Hymen: The Root of Membranes and Structures in Biology
Discover the intricate role of the word root "Hymen," derived from the Greek word for "membrane." This root forms the foundation of terms that describe biological barriers and significant taxonomic classifications, such as "hymen" and "hymenoptera." Explore how this root has shaped our understanding of biology, medicine, and more.
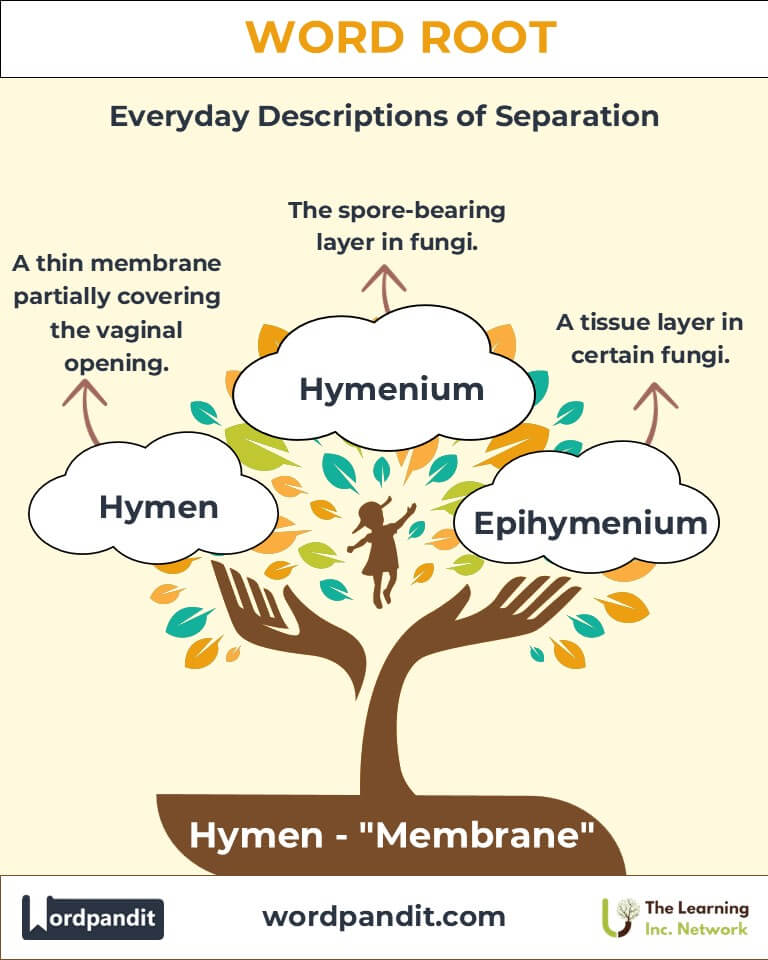
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Hymen
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hymen
- Common Hymen-Related Terms
- Hymen Through Time
- Hymen in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hymen in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Hymen Root
- The Hymen Family Tree
- FAQs about the Hymen Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Hymen Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Hymen
Introduction: The Essence of Hymen
What ties anatomical structures and insect classifications together? The answer lies in the root "Hymen," meaning "membrane." Pronounced HI-men, this Greek root encapsulates the concept of thin, often protective layers in biological contexts. From its use in describing delicate anatomical tissues to its significance in entomology, "Hymen" bridges diverse fields of knowledge.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Hymen" originates from the Greek word hymen, meaning "membrane." In ancient Greek, it also referred to the god Hymenaios, associated with marriage, likely due to the cultural symbolism of the hymen in virginity. Over time, the term evolved in scientific contexts to describe thin membranous structures and taxonomic groupings, such as Hymenoptera, a large order of insects.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Hymen
Imagine a translucent, protective film covering a precious object, symbolizing the root's meaning.
Mnemonic Device: "Hymen holds delicate structures in its membranous embrace."
Common Hymen-Related Terms
- Hymen (HI-men): A thin membrane partially covering the vaginal opening.
- Example: "The hymen is often a subject of cultural and medical discussions."
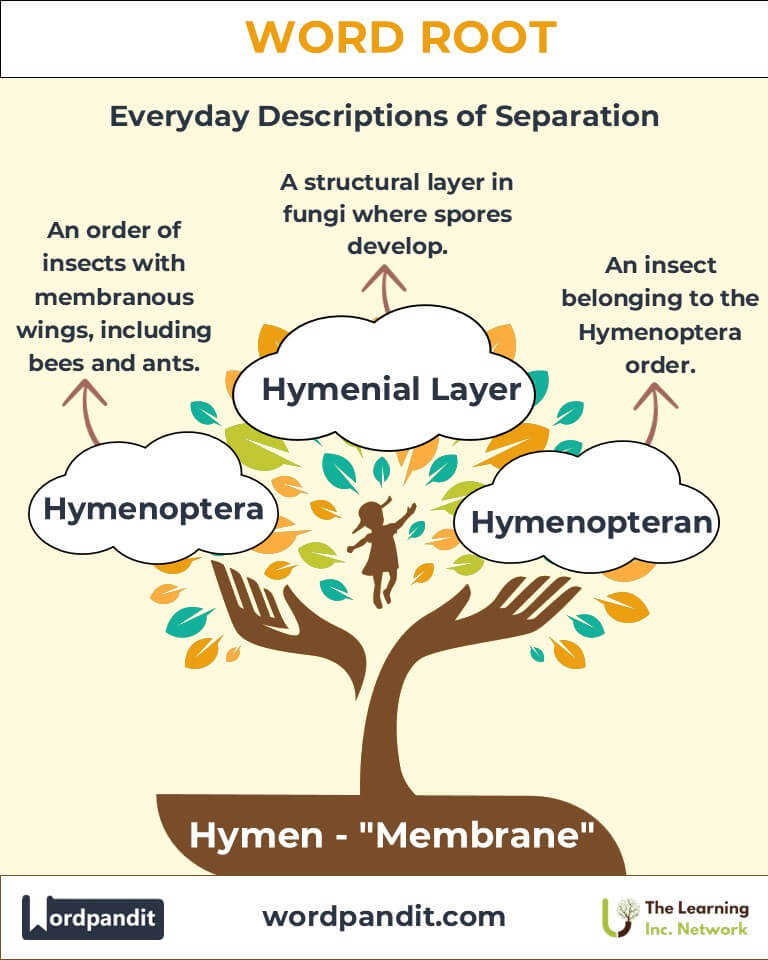
- Hymenoptera (HI-men-OP-ter-uh): An order of insects including bees, wasps, and ants, named for their membranous wings.
- Example: "Hymenoptera play crucial roles in pollination and ecosystems."
- Epihymenium (EP-ee-HI-men-ee-um): A layer of tissue in certain fungi.
- Example: "The epihymenium provides critical insights into fungal reproduction."
- Hymenium (HI-MEE-nee-um): The spore-bearing layer of a fungus.
- Example: "The hymenium is essential for understanding fungal growth cycles."
Hymen Through Time
- Ancient Context: In Greek culture, the hymen was both a physical and symbolic concept, linked to purity and marriage.
- Scientific Evolution: With advancements in taxonomy, the root expanded to describe structural membranes in insects and fungi.
Hymen in Specialized Fields
- Anatomy:
- Hymen: A membranous structure with varying forms and functions in the human body.
- Relevance: Medical understanding of the hymen has debunked myths surrounding its anatomy.
- Entomology:
- Hymenoptera: Named for their membranous wings, this order includes ecologically vital insects.
- Impact: Their study aids agriculture through pollination research.
- Mycology:
- Hymenium: The layer in fungi where spores develop.
- Significance: Crucial for understanding fungal reproduction and ecology.
Illustrative Story: Hymen in Action
Dr. Elena, a mycologist, was researching the hymenium of a rare mushroom species. While studying its spore-bearing structures under the microscope, she discovered a novel process of spore release, paving the way for advances in fungal biology. At the same time, her colleague, an entomologist, was analyzing hymenopteran insects’ wing membranes, finding new aerodynamic principles. Together, their work showcased the versatility of "Hymen" in scientific exploration.
Cultural Significance of the Hymen Root
The hymen has carried profound cultural symbolism, particularly in contexts of purity and tradition. This perception has influenced practices and beliefs worldwide. In science, however, the root transcends cultural connotations, providing a basis for studying membranes and structural systems.

The Hymen Family Tree
- Membr- (Latin):
- Membrane: A thin, pliable sheet of material.
- Example: "Cell membranes regulate the entry and exit of substances."
- Derm- (Greek):
- Epidermis: The outer layer of skin.
- Example: "The epidermis acts as a protective barrier."
- Tela- (Latin):
- Tela: A tissue or thin structure.
- Example: "The tela submucosa supports gastrointestinal linings."
FAQs About the Hymen Word Root
Q: What does "Hymen" mean, and where does it come from?
A: The root "Hymen" means "membrane" and originates from the Greek word hymen, which refers to thin, often protective or functional layers in biological contexts. The term's use spans anatomy, mycology (the study of fungi), and entomology, highlighting its adaptability across fields.
Q: What is Hymenoptera, and why is it significant?
A: Hymenoptera is an order of insects, including bees, ants, wasps, and sawflies. The name derives from their membranous wings (hymen meaning membrane, and ptera meaning wings). These insects play crucial ecological roles, such as pollination and pest control, making them indispensable to biodiversity and agriculture.
Q: Is the hymen always intact, and what influences its state?
A: No, the hymen’s state varies among individuals. It can stretch, tear, or even be absent due to natural differences, physical activities, or medical conditions. Its presence or condition does not reliably indicate virginity, debunking widespread cultural myths.
Q: What is the hymenium in fungi, and what role does it play?
A: The hymenium is a spore-producing tissue layer found in fungi, such as mushrooms and molds. It is critical for reproduction, as it houses specialized cells that generate and release spores into the environment for dispersal.
Q: How does the hymen relate to insects?
A: The root "Hymen" features prominently in the name Hymenoptera, an insect order characterized by membranous wings. These wings enable the remarkable flight abilities of bees, ants, and wasps, which are crucial for their ecological roles.
Q: What are membranes, and why are they important in biology?
A: Membranes are thin layers of tissue or material that protect, enclose, or facilitate specific functions in living organisms. Examples include cell membranes, which regulate the passage of substances, and fungal hymenia, which aid in spore production.
Q: Are there any artificial or technological uses inspired by membranes?
A: Yes, synthetic membranes are used in various fields, including water filtration, medical dialysis, and tissue engineering. These technologies mimic the selective and structural properties of natural membranes for innovative applications.
Q: Why is the study of hymenium and Hymenoptera essential in science?
A: The hymenium is pivotal for understanding fungal reproduction and ecosystem dynamics, while Hymenoptera contribute significantly to agriculture, biodiversity, and ecological balance. Together, they exemplify how biological membranes influence life on Earth.
Test Your Knowledge: Hymen Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Hymen" mean?
2. Which insects belong to Hymenoptera?
3. What is the hymenium?
4. Why is Hymenoptera important?
5. Which field studies the hymenium?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Hymen
The word root "Hymen" exemplifies the unifying theme of membranes across biological and cultural contexts. From the protective barriers in fungi to the membranous wings of insects, it reflects the delicate yet powerful nature of structures that define and connect life. By exploring its applications, we uncover a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the natural world.












