🚀 Space Exploration: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Space exploration represents one of humanity’s most ambitious endeavors, bridging science, technology, and philosophy to answer profound questions about our universe. RC passages on this topic often examine the history, challenges, and implications of exploring outer space. Whether discussing the geopolitical competition of the Space Race, the role of private companies in commercial spaceflight, or the quest to find life on Mars, these passages require readers to engage with both factual details and broader implications. By mastering the following concepts, you will enhance your ability to decode complex arguments and identify key themes.
📋 Overview
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- The Space Race
- Satellites and Spacecraft
- Human Spaceflight
- Space Telescopes
- Mars Exploration
- Astrobiology
- Space Debris
- Space Laws and Policies
- Commercial Spaceflight
- The Future of Space Exploration
🔍 Detailed Explanations
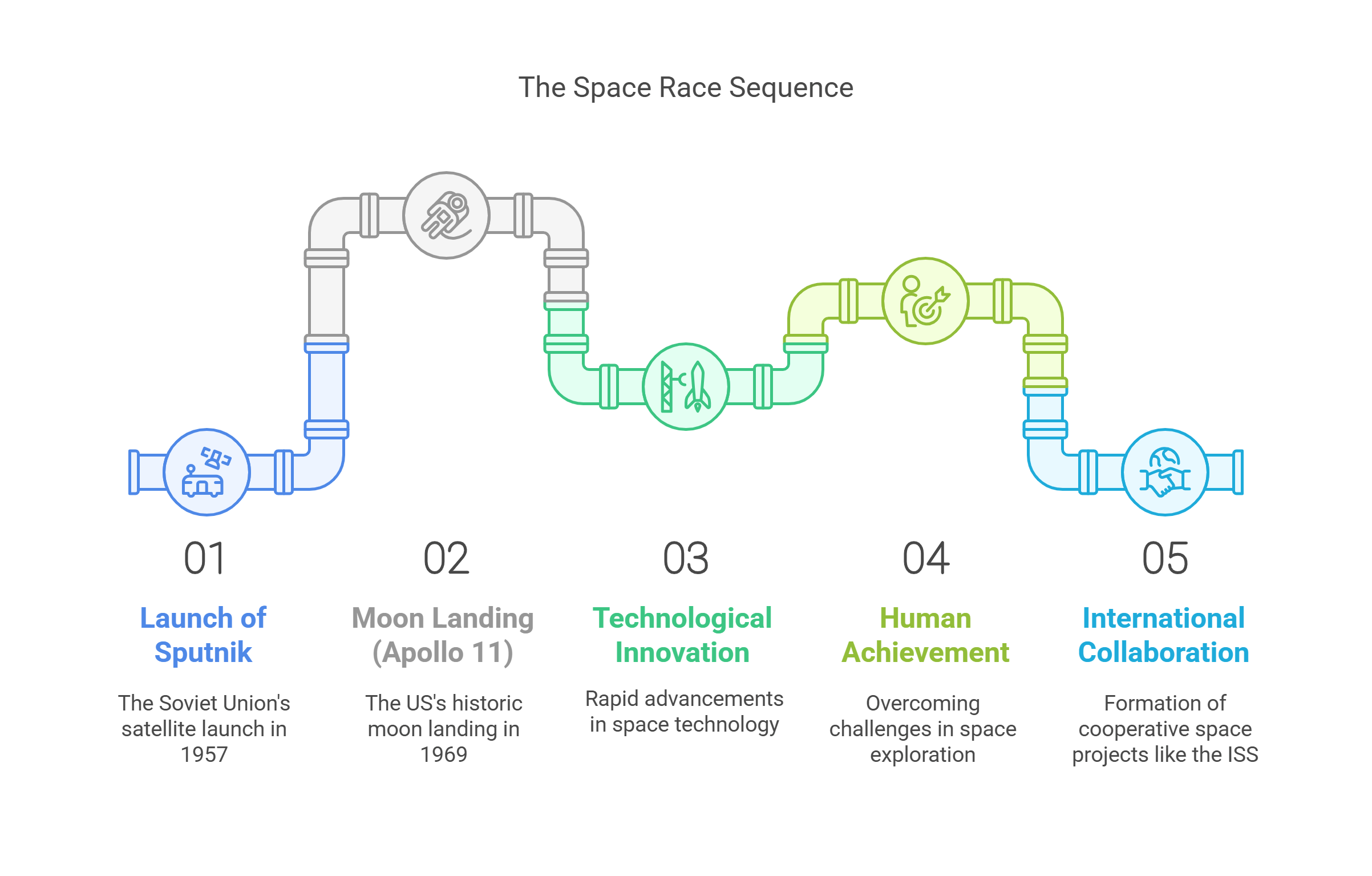
1. The Space Race
The Space Race was a defining chapter in 20th-century history, marking the Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union. The launch of Sputnik (1957) and the moon landing (Apollo 11, 1969) were pivotal milestones. This race wasn’t just about technological superiority—it symbolized ideological competition between democracy and communism.
- Sparked rapid technological innovation in rockets, satellites, and computing systems. Technologies developed during this period laid the groundwork for modern space exploration and satellite-based services.
- Showcased humanity’s drive to achieve the impossible, overcoming immense engineering and scientific challenges.
- Fostered collaboration despite initial rivalry, ultimately leading to projects like the International Space Station (ISS), where nations work together to advance space science.
Explained Simply: Imagine two kids trying to build the tallest tower out of blocks to show who’s the best builder. The Space Race was like that—but on a global scale with rockets, satellites, and the moon as the ultimate prize.
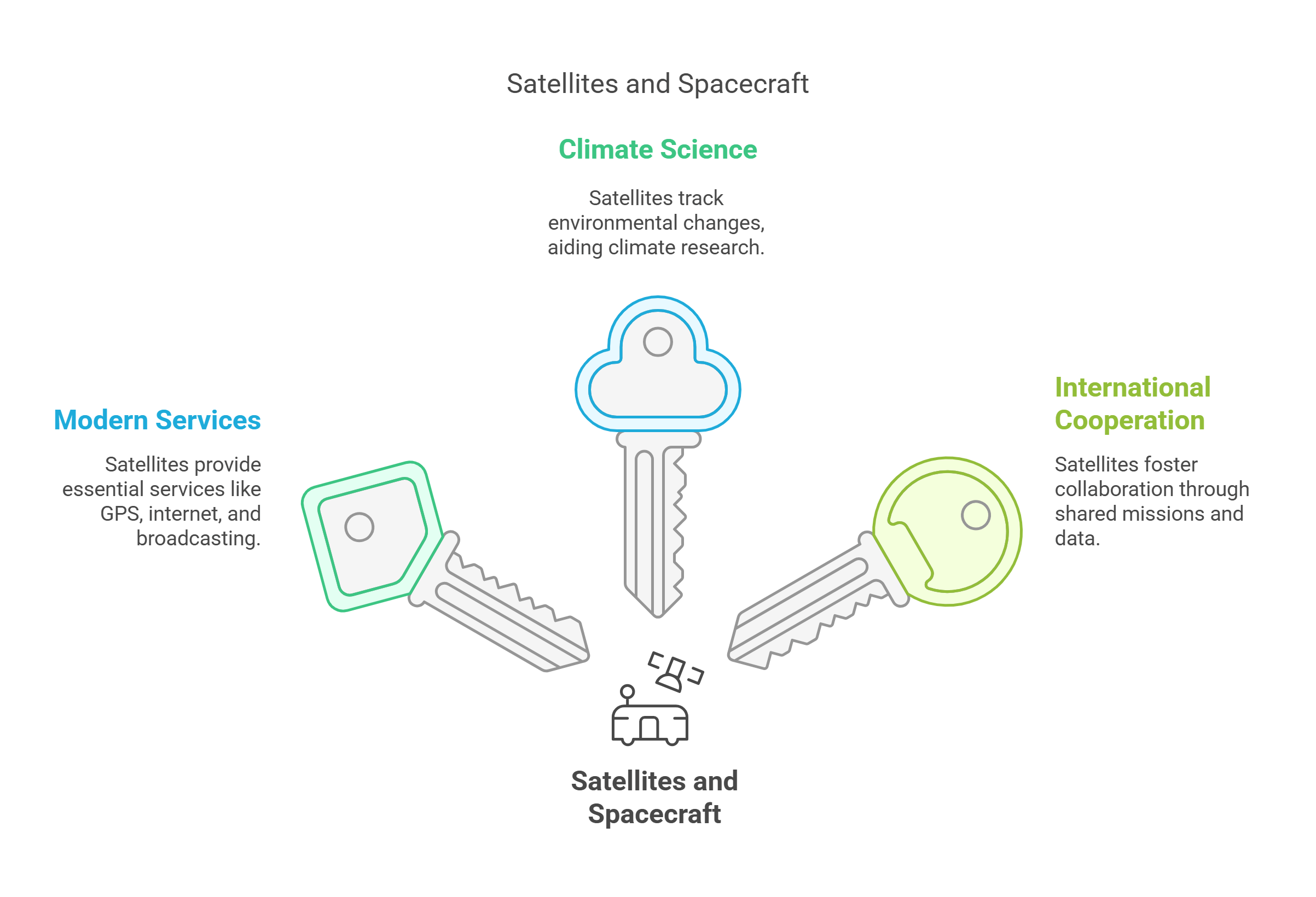
2. Satellites and Spacecraft
Satellites are artificial objects that orbit planets, performing tasks like communication, weather forecasting, and Earth observation. Spacecraft, designed for interplanetary missions, range from robotic explorers like Voyager to crewed vehicles like Orion.
- Facilitate essential modern services like GPS navigation, internet connectivity, and live television broadcasting. Without satellites, much of today’s interconnected world would cease to function.
- Revolutionize climate science by tracking environmental changes, from melting polar ice to deforestation.
- Promote international cooperation as countries collaborate on satellite launches and missions, sharing data for mutual benefit.
Explained Simply: Think of satellites as helpful spies in the sky, quietly watching over us to predict the weather, guide airplanes, and even broadcast your favorite TV shows. Spacecraft, meanwhile, are the adventurers exploring far-off destinations.
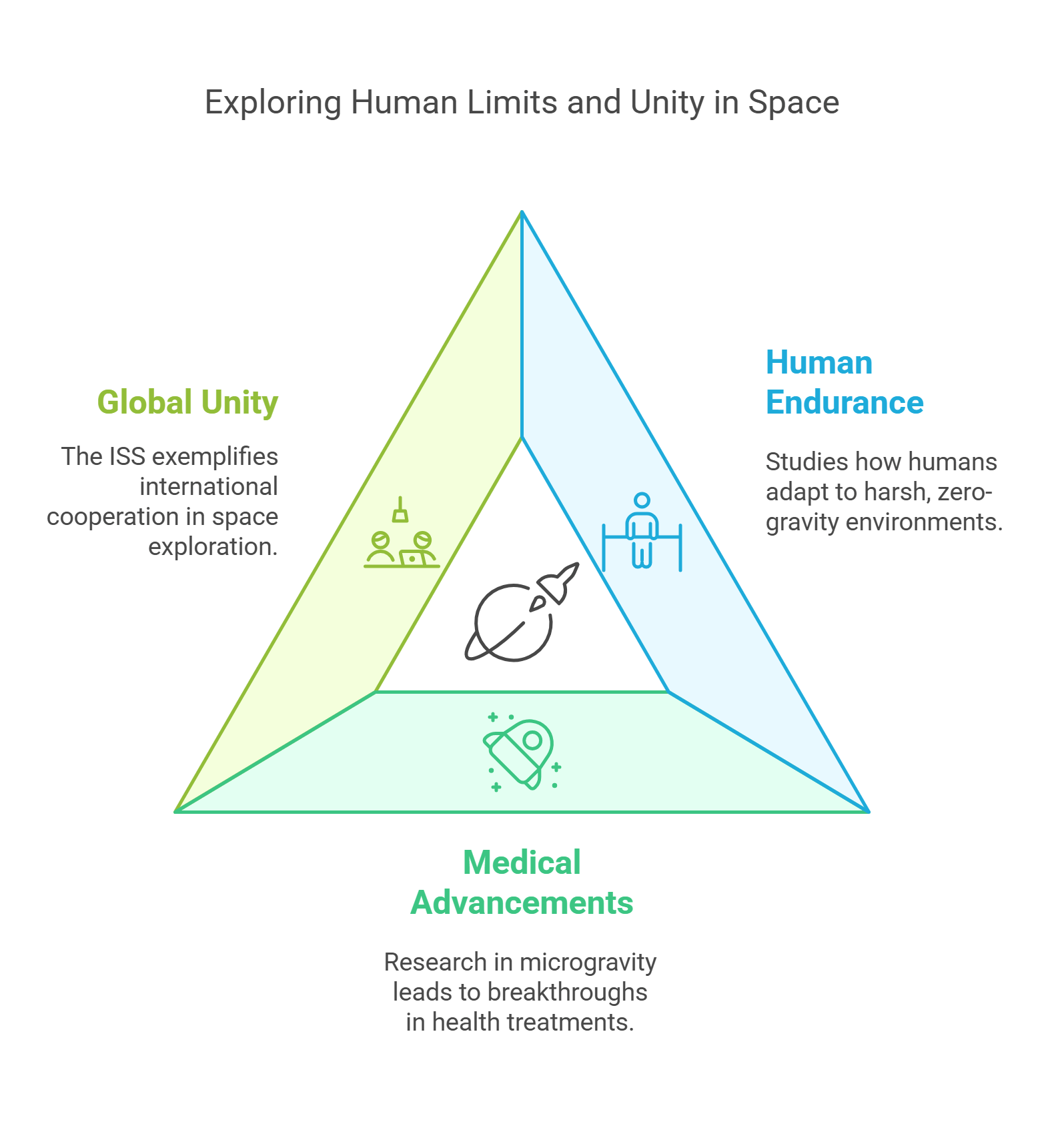
3. Human Spaceflight
Human spaceflight symbolizes the pinnacle of space exploration. From Yuri Gagarin’s historic orbit (1961) to the ISS, astronauts have ventured into space to conduct experiments and inspire generations.
- Explores the limits of human endurance in harsh, zero-gravity environments, providing insights into how the human body adapts.
- Advances medical knowledge through microgravity research, leading to breakthroughs in fields like osteoporosis and muscle atrophy treatment.
- Showcases global unity aboard the ISS, where astronauts from different nations live and work together.
Explained Simply: Sending astronauts into space is like climbing the highest mountain—dangerous but full of discoveries that benefit everyone on Earth.
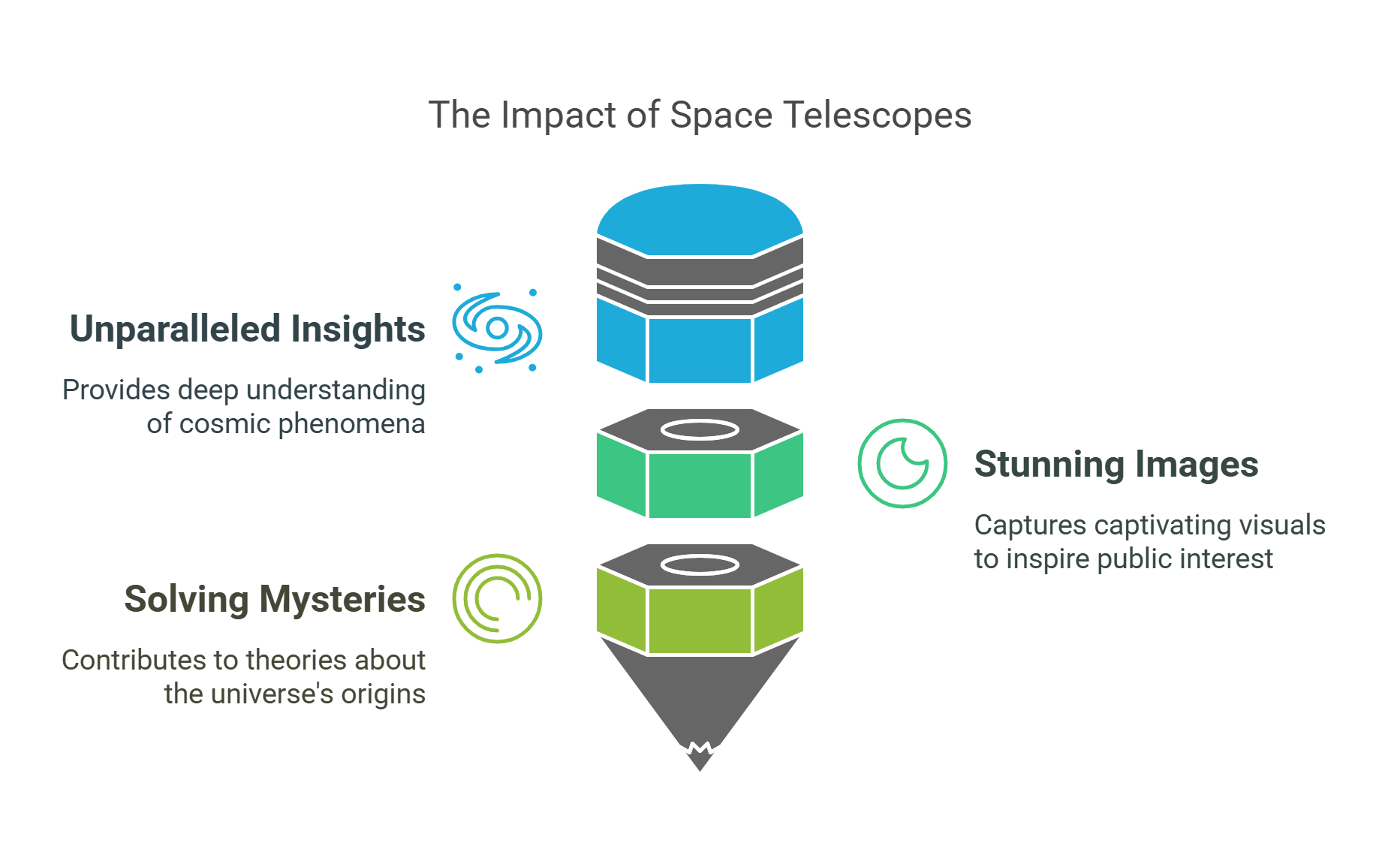
4. Space Telescopes
Space telescopes like the Hubble and James Webb revolutionize astronomy by observing the universe without atmospheric interference.
- Provide unparalleled insights into cosmic phenomena like black holes, supernovae, and the formation of galaxies.
- Capture stunning images, sparking public interest and inspiring the next generation of scientists.
- Solve mysteries about the origins of the universe, contributing to theories about the Big Bang and cosmic evolution.
Explained Simply: A space telescope is like a super-powerful pair of glasses that let us see stars and galaxies millions of miles away with crystal-clear clarity. 🌌
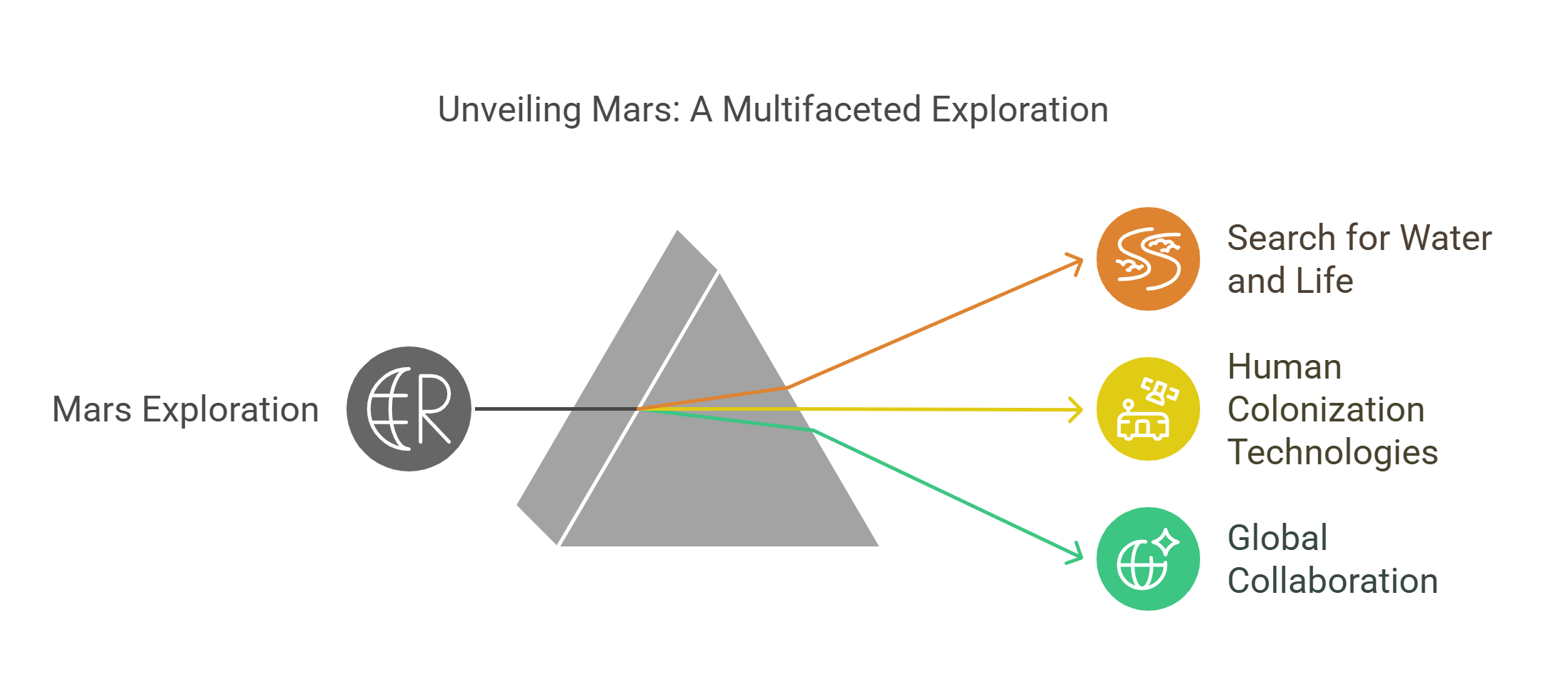
5. Mars Exploration
Mars has captured human imagination as a potential second home. Robotic missions like NASA’s Perseverance and ESA’s ExoMars explore its geology and search for signs of past life.
- Investigates whether Mars once harbored water and life, using sophisticated instruments to analyze soil and rock samples.
- Tests technologies for human colonization, including oxygen generation and sustainable habitats.
- Inspires global collaboration, with missions launched by multiple countries, fueling dreams of interplanetary living.
Explained Simply: Exploring Mars is like finding an old diary to see if it tells a story about life from millions of years ago.
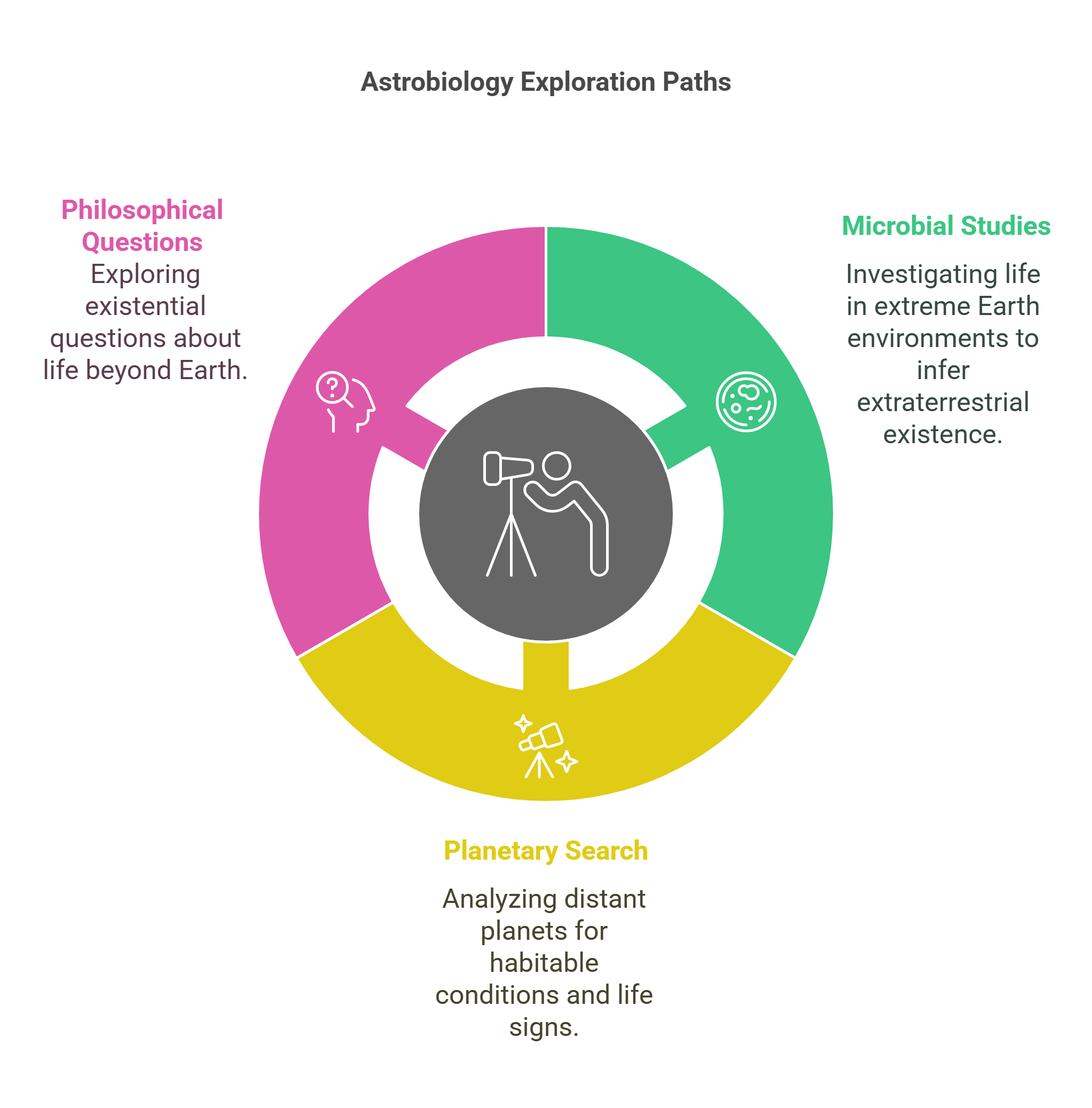
6. Astrobiology
Astrobiology examines the possibility of life beyond Earth, focusing on extreme environments as analogs for extraterrestrial habitats.
- Studies microbes in Earth’s harshest regions, like deep-sea vents and Antarctic ice, to model how life might exist elsewhere.
- Guides the search for habitable planets, analyzing atmospheres and conditions around distant stars.
- Raises profound questions about humanity’s place in the universe, blending science with philosophy.
Explained Simply: Astrobiology is like being a treasure hunter looking for signs of life on other planets by studying Earth’s toughest conditions.
7. Space Debris
Space debris, or “space junk,” includes abandoned satellites, rocket fragments, and other materials left in orbit. This growing issue threatens operational spacecraft and future missions.
- Requires international regulations to prevent collisions and clean up existing debris.
- Raises safety concerns for astronauts and functional satellites, with some orbits becoming increasingly congested.
- Sparks innovation in debris removal technologies, such as robotic arms and net-capturing systems.
Explained Simply: Imagine trying to play soccer on a field full of broken toys—it’s hard and dangerous! That’s what space debris does to satellites and astronauts. 🧩
8. Space Laws and Policies
Space law ensures that space remains a peaceful domain for all nations. Treaties like the Outer Space Treaty (1967) prohibit the militarization of celestial bodies.
- Governs mining, colonization, and commercial ventures, ensuring fair access to resources.
- Encourages cooperation while preventing monopolization of space assets by powerful nations.
- Balances exploration rights with environmental stewardship to preserve celestial bodies.
Explained Simply: Space laws are like playground rules—everyone gets to play, but no one is allowed to hog the slide or make it unsafe for others.
9. Commercial Spaceflight
Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are making space accessible through reusable rockets and space tourism.
- Reduces costs of reaching orbit, enabling smaller nations and private organizations to participate in space exploration.
- Spurs innovation through public-private partnerships, creating jobs and new industries.
- Raises ethical questions about space commercialization and equity of access.
Explained Simply: It’s like opening a travel agency for outer space—anyone (with enough money) can book a ticket to the stars!
10. The Future of Space Exploration
Space exploration’s future lies in sustainability and interplanetary travel. From lunar bases to asteroid mining, the possibilities are endless.
- Focuses on long-term human presence on the Moon and Mars, building infrastructure for self-sustaining colonies.
- Develops revolutionary technologies, like space elevators and nuclear-powered spacecraft.
- Envisions humanity as a multi-planetary species, reducing risks from Earth-based disasters.
Explained Simply: The future of space is like planning a road trip to the farthest corners of the map, except this map is the universe!
✨ Conclusion
Space exploration combines humanity’s boundless curiosity with groundbreaking science and technology. From studying astrobiology to solving space debris challenges, every step forward helps us understand the universe better. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be ready to navigate RC passages on this fascinating topic with confidence and insight. 🚀










