Semi: The Power of Halves in Language and Understanding
Byline: Discover the fascinating utility of the root "Semi," originating from Latin and meaning "half." From geometric terms like "semicircle" to technological innovations like "semiconductors," this root splits across disciplines, bridging science, mathematics, and everyday language.
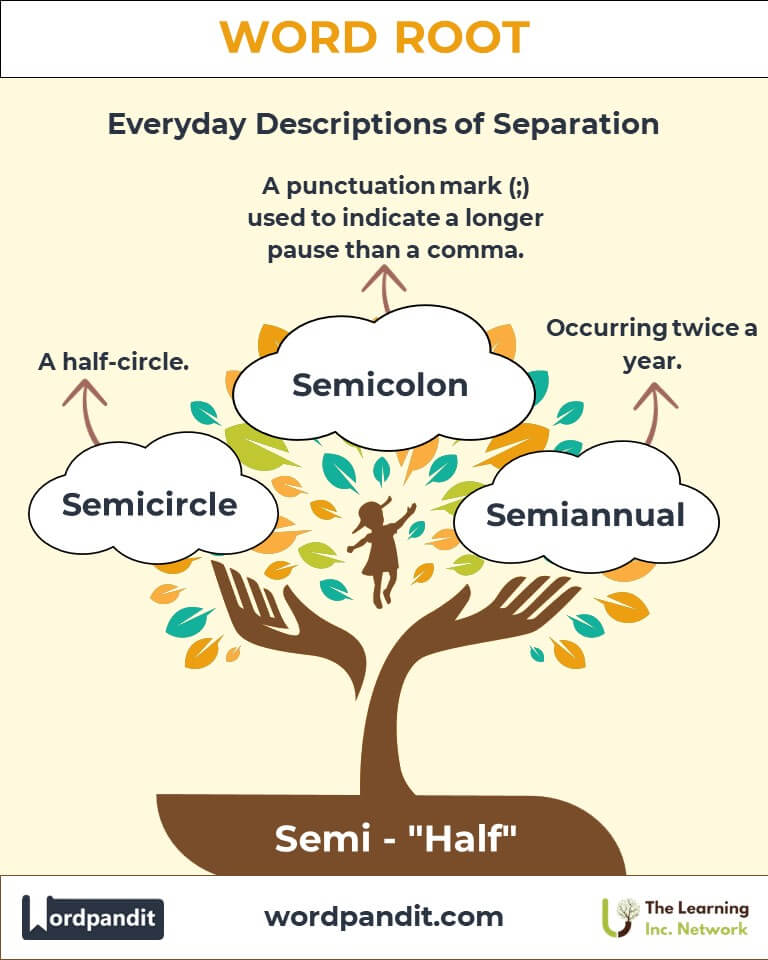
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Semi
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Semi
- Common Semi-Related Terms
- Semi Through Time
- Semi in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Semi in Action
- Cultural Significance of Semi
- The Semi Family Tree
- FAQs About the Semi Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Semi Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Semi
1. Introduction: The Significance of Semi
What do a semicircle, a semicolon, and a semiconductor have in common? They all derive from the Latin root "semi," meaning "half." Pronounced seh-mee or seh-my, this root cuts across languages and disciplines, symbolizing partiality, division, and shared attributes. Its applications range from mathematical concepts to cutting-edge technology, making "semi" a versatile and enduring part of our vocabulary.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Semi" stems from the Latin word semis, meaning "half." Its usage dates back to ancient Rome, where it described divisions in coins and measurements. Over time, "semi" migrated into Old French and Middle English, evolving into a prefix denoting partiality or incompleteness. Today, it is widely used in fields such as geometry, technology, and even daily speech.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Semi
Imagine a perfect circle sliced neatly into two equal parts. One half remains while the other fades away. This vivid image embodies the essence of "semi."
Mnemonic Device: "Semi splits things in two, leaving you with half a view!"
4. Common Semi-Related Terms
- Semicircle (seh-mee-sur-kuhl): A half-circle.
Example: "The children gathered in a semicircle around the storyteller." - Semicolon (seh-mee-koh-luhn): A punctuation mark (;) indicating a pause longer than a comma but shorter than a period.
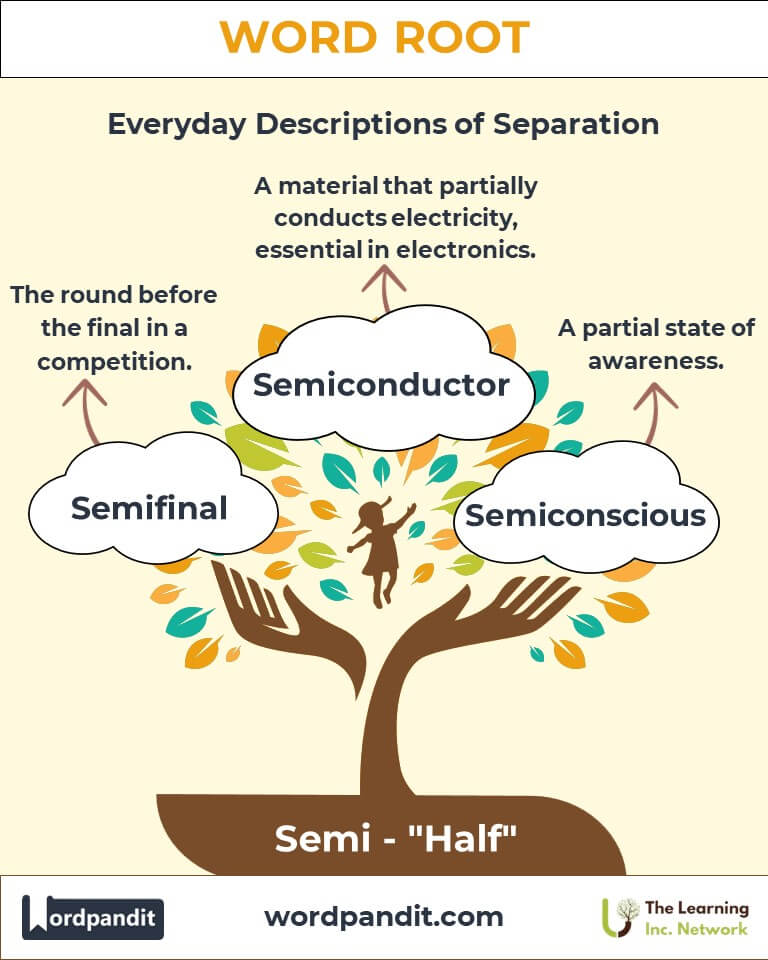
Example: "She used a semicolon to connect the two related sentences." - Semiconductor (seh-mee-kahn-duhk-tur): A material that conducts electricity partially, essential in electronic devices.
Example: "Silicon is a common semiconductor in computer chips." - Semifinal (seh-mee-fahy-nuhl): The round preceding the final in a competition.
Example: "Their team made it to the semifinals of the championship." - Semiannual (seh-mee-an-yoo-uhl): Occurring twice a year.
Example: "The company’s semiannual report was published in June."
5. Semi Through Time
- Semicircle: First used in ancient geometry, it symbolized perfect symmetry and balance. Today, it remains a foundational concept in mathematics and design.
- Semicolon: Introduced in 1494 by Italian printer Aldus Manutius, the semicolon bridged ideas in an era of evolving written expression.
6. Semi in Specialized Fields
- Geometry: Semicircle represents half of a circle, vital in architectural design and engineering calculations.
Example: Dome-shaped buildings often incorporate semicircles in their designs. - Technology: Semiconductors power the modern digital world, used in devices from smartphones to solar panels.
Example: Advances in semiconductor technology drive the development of artificial intelligence. - Medicine: Semiconscious refers to a partial state of awareness, critical in emergency care.
Example: The paramedics treated the semiconscious patient with utmost care.
7. Illustrative Story: Semi in Action
Maya, a tech-savvy student, was fascinated by semiconductors. During a class project, she demonstrated how these materials enable the functioning of everyday devices like smartphones. Her semicircular presentation diagram made it easy for her classmates to grasp complex concepts. By connecting the dots—literally and figuratively—Maya showed how "semi" plays a vital role in technology and education.
8. Cultural Significance of Semi
From the semicircles adorning ancient amphitheaters to semicolons shaping literary style, "semi" reflects humanity’s affinity for balance and partiality. In modern times, it symbolizes transitions—halves leading to wholes—and bridges gaps in communication, design, and innovation.

9. The Semi Family Tree
- Hemi- (Greek: "half"): Hemisphere: Half of a spherical object, often used in geography.
Example: "The Earth’s northern hemisphere experiences winter in December." - Demi- (French: "half"): Demi-god: A being with partial divine status.
Example: "Hercules, a demi-god, was renowned for his strength." - Semi-related suffixes: -partial: Indicates a fraction or part.
Example: "Partiality refers to an unfair preference."
10. FAQs About " Semi "
Q: What does "semi" mean?
A: "Semi" means "half" and is derived from the Latin root semis. It is commonly used as a prefix in English to indicate something that is partial, incomplete, or split into two parts, such as "semicircle" (half of a circle) or "semiannual" (happening twice a year).
Q: Why is "semi" significant in mathematics?
A: "Semi" appears in terms like "semicircle," representing half of a geometrical shape. This concept is crucial for dividing and understanding proportions, symmetry, and calculations in various fields, from engineering to design.
Q: How is "semiannual" different from "biennial"?
A: "Semiannual" means something happens twice a year (every six months), while "biennial" refers to events occurring every two years. These terms are often confused because they both deal with time intervals.
Q: What is the purpose of a semicolon in writing?
A: A semicolon (;) connects two closely related independent clauses or separates complex items in a list. It provides a pause stronger than a comma but weaker than a period, enhancing readability and flow.
Q: What are semiconductors, and why are they important?
A: Semiconductors are materials that partially conduct electricity, unlike conductors (e.g., copper) or insulators (e.g., rubber). They are the foundation of modern electronics, enabling the functionality of devices like computers, smartphones, and solar panels.
11. Test Your Knowledge: "Semi " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "semi" mean?
2. Which term describes half of a circle?
3. What is the significance of semiconductors?
4. What punctuation mark does "semi" describe?
5. Which "semi" word relates to competitions?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Semi
The root "Semi" elegantly splits meanings and applications across fields. From shaping geometric principles to advancing modern technology, it reflects the power of halves in bridging wholes. As society evolves, "semi" continues to inspire new innovations and ideas, highlighting the beauty of balance and partiality. Dive deeper into the world of "semi," and discover the halves that shape our understanding of the universe!












