Labi: The Root of Lips in Language and Anatomy
Discover how the word root "labi," derived from the Latin word for "lip," forms the foundation of terms describing both anatomy and phonetics. From labial sounds to labiodental consonants, this root highlights the importance of lips in communication and expression.
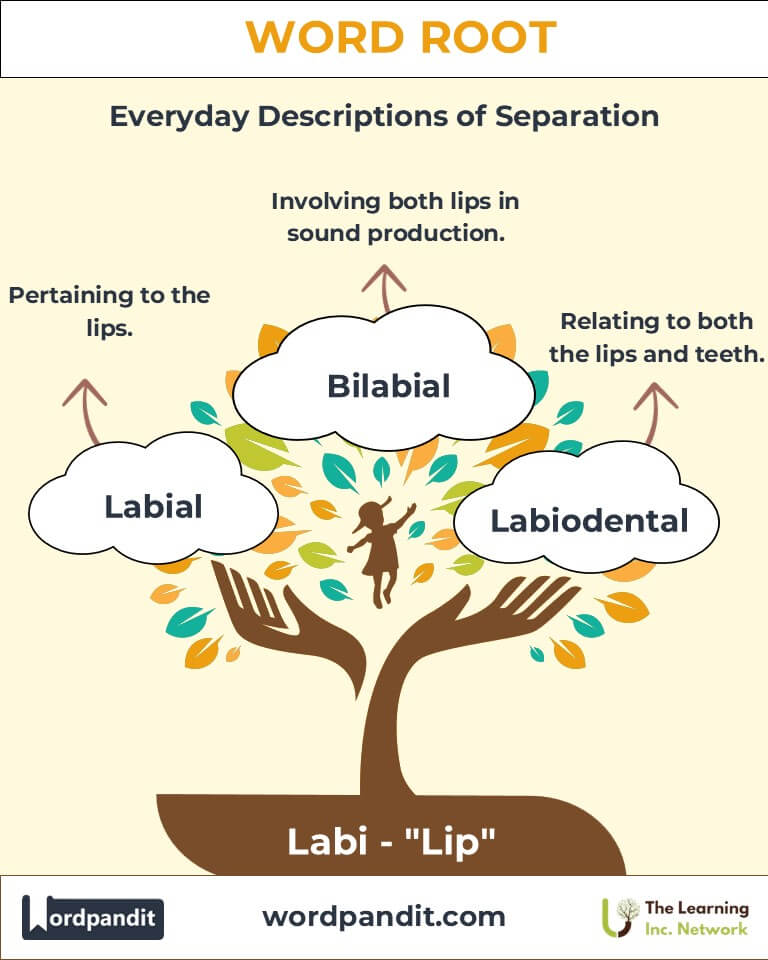
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Labi
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Labi
- Common Labi-Related Terms
- Labi Through Time
- Labi in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Labi in Action
- Cultural Significance of Labi
- The Labi Family Tree
- FAQs about the Labi Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Labi Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Labi
Introduction: The Significance of Labi
When we think of lips, we often associate them with speech, emotion, and aesthetics. The word root "labi" (pronounced lay-bee), derived from the Latin word labium, meaning "lip," underpins various terms across anatomy, linguistics, and dentistry. Whether describing labial consonants in speech or the shape and function of lips in anatomy, "labi" serves as a linguistic bridge connecting diverse fields of study.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "labi" originates from the Latin word labium (plural: labia), meaning "lip." In ancient Rome, labium was used not only to refer to the lips of the mouth but also as a metaphor for edge-like structures, influencing terms in anatomy and botany. The root traveled through Old French and Middle English, evolving into words like "labial" in phonetics and anatomy, emphasizing the role of lips in articulation and structure.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Labi
To remember "labi," picture a pair of lips forming a smile, emphasizing the word root's connection to the lips.
Mnemonic: "Labi means lips, where language begins and smiles take shape."
Common Labi-Related Terms
- Labial (lay-bee-uhl):
- Definition: Pertaining to the lips.
- Example: "Labial consonants, like 'b' and 'p,' are produced using the lips."
- Labiodental (lay-bee-oh-den-tuhl):
- Definition: Relating to both the lips and teeth.
- Example: "Labiodental sounds, such as 'f' and 'v,' involve the upper teeth and lower lip."
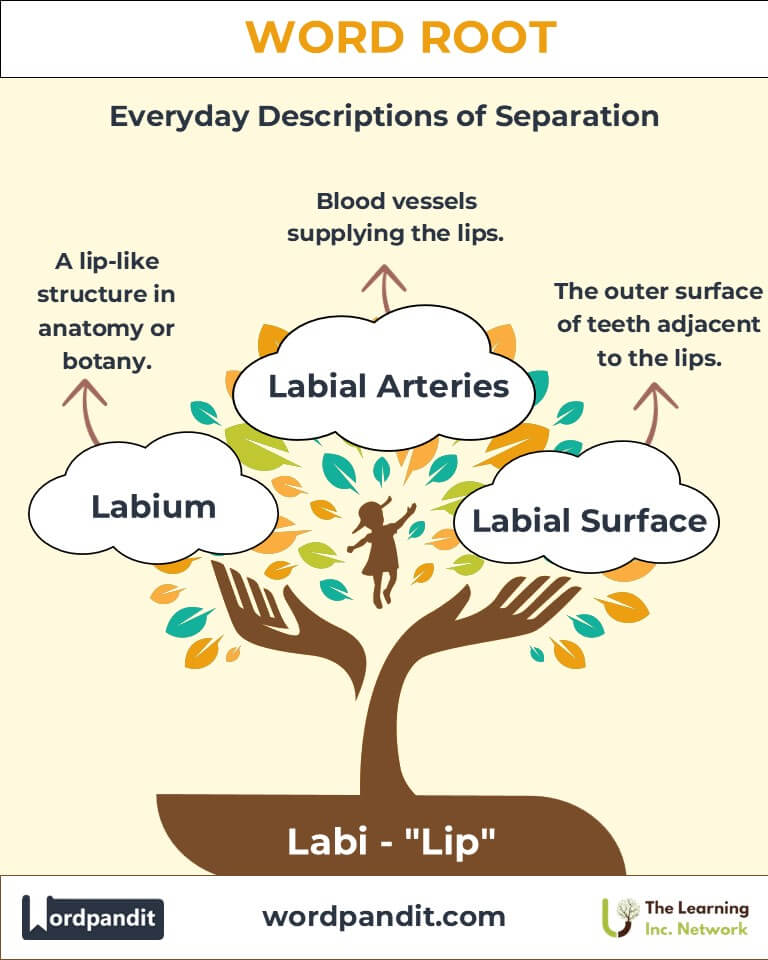
- Labium (lay-bee-um):
- Definition: A lip-like structure in anatomy or botany.
- Example: "In insects, the labium functions as a lower lip, aiding in feeding."
- Bilabial (bye-lay-bee-uhl):
- Definition: Involving both lips.
- Example: "'M' and 'p' are bilabial sounds produced by closing both lips."
- Labialize (lay-bee-uh-lize):
- Definition: To articulate a sound with rounded lips.
- Example: "In some languages, vowels are labialized to produce distinct sounds."
Labi Through Time
- Labial (Ancient Usage): In classical phonetics, "labial" described sounds articulated with the lips, such as in Greek and Latin grammar studies.
- Labiodental (Modern Context): In linguistics, "labiodental" emerged as a specific term to classify sounds made with both the lips and teeth, a refinement of earlier phonetic categories.
Labi in Specialized Fields
- Linguistics:
- Labiodental Consonants: Sounds like "f" and "v" are classified as labiodental because they involve both the upper teeth and lower lip.
- Bilabial Sounds: Produced with both lips, common in languages worldwide.
- Anatomy:
- Labial Arteries and Veins: Vascular structures supplying the lips, crucial for facial expression and speech.
- Dentistry:
- Labial Surfaces: Refers to the outer surface of teeth adjacent to the lips.
- Botany:
- Labium in Flowers: Lip-like structures in certain flowers, aiding pollination.
Illustrative Story: Labi in Action
In a small linguistics class, Professor Elena demonstrated how labial and labiodental sounds shaped different languages. She asked her students to place a hand on their lips while saying "p" and "b" to feel the closure of their lips. Then, she introduced "f" and "v," showing how the lower lip and upper teeth interact. The students, fascinated by the tactile experience of sound production, began to see their lips as instruments of expression, not just for speech but for music, art, and emotion.
Cultural Significance of Labi
Lips hold symbolic significance across cultures, from representing beauty in art to their role in communication and intimacy. Terms like "labial consonants" underscore the foundational role of lips in spoken language, while anatomical terms reflect their critical function in biology and medicine.

The Labi Family Tree
- Lingua- (Tongue):
- Example: Lingual: Pertaining to the tongue.
- Example: Sublingual: Under the tongue.
- Dent- (Tooth):
- Example: Dental: Related to the teeth.
- Example: Dentition: The arrangement of teeth.
- Or- (Mouth):
- Example: Oral: Pertaining to the mouth.
- Example: Oratory: The art of public speaking.
FAQs About the Labi Word Root
Q: What does "labi" mean?
A: "Labi" originates from the Latin word labium, meaning "lip." It is a root used in various terms related to lips, their structure, and their role in speech, anatomy, and more.
Q: What are labiodental sounds?
A: Labiodental sounds are produced when the lower lip comes into contact with the upper teeth. Examples include the sounds "f" and "v." These sounds demonstrate the combined role of lips and teeth in articulating certain phonetic elements.
Q: How do labial sounds differ from labiodental sounds?
A: Labial sounds involve only the lips (e.g., "b," "p," and "m"), while labiodental sounds require the interaction of the lower lip with the upper teeth (e.g., "f" and "v"). The distinction lies in the articulators used to produce these sounds.
Q: What is the anatomical significance of labia?
A: In anatomy, "labia" refers to lip-like structures, such as the labia oris (lips of the mouth) or labia majora/minora in human reproductive anatomy. These structures serve protective, functional, and aesthetic roles in the body.
Q: Are bilabial and labial the same?
A: Not exactly. While both terms involve the lips, "bilabial" specifically refers to sounds made by bringing both lips together (e.g., "p," "b," "m"). "Labial" is a broader term encompassing all sounds or structures associated with the lips.
Q: What is labialize?
A: To labialize means to produce a sound with rounded lips, such as when pronouncing "w" in English. This technique is used in many languages to modify the quality of vowels or consonants for linguistic distinction.
Q: What are labial consonants?
A: Labial consonants are speech sounds produced with one or both lips. Examples include "p," "b," and "m" (bilabial) and "f" and "v" (labiodental). These sounds highlight the importance of lips in articulation.
Q: How does "labi" connect to botany?
A: In botany, labium refers to lip-like structures in flowers, such as those found in the orchid family. These structures often assist in pollination by providing landing platforms for insects.
Test Your Knowledge: Labi Mastery Quiz
1. What does "labi" mean?
2. Which sounds are labiodental?
3. What does "bilabial" mean?
4. Which of these is a labial sound?
5. What does "labialize" mean?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Labi
The word root "labi" highlights the essential role of lips in communication, anatomy, and expression. From producing sounds to enhancing facial aesthetics, the legacy of "labi" spans cultures and disciplines. As we speak, smile, or sing, we celebrate the root that reminds us of the significance of lips in our lives.












