Struct: The Building Blocks of Language and Innovation
Explore the transformative power of the root "struct," derived from Latin, meaning "to build." From fundamental concepts like "structure" to advanced ideas such as "infrastructure," this versatile root forms the foundation of innovation, architecture, and creativity.
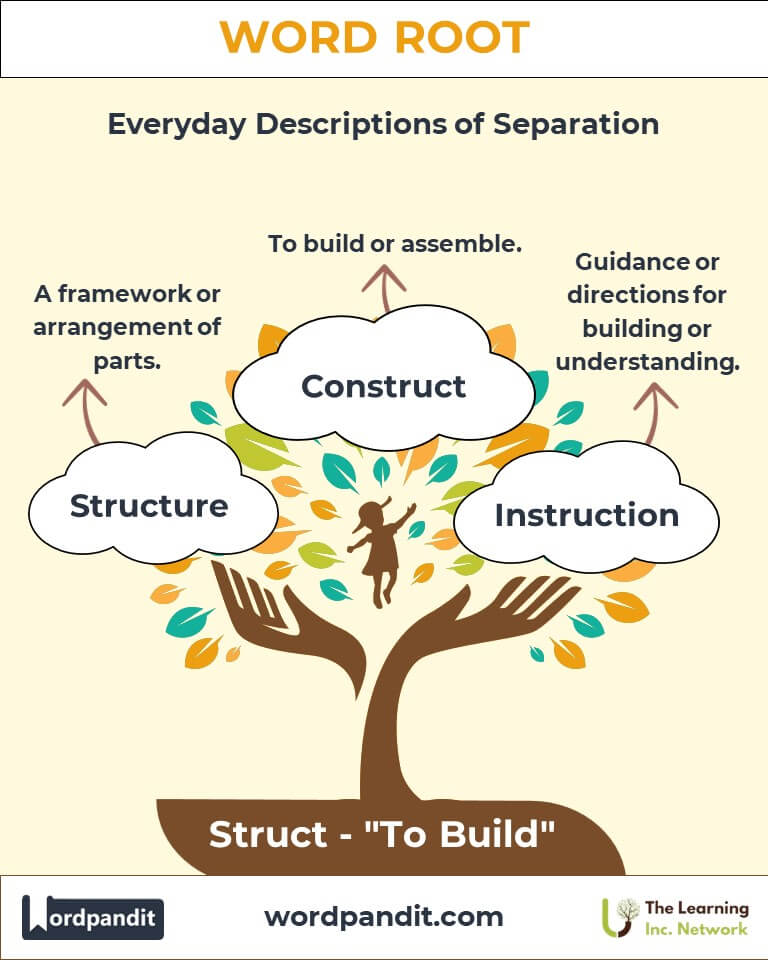
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Struct
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Struct
- Common Struct-Related Terms
- Struct Through Time
- Struct in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Struct in Action
- Cultural Significance of Struct
- The Struct Family Tree
- FAQs About the Struct Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Struct Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Struct
1. Introduction: The Essence of Struct
What do skyscrapers, storytelling, and software design have in common? The answer lies in "struct," a root that encapsulates the idea of building or constructing. Originating from the Latin word struere (to pile up or arrange), this root appears in words that denote organization, creation, and design. Its widespread usage connects disciplines as diverse as engineering, literature, and technology.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root struct traces back to the Latin struere, which means "to heap up" or "to build." It entered English through Old French during the Middle Ages, gaining prominence in words related to physical and abstract constructions. By the Renaissance, struct had become a cornerstone in the language of architecture, social systems, and emerging sciences.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Struct
Imagine a master builder laying bricks to create a towering structure. Each brick symbolizes a concept or idea, coming together to form a cohesive whole.
Mnemonic Device:
"Struct is the architect of words, building bridges between ideas and innovation."
4. Common Struct-Related Terms
- Structure (struhk-chur)
Definition: A framework or arrangement of parts.
Example: "The bridge's structure was designed to withstand earthquakes." - Construct (kuhn-struhkt)
Definition: To build or assemble.
Example: "They constructed a model of the solar system for the science fair." - Instruction (in-struhk-shun)
Definition: Guidance or directions for building or understanding.
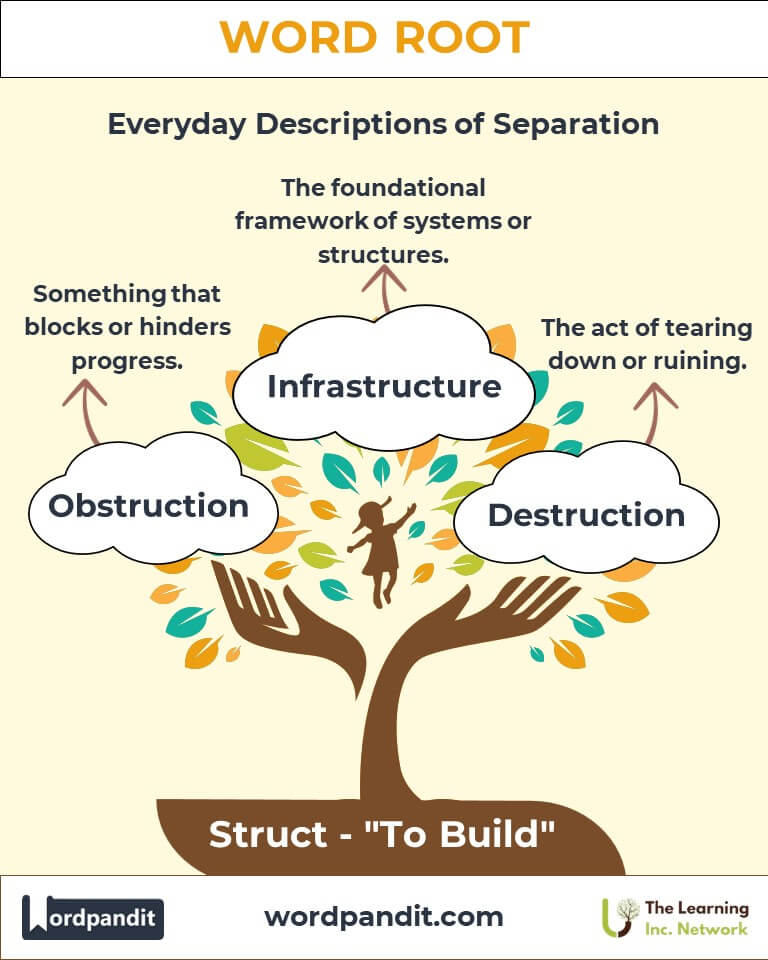
Example: "The instruction manual helped assemble the furniture." - Destruction (de-struhk-shun)
Definition: The act of tearing down or ruining.
Example: "The hurricane caused widespread destruction in the region." - Infrastructure (in-fruh-struhk-chur)
Definition: The foundational framework of systems or structures.
Example: "Investments in infrastructure improve transportation and connectivity." - Obstruction (ob-struhk-shun)
Definition: Something that blocks or hinders progress.
Example: "The fallen tree created an obstruction on the road."
5. Struct Through Time
- Medieval Era: Words like structure referred to architectural frameworks.
- Industrial Revolution: Terms like infrastructure gained prominence, reflecting the need for organized systems.
- Modern Era: Concepts like constructivism emerged, applying the root to psychology, art, and education.
6. Struct in Specialized Fields
Engineering
Infrastructure: Refers to essential systems like roads and bridges.
Impact: Critical for urban planning and disaster management.
Education
Instruction: The process of teaching and conveying knowledge.
Significance: Ensures effective learning.
Psychology
Construct: A theoretical framework or concept.
Application: Used in research and cognitive studies.
Medicine
Obstruction: A blockage in bodily systems (e.g., intestinal obstruction).
Importance: Requires timely diagnosis and treatment.
7. Illustrative Story: Struct in Action
As an architect, Maria envisioned building a green, sustainable community. She started by constructing a framework of eco-friendly infrastructure, integrating solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems. Her approach also involved instructing local residents on maintaining their homes. Overcoming obstructions like limited resources, Maria’s perseverance led to a model community that inspired others worldwide.
8. Cultural Significance of Struct
The root struct reflects humanity's innate desire to create and organize. It resonates in art, where we construct stories, and in architecture, where we build enduring monuments. From the Great Wall of China to modern skyscrapers, struct symbolizes progress and innovation.

9. The Struct Family Tree
- Stru- (Latin, build):
- Instrument: A tool or means for building.
- Construe: To interpret or build meaning.
- Tract- (Latin, pull):
- Attract: To pull or draw towards.
- Contract: To draw together or agree formally.
- Fract- (Latin, break):
- Fracture: A break in structure.
- Refract: To bend or alter, as in light.
10. FAQs About the Word Root "Struct"
Q: What does "struct" mean?
A: Struct originates from the Latin struere, meaning "to build" or "to arrange." This root is central to many words related to construction, organization, and systems.
Q: How does "construct" differ from "structure"?
A: Construct refers to the act of building or creating something, while structure describes the finished framework or arrangement of parts. For example, you construct a bridge, and the result is its structure.
Q: What does "destruction" mean, and how is it related to "struct"?
A: Destruction refers to the act of tearing down or ruining something. It combines the prefix de- (meaning "down" or "undo") with struct to signify the dismantling of a built system or object.
Q: What is "infrastructure"?
A: Infrastructure refers to the foundational systems or frameworks that support a society or organization, such as roads, utilities, and communication networks. It highlights how struct applies to large-scale societal "building blocks."
Q: What is "obstruction," and how does it relate to building?
A: Obstruction means something that blocks or impedes progress. In a construction or organizational context, it refers to a hindrance preventing smooth functioning or movement.
Q: Why is "instruction" connected to the root struct?
A: Instruction derives from the idea of "building knowledge." It involves providing guidance or steps that help construct understanding, similar to how physical instructions help assemble objects.
Q: What are some specialized fields where struct is used?
A: Fields like engineering (infrastructure), education (instruction), medicine (obstruction), and psychology (construct) heavily rely on words derived from struct. Each application ties back to the concept of organizing or building systems.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Struct Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "struct" signify?
2. Which word refers to societal systems like roads and utilities?
3. What does "construct" mean?
4. What is "destruction"?
5. What is obstruction in medicine?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Struct
The root struct serves as a testament to humanity’s capacity for creation and innovation. Whether in physical buildings or abstract systems, struct represents the essence of progress. As we continue to build a better future, this timeless root will remain a cornerstone of our language and imagination.












