Meso: Exploring the Middle Ground in Language and Science
Byline: Discover the fascinating world of the word root "meso," meaning "middle," and its role in words like "mesosphere" and "mesoderm." Learn how this versatile root bridges the gap between extremes, weaving its way into science, geography, and everyday language.
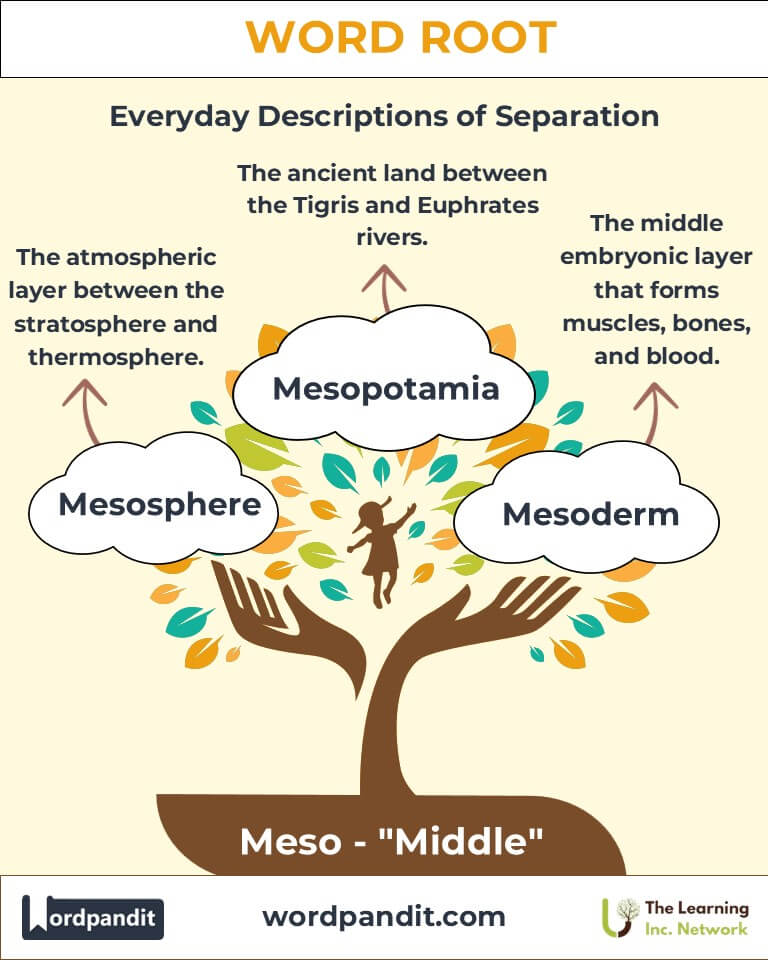
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Meso
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meso
- Common Meso-Related Terms
- Meso Through Time
- Meso in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Meso in Action
- Cultural Significance of Meso
- The Meso Family Tree
- FAQs About the Meso Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Meso Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Versatility of Meso
Introduction: The Significance of Meso
The word root "meso" (pronounced meh-so) comes from the Greek word mesos, meaning "middle." Like the mesosphere that lies between the stratosphere and the thermosphere, "meso" signifies the intermediary or central point. This root is foundational in words across disciplines, from biology to atmospheric science, reflecting its bridging nature.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "meso" originates from ancient Greek, where it meant "middle" or "intermediate." It found prominence in scientific nomenclature, such as describing Earth's atmospheric layers or embryonic tissues. As knowledge expanded, "meso" adapted to describe transitional states, emphasizing balance and centrality.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meso
Imagine a person standing on a bridge, connecting two distant lands. The bridge, like "meso," symbolizes the middle ground that unites extremes.
Mnemonic Device: "Meso is the bridge that balances and connects."
Common Meso-Related Terms
- Mesosphere (meh-so-sfeer): The atmospheric layer between the stratosphere and thermosphere.
Example: "Meteors burn up in the mesosphere before reaching Earth." - Mesoderm (meh-so-derm): The middle layer of an embryo, giving rise to muscles, bones, and blood.
Example: "The mesoderm is crucial for organ development." - Mesopotamia (meh-so-puh-tay-mee-uh): Ancient land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Example: "Mesopotamia is often called the cradle of civilization." - Mesomorph (meh-so-morf): A body type characterized by a muscular and well-proportioned build.
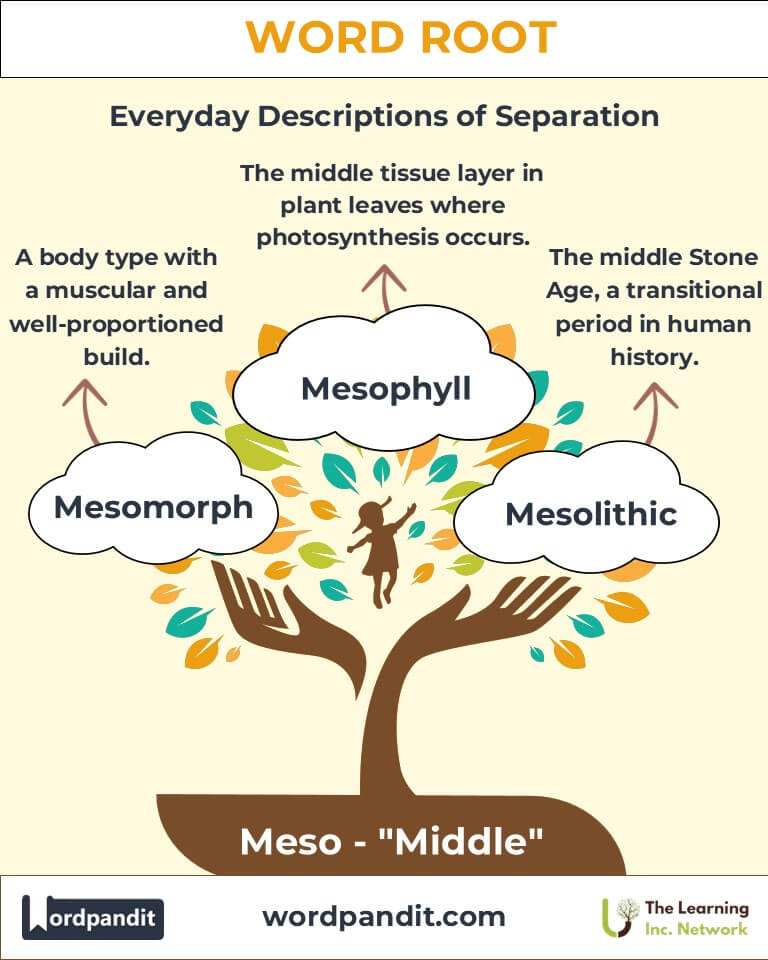
Example: "Athletes with a mesomorph physique excel in strength-based sports." - Mesophyll (meh-so-fill): The middle tissue layer in plant leaves, where photosynthesis occurs.
Example: "The mesophyll contains chloroplasts for energy conversion."
Meso Through Time
- Mesolithic (Ancient): Describes the middle Stone Age, a transitional period between the Paleolithic and Neolithic eras.
Relevance: Marks significant cultural and technological advancements. - Mesomerism (Modern): A concept in chemistry describing resonance structures within molecules.
Impact: Enhanced understanding of molecular stability.
Meso in Specialized Fields
- Atmospheric Science: Mesosphere: Studies focus on meteor impacts and atmospheric phenomena.
- Biology: Mesoderm: Explored in developmental biology and regenerative medicine.
- Geography: Mesopotamia: Central to understanding ancient human civilizations.
- Botany: Mesophyll: Crucial for plant physiology research.
Illustrative Story: Meso in Action
In a remote lab, Dr. Elena Garcia studied the mesosphere’s role in burning meteors. Simultaneously, her colleague, Dr. Raj, examined mesoderm cells in regenerative therapies. One day, Elena's findings inspired Raj to use meteor minerals to enhance cell regeneration. Together, they bridged the gap between space science and biology, embodying the essence of "meso."
Cultural Significance of Meso
The root "meso" represents balance and transition, values deeply embedded in many cultures. For example, Mesopotamia’s role as a cultural hub reflects "meso" as a bridge between civilizations. Similarly, concepts like the "middle path" in philosophy and spirituality echo the root’s essence of moderation and unity.

The Meso Family Tree
- Meta (Greek: "beyond, change")
Metaphor: A figure of speech representing change or transformation.
Metamorphosis: Biological transformation. - Med (Latin: "middle")
Median: The middle value in a data set.
Medieval: Pertaining to the Middle Ages. - Inter (Latin: "between")
Interact: To engage or connect.
Intersection: The point where paths cross.
FAQs About the Meso Root
Q: What does "meso" mean?
A: The root "meso" comes from the Greek word mesos, meaning "middle." It is used to signify something that is intermediate or located between two extremes, whether in physical space, time, or conceptual states.
Q: What is the mesosphere?
A: The mesosphere is the third layer of Earth's atmosphere, situated above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere. It is known for being the region where most meteors burn up upon entry due to friction with atmospheric particles, preventing them from reaching Earth's surface.
Q: What does mesoderm develop into?
A: The mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in an embryo. It forms critical structures such as muscles, bones, connective tissues, the circulatory system (including the heart and blood vessels), and the kidneys. This layer is essential for building the structural and functional framework of the body.
Q: Why is Mesopotamia significant?
A: Mesopotamia, meaning "land between rivers" in Greek, is the ancient region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. It is considered the cradle of civilization because it was home to some of the earliest human societies, innovations like writing (cuneiform), and the development of laws (Code of Hammurabi).
Q: How is "meso" used in botany?
A: In botany, "meso" appears in terms like mesophyll, which is the middle tissue layer of a plant leaf. The mesophyll contains chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis. It plays a crucial role in converting sunlight into energy for the plant.
Q: What is mesomorphism?
A: Mesomorphism refers to a somatotype, or body type, characterized by a muscular, well-proportioned build. People with this body type often have an easier time building muscle and maintaining a lean physique, making it ideal for physical activities and athletics.
Q: What does "mesolithic" mean?
A: The term mesolithic refers to the "middle Stone Age," a transitional period between the Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) and Neolithic (New Stone Age). This era marked significant advancements in tool-making, the domestication of animals, and the beginning of settled agriculture.
Test Your Knowledge: Meso Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "meso" signify?
2. Which layer lies between the stratosphere and thermosphere?
3. What does the mesoderm form?
4. What does mesophyll do?
5. What does Mesopotamia mean?
Conclusion: The Versatility of Meso
The root "meso" beautifully captures the idea of connection, transition, and centrality. From the mesosphere that shields Earth to the mesoderm that builds our bodies, "meso" plays a vital role in bridging gaps across fields. As we continue to explore the middle ground, "meso" remains a timeless reminder of the power of balance and unity.












