Leuc: The White Essence in Science and Medicine
Byline: Explore the versatile root "Leuc", derived from the Greek word "leukos," meaning white. From critical biological terms like leucocyte to the essential amino acid leucine, this root signifies purity and clarity across various fields.
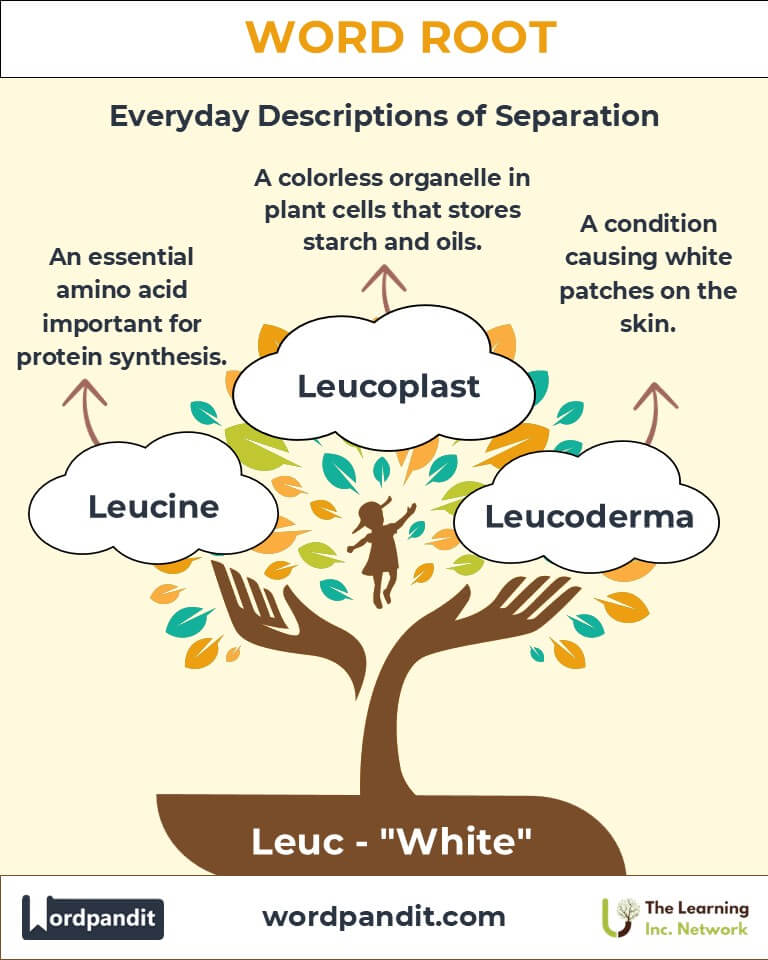
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Leuc"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Leuc"
- Common "Leuc"-Related Terms
- "Leuc" Through Time
- "Leuc" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Leuc" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Leuc"
- The "Leuc" Family Tree
- FAQs About the Leuc Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Leuc Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Kerat
Introduction: The Essence of "Leuc"
When we think of white, the idea of clarity, purity, and health often comes to mind. This is precisely what the root "Leuc" (pronounced look) represents. Originating from the Greek "leukos," meaning white or bright, this root finds prominence in the scientific and medical lexicon. Whether describing white blood cells (leucocytes) or amino acids (leucine), the root "Leuc" is a beacon of biological significance.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Leuc" traces its origins to Ancient Greece. Leukos denoted lightness or whiteness, a symbolic representation of clarity and purity. The term was adopted into Latin as leucos and later evolved into modern medical and scientific terminology. By the 19th century, with advancements in biology, "Leuc" became a cornerstone in describing structures and functions associated with whiteness, particularly in cellular biology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Leuc"
To remember "Leuc", imagine a white spotlight illuminating the stage. Think: "Leuc = light = clarity." This mental image reinforces the root's association with purity and brightness.
Common "Leuc"-Related Terms
- Leucocyte (loo-coh-site):
- Definition: A white blood cell involved in the body’s immune response.
- Example: "The doctor noted an increase in leucocytes, indicating an infection."
- Leucine (loo-seen):
- Definition: An essential amino acid crucial for protein synthesis and muscle repair.
- Example: "Athletes often consume leucine-rich supplements for muscle recovery."
- Leukemia (loo-kee-mee-uh):
- Definition: A type of cancer affecting white blood cells.
- Example: "Advancements in treatment have improved survival rates for leukemia patients."
- Leucoderma (loo-koh-dur-muh):
- Definition: A condition causing white patches on the skin due to pigment loss.
- Example: "Leucoderma is often confused with vitiligo but has distinct characteristics."
- Leucoplast (loo-coh-plast):
- Definition: A colorless organelle in plant cells that stores starch and oils.
- Example: "The leucoplasts in the plant cell were crucial for storing energy."
"Leuc" Through Time
- Leukos in Ancient Greece:
In Ancient Greek medicine, whiteness was associated with purity and health, forming the basis of early anatomical studies.
- Leukemia in Modern Medicine:
First described in the 19th century, leukemia—stemming from "leuc"—highlighted the root’s role in identifying critical medical conditions.
"Leuc" in Specialized Fields
- Biology and Medicine:
- Leucocytes: Essential for fighting infections.
- Leucoderma: Studied in dermatology to understand pigment disorders.
- Biochemistry:
- Leucine: Studied for its role in metabolic pathways and protein synthesis.
- Botany:
- Leucoplasts: Investigated for their function in plant storage systems.
Illustrative Story: "Leuc" in Action
Dr. Clara Jones, an immunologist, was analyzing a patient’s blood sample. Noticing an abnormal leucocyte count, she identified early signs of infection. Meanwhile, her colleague in biochemistry studied leucine’s effects on protein synthesis, pioneering a new supplement for malnourished children. Their combined efforts showcased the far-reaching impact of "Leuc" in science and medicine.
Cultural Significance of "Leuc"
In many cultures, the color white symbolizes purity, health, and renewal. The word root "Leuc" encapsulates these ideas in scientific contexts, emphasizing the intrinsic link between language and human understanding of health and wellness.

The "Leuc" Family Tree
- Leuk- (white):
- Leukocyte: White blood cell.
- Leukemia: Cancer of white blood cells.
- Alb- (white):
- Albino: An organism with a lack of pigmentation.
- Albedo: Reflectivity of a surface.
- Blanc (white):
- Blanch: To whiten or bleach.
- Blanco: Spanish word for white.
FAQs About the Leuc Word Root
Q: What does the root "Leuc" signify?
A: The root "Leuc" comes from the Greek word "leukos," meaning white or bright. It commonly appears in biological and medical terms, often referring to white or colorless elements, such as white blood cells (leucocytes) or white patches on the skin (leucoderma).
Q: What are leucocytes, and why are they important?
A: Leucocytes, or white blood cells, are a key component of the immune system. They help protect the body against infections by attacking bacteria, viruses, and other foreign invaders. An abnormal leucocyte count can indicate health conditions like infections, inflammation, or blood disorders such as leukemia.
Q: How does leucine benefit the body?
A: Leucine is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce it and must obtain it from food or supplements. It plays a vital role in protein synthesis, muscle repair, and regulating blood sugar levels. It’s especially important for athletes and individuals recovering from injuries to rebuild muscle tissue.
Q: What is leucoderma, and how does it differ from vitiligo?
A: Leucoderma refers to a loss of pigmentation in the skin, causing white patches. It can result from burns, injuries, or certain conditions. While vitiligo is a type of leucoderma caused by autoimmune destruction of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells), leucoderma can have other causes, such as chemical exposure or scarring.
Q: What are leucoplasts, and what is their role in plants?
A: Leucoplasts are colorless organelles in plant cells. They serve as storage centers for starch, lipids, and proteins, which are essential for plant growth and metabolism. Unlike chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis, leucoplasts are involved in storing and synthesizing materials needed for energy.
Q: How is the root "Leuc" used in medical conditions like leukemia?
A: In leukemia, the term "leuc" refers to the white blood cells. Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the body produces an excessive number of abnormal white blood cells, disrupting normal blood function and immunity.
Q: Why is the root "Leuc" significant in both science and language?
A: The root "Leuc" provides a linguistic foundation for describing whiteness and brightness across multiple contexts, including biology, medicine, and botany. Its presence highlights the importance of white or colorless phenomena in health and nature.
Test Your Knowledge: Leuc Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Leuc" signify?
2. Which term describes white blood cells?
3. What is leucine?
4. What does leucoderma affect?
5. What are leucoplasts?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Leuc"
The root "Leuc" represents purity, health, and clarity. From leucocytes guarding our immunity to leucine supporting muscle health, its presence in language reflects its biological importance. As science progresses, the applications of "Leuc" will continue to illuminate pathways to understanding and healing.












