Palaeo: Unearthing the Ancient in Words and Knowledge
Dive into the depths of time with "Palaeo," a root that means "ancient." Originating from Greek, this root brings to life fields like paleontology, where the remnants of Earth's distant past reveal the secrets of prehistoric life. Explore how this root enriches our understanding of ancient times, connecting modern science, history, and culture.
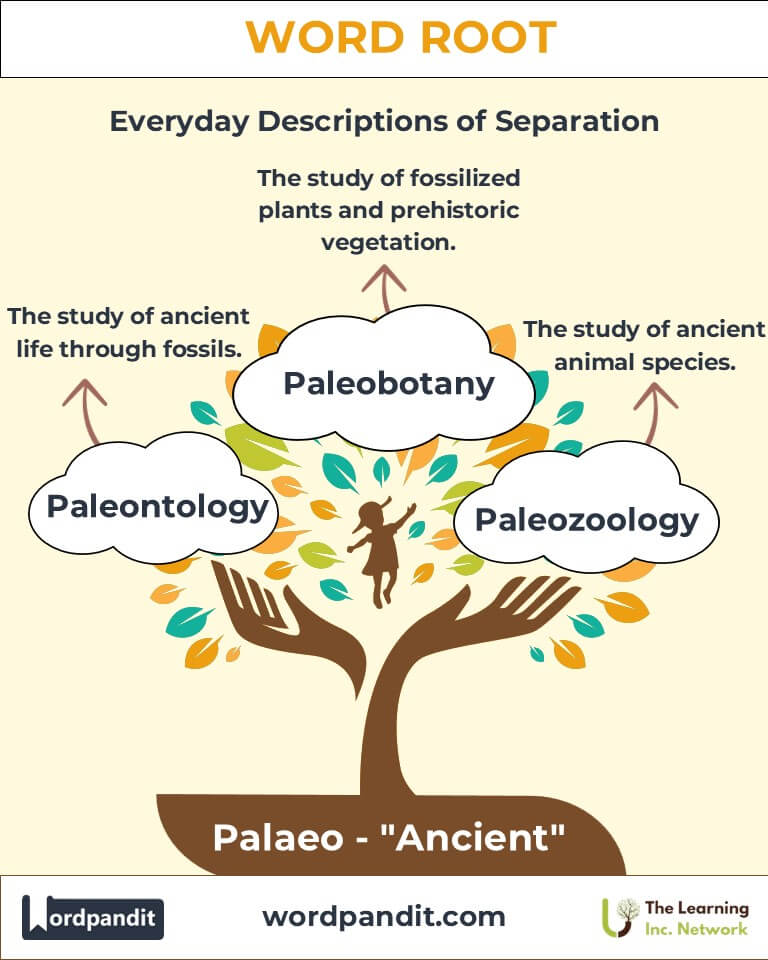
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Timeless Essence of Palaeo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Palaeo
- Common Palaeo-Related Terms
- Palaeo Through Time
- Palaeo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Palaeo in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Palaeo Root
- The Palaeo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Palaeo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Palaeo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Palaeo
Introduction: The Timeless Essence of Palaeo
When you hear "Palaeo," your mind might drift to fossils, ancient civilizations, or the secrets of prehistoric times. Derived from the Greek root "palaios," meaning "ancient" or "old," this root has shaped words that delve into the depths of time. Fields like paleontology and the Paleolithic era owe their names—and insights—to this linguistic gem, bridging the ancient with the modern.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Palaeo" originates from the Greek "palaios," meaning "of long ago" or "ancient." Early scholars used this term to describe antiquities and historical epochs. In the 19th century, with the rise of sciences like geology and archaeology, "Palaeo" gained prominence in words such as "paleontology" (the study of ancient life) and "Paleolithic" (the early Stone Age).
This evolution underscores humanity’s enduring fascination with the ancient past, from uncovering fossils to studying ancient artifacts.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Palaeo
To remember "Palaeo," think of an ancient cave painting, a testament to a world long gone. Imagine it as a bridge linking past and present, bringing "ancient" knowledge into today's understanding.
Mnemonic Device:
"Palaeo paints the past with the brush of time, revealing ancient stories in stone and bone."
Common Palaeo-Related Terms
- Paleontology (pay-lee-ON-tuh-gee):
Definition: The study of ancient life forms through fossils.
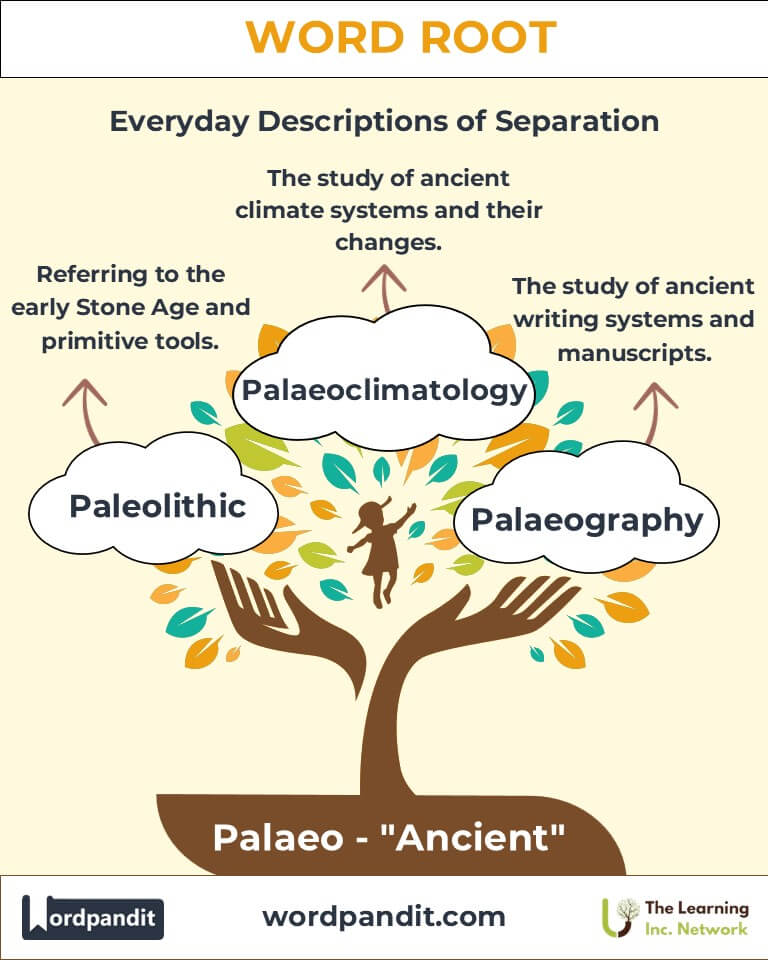
Example: "Paleontology has revealed the age and extinction of dinosaurs." - Paleolithic (pay-lee-oh-LITH-ik):
Definition: Referring to the early Stone Age, characterized by primitive tools.
Example: "The Paleolithic era marked humanity's first use of stone tools." - Palaeography (pay-lee-OG-ruh-fee):
Definition: The study of ancient writing systems and historical manuscripts.
Example: "Palaeography helps historians decipher ancient texts." - Palaeobotany (pay-lee-oh-BOT-uh-nee):
Definition: The study of fossilized plants and ancient vegetation.
Example: "Palaeobotany uncovers how prehistoric plants shaped Earth's environment." - Palaeozoology (pay-lee-oh-zoo-OL-uh-jee):
Definition: The study of ancient animal species.
Example: "Palaeozoology offers insights into extinct creatures' ecosystems."
Palaeo Through Time
- Paleolithic: Once solely associated with early stone tools, this term has expanded to include studies of prehistoric art and culture.
- Palaeontology: Originally focused on dinosaur bones, the field now encompasses ancient ecosystems, including microorganisms and prehistoric climate patterns.
Palaeo in Specialized Fields
- Archaeology:
Terms like "Palaeolithic" describe cultural and technological milestones of early humans. - Environmental Science:
Palaeoclimatology examines Earth's ancient climate systems, providing insights into modern climate change. - Medicine:
Palaeopathology explores ancient diseases and injuries, offering clues to human evolution and resilience.
Illustrative Story: Palaeo in Action
Dr. Harper, a paleontologist, carefully brushed away layers of dirt from a newly discovered fossil. It was a giant tooth from a long-extinct species. Nearby, her colleague examined pollen grains fossilized in amber, tracing the environment of this ancient creature’s world. Together, their work illuminated not only the past but also the delicate connections that shape life today.
Cultural Significance of the Palaeo Root
From the cave paintings of Lascaux to myths about ancient worlds, "Palaeo" resonates deeply in human culture. It reminds us of our quest to understand origins, whether through art, science, or storytelling. The root also appears in phrases like "palaeo diet," reflecting modern reinterpretations of ancient practices.

The Palaeo Family Tree
- Neo- (New):
- Neolithic: Referring to the "New Stone Age."
- Example: Neolithic agriculture transformed human societies.
- Archaeo- (Ancient):
- Archaeology: The study of human history through artifacts.
- Example: Archaeology unveils civilizations buried beneath time.
- Proto- (First):
- Protohuman: An early human ancestor.
- Example: Protohumans marked the dawn of tool use.
FAQs About the Palaeo Word Root
Q: What does "Palaeo" mean?
A: "Palaeo" means "ancient" or "of long ago." It comes from the Greek root "palaios," which reflects something that existed in the distant past. This root appears in terms related to history, science, and prehistory, emphasizing the study or understanding of the ancient world.
Q: What is paleontology?
A: Paleontology is the scientific study of ancient life forms through fossils. This field examines fossilized remains of animals, plants, and microorganisms, helping scientists understand Earth's biological and ecological history.
Q: What does "Paleolithic" refer to?
A: The term "Paleolithic" describes the early Stone Age, marked by the first use of stone tools by humans. It spans from approximately 2.5 million years ago to around 10,000 BCE, representing a significant period in human evolution.
Q: Is "Palaeo" only used in science?
A: No, "Palaeo" is not limited to science. While it is prominently used in fields like paleontology and palaeoclimatology, it also appears in cultural references like the "palaeo diet," which reflects an interest in replicating ancient dietary habits.
Q: What is palaeoclimatology?
A: Palaeoclimatology is the study of ancient climate systems. By analyzing ice cores, sediment, and fossils, scientists reconstruct Earth's climate history, providing insights into natural cycles and modern climate change.
Q: How does "Palaeo" differ from "Archaeo"?
A: While "Palaeo" emphasizes the distant or ancient past, "Archaeo" is more focused on the study of human history through material remains. For example, archaeology deals with artifacts and human structures, while palaeontology deals with fossilized life.
Q: Why is studying "Palaeo" fields important?
A: Studying "Palaeo" fields like paleontology and palaeoclimatology helps us understand Earth's history, the evolution of life, and the natural changes that have shaped the planet. This knowledge informs current scientific advancements and environmental conservation efforts.
Test Your Knowledge: Palaeo Word Root Quiz
1. What does "Palaeo" mean?
2. What does "Paleolithic" refer to?
3. What does paleontology study?
4. Which field studies fossilized plants?
5. What is palaeoclimatology?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Palaeo
The root "Palaeo" takes us on a journey to the ancient past, enriching our understanding of history, science, and culture. As we continue to uncover the mysteries of early life, the enduring relevance of "Palaeo" reminds us of our shared origins and the lessons they hold for the future.












