popular for spaces requiring effective communication.
Q: What does hemizygous mean in genetics?
A: Hemizygous describes having only one copy of a gene in a pair of chromosomes. This term often applies to X-linked genes in males, where the single X chromosome carries a unique genetic configuration. Understanding hemizygosity is critical for studying genetic traits and disorders.
Q: What is a hemistich in literature?
A: A hemistich is half of a poetic line or verse, often separated by a pause. It is used to create rhythm and balance in poetry, especially in classical and epic literature.
Test Your Knowledge: Hemi Mastery Quiz
1. What does "hemi" mean?
2. Which term refers to half of the Earth?
3. What does hemiplegia describe?
4. Which of the following is a genetic term?
5. Which structure is semicircular in design?
Conclusion: The Legacy of "Hepat"
The root "hepat" exemplifies the liver's crucial role in human health. From ancient beliefs to cutting-edge hepatology, this root reflects humanity's enduring quest to understand and protect the liver. As medicine advances, the "hepat" root will continue to guide our efforts in ensuring liver health and vitality for future generations.












