Peps: Unlocking the Digestive Mysteries of Language and Science
Discover the transformative power of the root "peps," derived from the Greek word for digestion. Explore its role in both language and biology, from ancient understandings to modern medical terms like "pepsin" and "dyspepsia." This root connects the processes of digestion to cultural and scientific evolution.
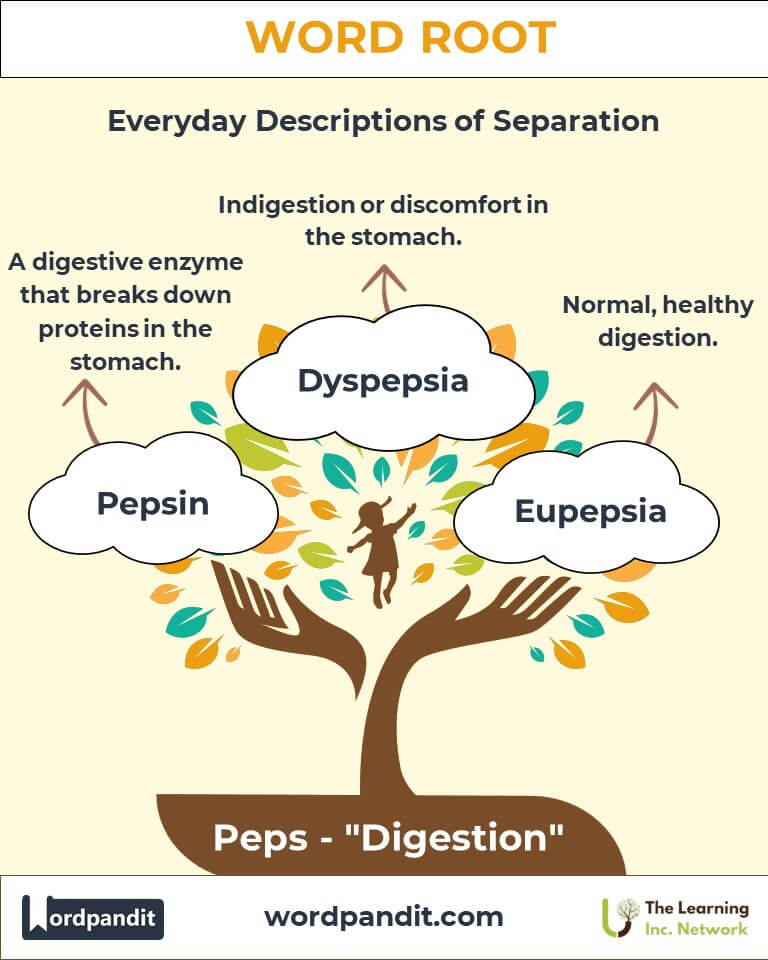
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Peps"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Peps
- Common Peps-Related Terms
- Peps Through Time
- Peps in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Peps in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Peps" Root
- The "Peps" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Peps" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Peps" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Digestive Legacy of "Peps"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Peps"
When you think of digestion, images of food breaking down into nutrients come to mind. But the root peps, pronounced as "pehps," goes beyond the physiological process. It stems from the Greek word pepsis, meaning digestion, and has lent itself to terms that describe not just biological processes but also states of ease or difficulty in the digestive system. Whether it's enzymes like "pepsin" or conditions like "dyspepsia," this root has a profound presence in science and language.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root peps finds its origin in the Greek word pepsis, which translates directly to digestion. In ancient Greek medicine, pepsis symbolized the transformation of food into vital energy, a concept central to their understanding of health. The term entered Latin as peptos and eventually evolved into modern English derivatives like "peptic" and "pepsin." Over centuries, it became a cornerstone in medical vocabulary, bridging ancient theories of digestion with contemporary biomedical science.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Peps
Mnemonic Device: "Peps powers digestion like pepsin preps proteins."
Visualize pepsin as a cheerful chef in your stomach, energetically breaking down proteins into smaller pieces to help your body absorb nutrients.
4. Common Peps-Related Terms
- Pepsin (pep-sin): An enzyme that breaks down proteins in the stomach.
Example: "Pepsin is essential for digesting the steak you just ate." - Dyspepsia (dis-pep-see-uh): Indigestion or discomfort in the stomach.
Example: "After a heavy meal, he often suffered from dyspepsia." - Peptic (pep-tik): Relating to digestion, particularly in the stomach.
Example: "Peptic ulcers are caused by excess stomach acid." - Eupepsia (yoo-pep-see-uh): Normal, healthy digestion.
Example: "Her eupepsia was a result of a balanced diet."
5. Peps Through Time
- Ancient Usage: In Greek medicine, pepsis referred to the balance of bodily humors achieved through proper digestion.
- Modern Evolution: The discovery of pepsin in the 19th century revolutionized biochemistry and led to a deeper understanding of protein metabolism.
6. Peps in Specialized Fields
- Biochemistry: Pepsin plays a crucial role in breaking down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Gastroenterology: Disorders like dyspepsia highlight the importance of understanding digestive processes.
- Pharmacology: Medications aimed at treating peptic ulcers target excess stomach acid and enhance digestion.
7. Illustrative Story: Peps in Action
In a small village, Dr. Elena was known for her remedies that eased digestive troubles. One day, she encountered a boy, Leo, complaining of persistent dyspepsia. With careful observation, she identified that his meals lacked balance. She explained the role of enzymes like pepsin in breaking down food and recommended a diet rich in proteins and vegetables. Within weeks, Leo’s digestion improved, and he returned to playing with his friends. Dr. Elena’s understanding of "peps" had transformed his health.
8. Cultural Significance of the "Peps" Root
From ancient Greek physicians emphasizing pepsis as a symbol of health to modern diets focusing on gut wellness, the concept of digestion has held a central place in cultural narratives. The root peps reminds us that good digestion is integral to overall well-being, shaping not just health but culinary traditions and social practices.

9. The "Peps" Family Tree
Explore related roots and their meanings:
- Pept- (to digest):
- Examples: Peptide, peptone.
- Gastro- (stomach):
- Examples: Gastroenterology, gastritis.
- Eu- (good):
- Examples: Eupepsia, euphoria.
10. FAQs About the "Peps" Word Root
Q: What does the root "peps" mean?
A: The root "peps" comes from the Greek word pepsis, meaning digestion. It refers to the process of breaking down food into simpler substances that the body can absorb and use for energy and growth. This concept is central to both biology and medical terminology.
Q: What is pepsin, and what does it do?
A: Pepsin is a digestive enzyme produced in the stomach. It helps break down proteins in food into smaller peptides, making it easier for the body to absorb nutrients. Pepsin is most active in the highly acidic environment of the stomach.
Q: What is dyspepsia?
A: Dyspepsia, commonly known as indigestion, refers to discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen. Symptoms may include bloating, nausea, and a feeling of fullness after eating. It is often caused by overeating, stress, or certain medical conditions like ulcers.
Q: What are peptic ulcers, and what causes them?
A: Peptic ulcers are sores that form on the lining of the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine. They are caused by an imbalance between stomach acid and the protective mucous lining, often linked to Helicobacter pylori bacteria or the overuse of NSAID pain relievers.
Q: What is eupepsia, and how is it different from dyspepsia?
A: Eupepsia refers to normal and healthy digestion. Unlike dyspepsia, which is marked by discomfort or difficulty digesting food, eupepsia signifies a balanced and efficient digestive process, often associated with good dietary habits.
Q: How is the root "peps" used metaphorically?
A: While "peps" is rooted in biological processes, it can metaphorically signify transformation or breaking down complex ideas into simpler, digestible concepts, akin to how digestion works in the body.
Q: What role does pepsin play in protein metabolism?
A: Pepsin initiates the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides, which are then further processed in the small intestine by other enzymes like trypsin. This first step is critical for proper protein metabolism and nutrient absorption.
11. Test Your Knowledge: "Peps" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "peps" signify?
2. Which enzyme is directly associated with the root "peps"?
3. What does "dyspepsia" describe?
4. What term describes healthy digestion?
5. What is a common cause of peptic ulcers?

12. Conclusion: The Digestive Legacy of "Peps"
The root "peps" bridges ancient wisdom with modern science, underscoring the importance of digestion in both health and language. From enzymes like pepsin to conditions like dyspepsia, its legacy is a testament to humanity’s enduring curiosity about the body’s inner workings. As our understanding deepens, "peps" will continue to inspire innovation and appreciation for the complex processes that sustain life.











