Sta, Stat: Standing Tall Across Language and Meaning
Discover the strength and versatility of the roots "sta" and "stat," derived from Latin, meaning "stand." These roots form the foundation of numerous words, from the everyday "static" to the foundational "station," capturing concepts of standing, stability, and position in both physical and metaphorical contexts.
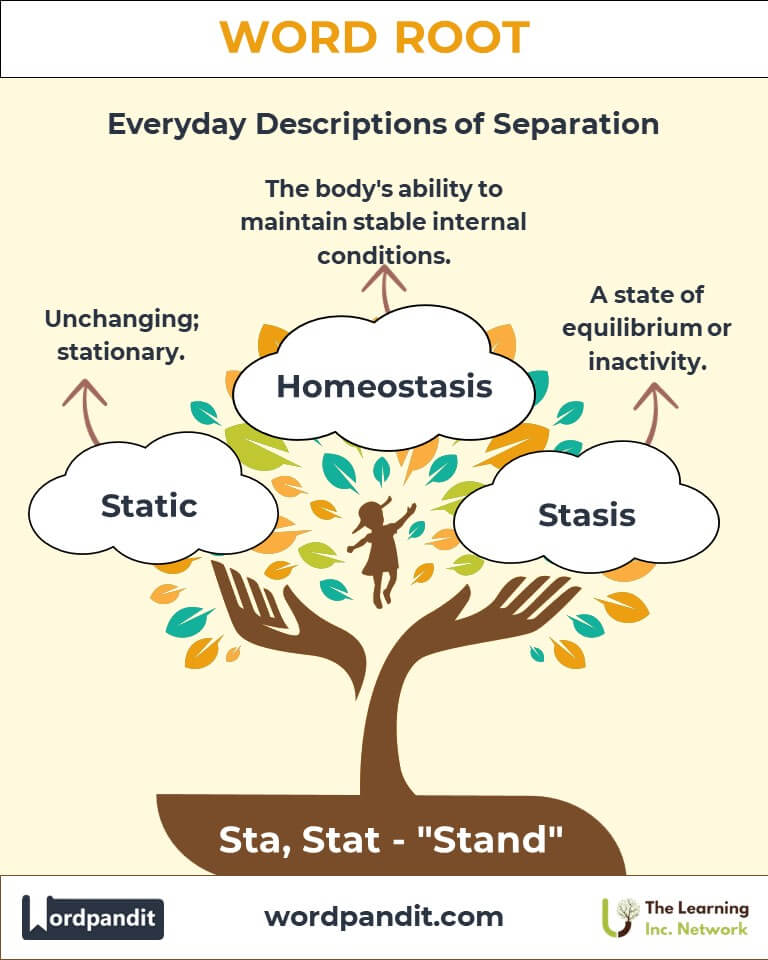
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Sta and Stat
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sta and Stat
- Common Sta/Stat-Related Terms
- Sta and Stat Through Time
- Sta and Stat in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Sta and Stat in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Sta/Stat Roots
- The Sta/Stat Family Tree
- FAQs About the Sta/Stat Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Sta/Stat Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of " Sta/Stat "
Introduction: The Power of Sta and Stat
Imagine the solid stance of a pillar, holding steady against the elements. The roots "sta" and "stat" embody this essence of standing firm, originating from the Latin stare, meaning "to stand." These roots weave through various words, representing stability, position, and state. From the stillness of "static" to the centrality of a "station," "sta" and "stat" anchor language with the power of presence.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The Latin root stare gave rise to "stat," which evolved into terms denoting standing, placement, and condition. In medieval Europe, "station" described ecclesiastical assignments and later expanded to include physical and figurative stops. With the scientific revolution, "static" emerged to denote stillness or unchanging states, reflecting the enduring influence of these roots.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sta and Stat
To remember "sta" and "stat," visualize a statue standing tall, unyielding through centuries. This image encapsulates the essence of stability and presence.
Mnemonic Device:
"Sta is the statue that stands; stat is the state that withstands."
Common Sta/Stat-Related Terms
- Static (stat-ik): Unchanging; stationary.
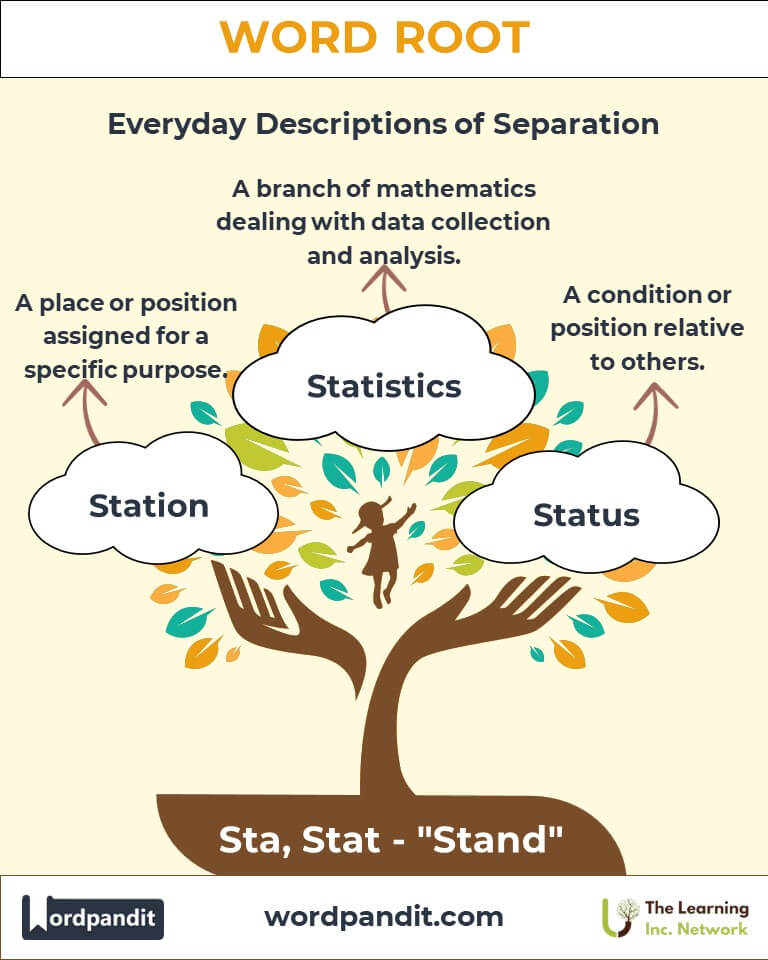
Example: "The static electricity crackled as she brushed her sweater." - Station (stay-shun): A place or position assigned for a specific purpose.
Example: "He waited for the train at the bustling station." - Status (stat-us): A condition or position relative to others.
Example: "Her status as a leading researcher was undeniable." - Statue (stat-yoo): A carved or cast figure of a person or animal, often standing.
Example: "The statue of liberty stood tall against the sky." - Statistics (stuh-tis-tiks): A branch of mathematics dealing with data collection and analysis.
Example: "Statistics reveal patterns in population growth." - Stasis (stay-sis): A state of equilibrium or inactivity.
Example: "The negotiation reached a stasis, with neither side yielding."
Sta and Stat Through Time
- Stature (Medieval Latin): Initially referring to physical height, it evolved to signify moral or social standing.
- Static (18th Century): First used in physics to describe forces at rest, now applied broadly to stillness.
Sta and Stat in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Homeostasis: The body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions.
Application: Essential in understanding health and disease. - Physics:
Statics: The study of forces in equilibrium.
Application: Key to engineering and structural design. - Technology:
Status Bar: An interface element indicating progress or state.
Application: Enhances user experience in digital platforms. - Sociology:
Social Status: A person's position in a societal hierarchy.
Application: Central to analyzing social structures.
Illustrative Story: Sta and Stat in Action
Sophia, an architect, faced the challenge of designing a station in an earthquake-prone city. Drawing on principles of statics, she created a structure that could withstand tremors while maintaining its elegant stature. Her design became a symbol of stability amidst unpredictability, showcasing the enduring power of "sta" and "stat."
Cultural Significance of the Sta/Stat Roots
The concept of standing is deeply ingrained in cultural narratives. Statues symbolize ideals, from liberty to justice, while societal status shapes identity and interactions. These roots underscore humanity's enduring quest for stability and recognition.

The Sta/Stat Family Tree
- Stab (Latin: "to stand firm"):
Example: Establish: To set up firmly. - Pos (Latin: "to place or position"):
Example: Position: A place where something is located. - Sist (Latin: "to cause to stand"):
Example: Insist: To stand firm on a demand.
FAQs About " Sta " and " Stat "
Q: What do the roots "sta" and "stat" mean?
A: The roots "sta" and "stat" come from the Latin word stare, meaning "to stand." They signify stability, position, or condition. These roots are foundational for words that describe standing firm, stillness, or a fixed state, such as "stationary" (not moving) and "statue" (a figure standing still).
Q: How are "sta" and "stat" used in science?
A: In science, these roots are integral to terms like "static" (unchanging or at rest) and "homeostasis" (the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions). They capture concepts of equilibrium and balance, vital in physics, biology, and medicine.
Q: What is the origin of the word "station"?
A: The word "station" comes from the Latin statio, meaning "a standing place" or "a post." Originally referring to a specific location where someone or something stands, it now includes meanings like a transportation hub (e.g., a train station) or a role (e.g., a military station).
Q: What does "stasis" mean in different contexts?
A: "Stasis" refers to a state of balance, stillness, or inactivity. In medicine, it describes the cessation of normal fluid flow (e.g., blood or lymph). In history or politics, it can mean a standstill or period of inactivity, often during conflicts or negotiations.
Q: Are "status" and "statue" related?
A: Yes, both words derive from the Latin stare. "Status" refers to a person's standing or condition, whether social, legal, or professional. "Statue," on the other hand, refers to a figure that literally stands, often symbolizing a concept, person, or idea.
Q: What does "static electricity" mean?
A: "Static electricity" refers to the accumulation of electric charge on a surface that is not moving or flowing. The word "static" here captures the root’s meaning of "still" or "unchanging," as the charge remains in one place rather than moving like current electricity.
Test Your Knowledge: " Sta " and " Stat " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "stat" mean?
2. Which term describes data analysis?
3. What is "stasis"?
4. What does "stationary" mean?
5. What root relates to equilibrium in medicine?
Conclusion: The Enduring Strength of Sta and Stat
The roots "sta" and "stat" exemplify stability, a cornerstone of language and life. From scientific concepts to societal roles, they remind us of the importance of standing firm. As language evolves, these roots continue to anchor meaning and inspire resilience.












