🤖 Artificial Intelligence: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human cognition, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. AI has transformed industries ranging from healthcare to entertainment, making it a central topic in discussions about technology and society. RC passages on AI often focus on its applications, ethical implications, and future potential. Understanding these concepts will enhance your ability to analyze complex arguments and evaluate technological advancements.
📋 Overview
This guide will explore the following essential AI concepts:
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Neural Networks
- Computer Vision
- Robotics and Automation
- Ethics in AI
- Bias in AI
- AI in Healthcare
- AI in Autonomous Systems
- The Future of AI
🔍 Detailed Explanations
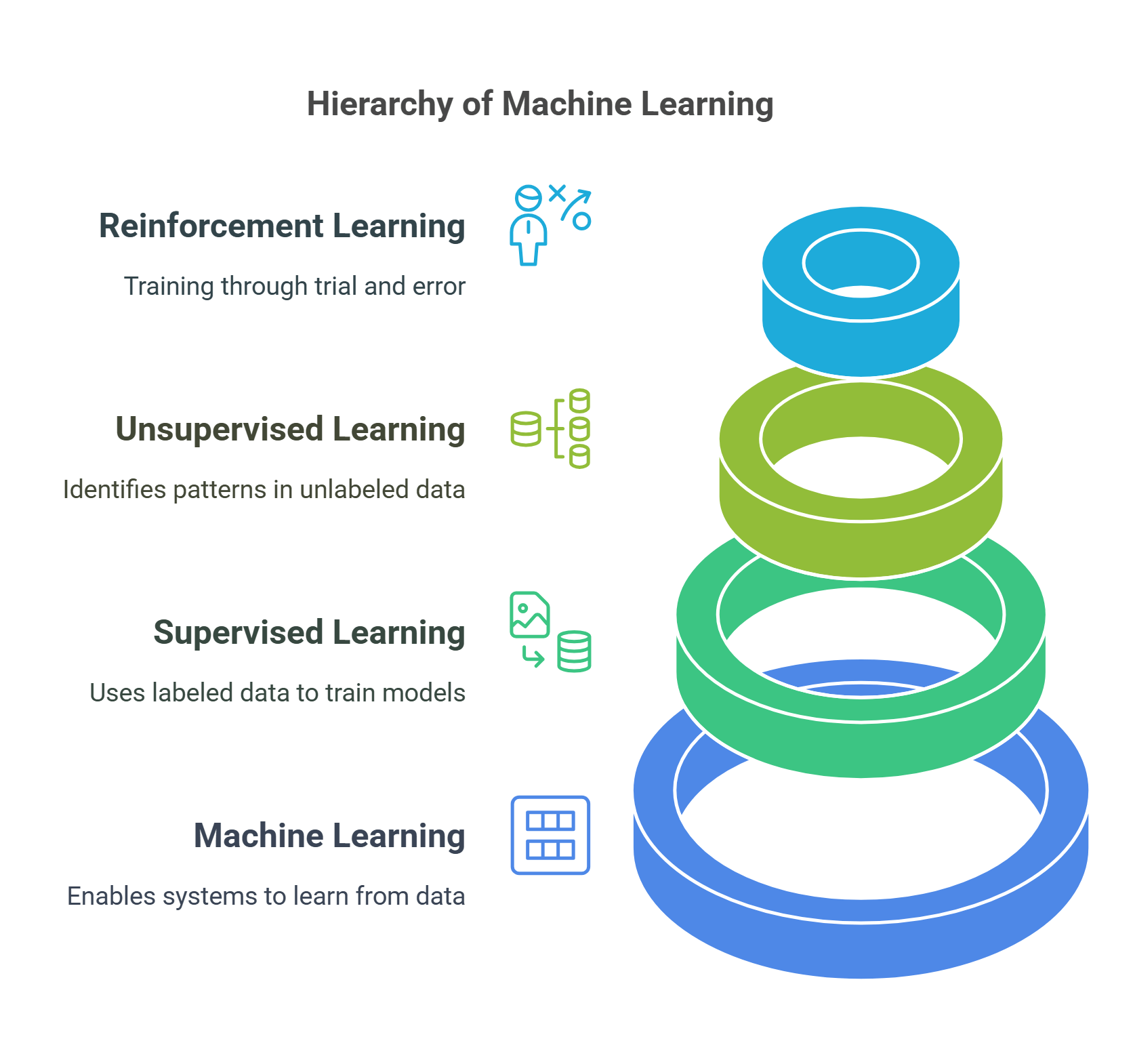
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Detailed Explanation: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. Algorithms process large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions.
- Supervised Learning: Uses labeled data to train models, such as email spam filters.
- Unsupervised Learning: Identifies patterns in unlabeled data, like clustering customer preferences.
- Reinforcement Learning: Involves training models through trial and error, as seen in game-playing AI.
Explained Simply: Machine learning is like teaching a student to solve math problems by showing them examples and letting them practice until they get it right.
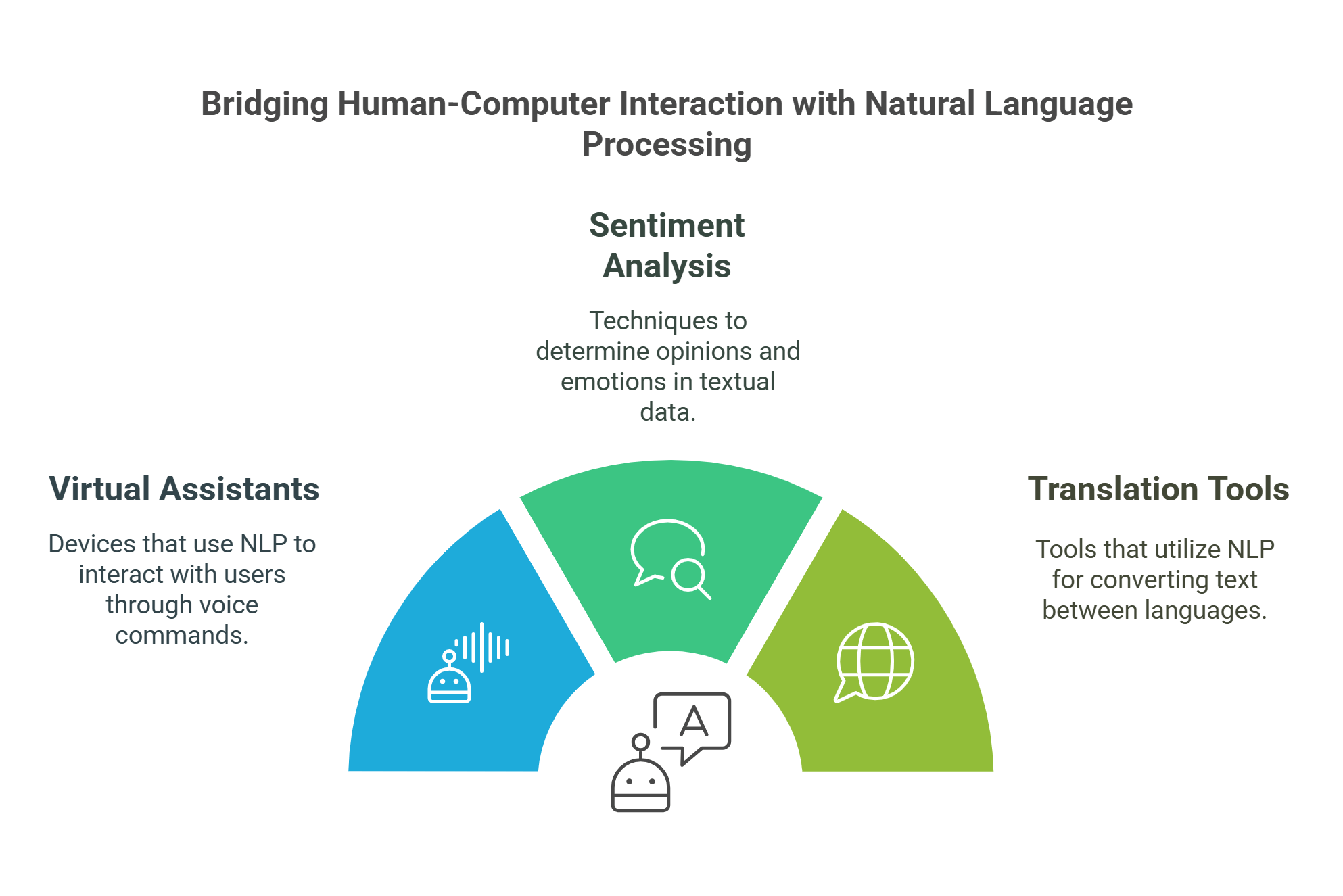
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Detailed Explanation: NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. This field bridges communication between humans and computers.
- Examples: Virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri rely on NLP to process voice commands.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP is used to gauge opinions in customer reviews or social media posts.
- Translation Tools: Platforms like Google Translate leverage NLP for accurate language translation.
Explained Simply: NLP is like teaching a computer to understand and respond to conversations, whether it’s a text or voice command.
3. Neural Networks
Detailed Explanation: Neural networks are algorithms inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of layers of nodes (neurons) that process information and make decisions.
- Deep Learning: A subset of neural networks with multiple layers, enabling advanced tasks like image recognition.
- Applications: Neural networks power facial recognition systems and fraud detection in banking.
- Training Process: Involves feeding data through layers to adjust weights and improve accuracy.
Explained Simply: Neural networks are like a digital brain that learns to recognize patterns, such as identifying a face in a photo.
4. Computer Vision
Detailed Explanation: Computer vision enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data from the world around them, such as images and videos.
- Applications: Used in facial recognition, medical imaging, and autonomous vehicles.
- Object Detection: Identifies and classifies objects within images, like detecting pedestrians for self-driving cars.
- Image Processing: Enhances image quality and identifies patterns for analysis.
Explained Simply: Computer vision is like giving machines the ability to see and understand what’s in a picture or video.
5. Robotics and Automation
Detailed Explanation: Robotics involves designing and operating machines that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. Automation refers to the use of these machines to replace or augment human labor.
- Industrial Robots: Used in manufacturing for repetitive tasks, such as assembling cars.
- Service Robots: Assist in healthcare, hospitality, and customer service, like robotic nurses or hotel assistants.
- Challenges: Include designing robots for complex environments and ensuring safety in human-robot interactions.
Explained Simply: Robotics and automation are like building smart machines to help humans work faster and more efficiently.
6. Ethics in AI
Detailed Explanation: Ethical considerations in AI address the societal impact of deploying intelligent systems, ensuring they are used responsibly and fairly.
- Privacy Concerns: AI systems often collect sensitive user data, raising issues about consent and data protection.
- Transparency: Ensures users understand how AI makes decisions.
- Accountability: Establishing who is responsible when AI systems cause harm, such as accidents involving self-driving cars.
Explained Simply: Ethics in AI is like setting rules to ensure that smart machines are used fairly and responsibly.
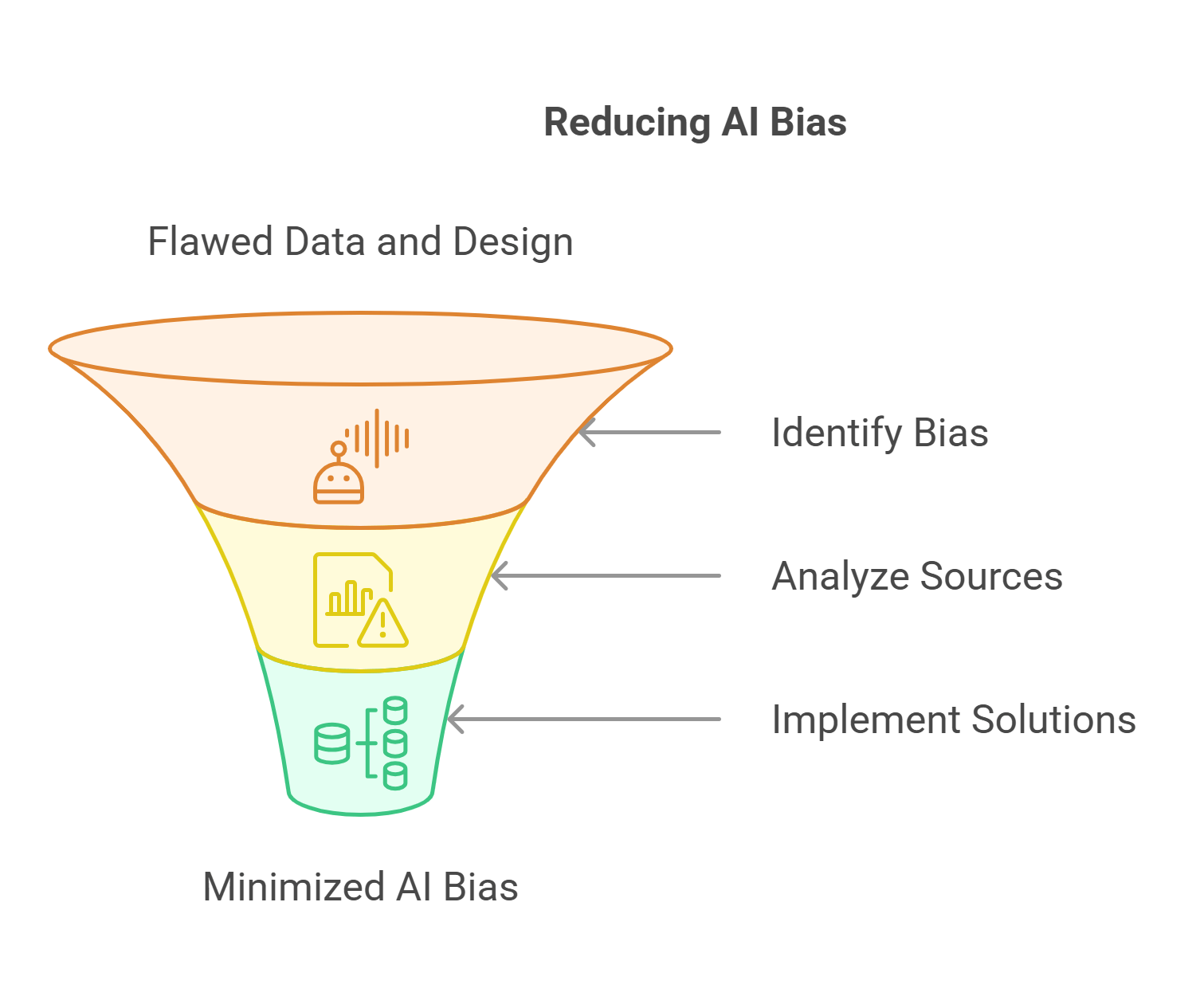
7. Bias in AI
Detailed Explanation: Bias in AI occurs when algorithms produce unfair outcomes due to flawed data or design. This can perpetuate inequality and discrimination.
- Examples: Facial recognition systems misidentifying individuals from minority groups.
- Sources of Bias: Include unrepresentative training data and programmer assumptions.
- Solutions: Involve diverse datasets and thorough testing to minimize bias.
Explained Simply: Bias in AI is like teaching a machine with incomplete or one-sided information, leading to skewed results.
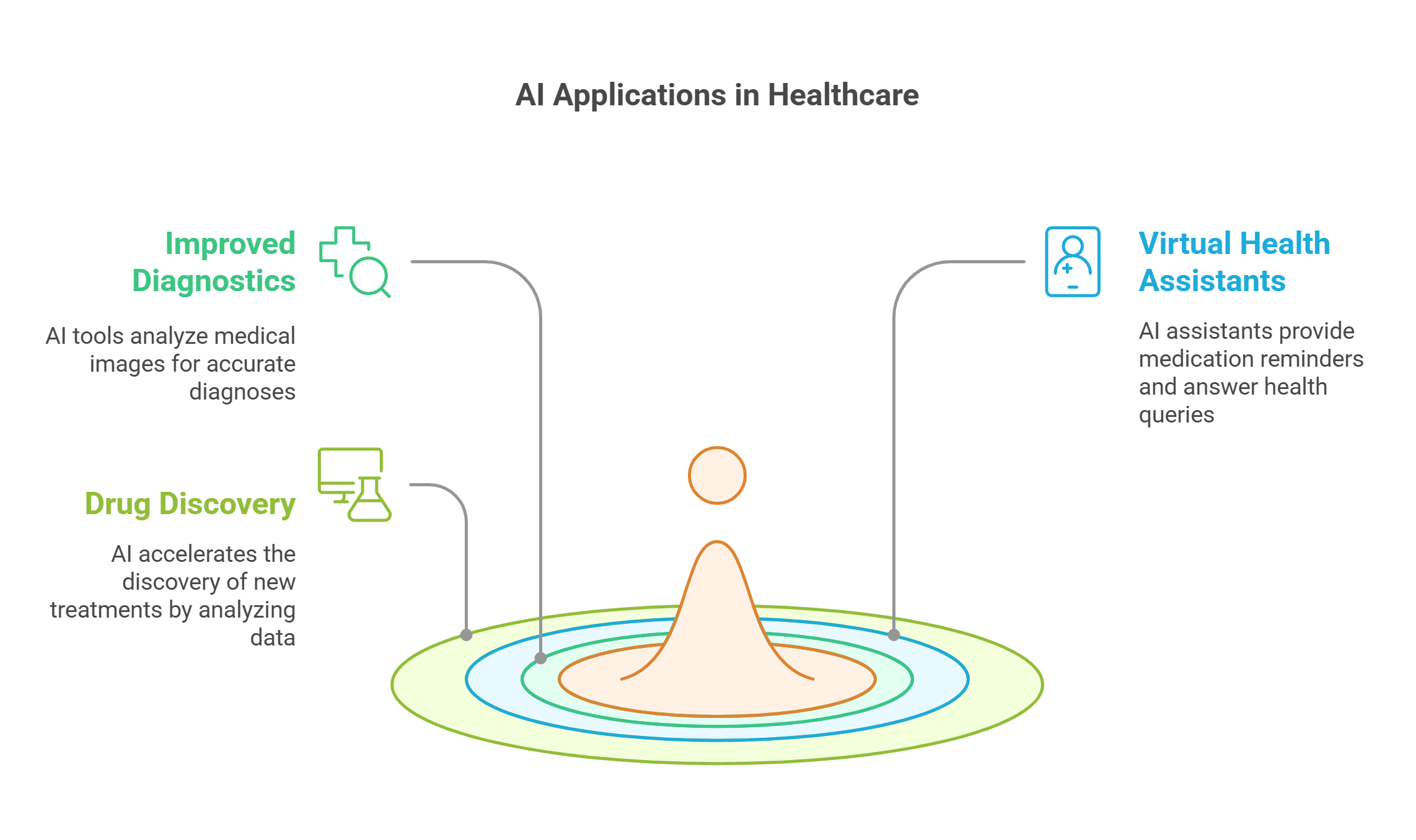
8. AI in Healthcare
Detailed Explanation: AI has revolutionized healthcare by improving diagnostics, treatment plans, and patient care.
- Examples: AI tools analyze medical images to detect conditions like cancer or heart disease.
- Virtual Health Assistants: Provide reminders for medications and answer health-related questions.
- Drug Discovery: Speeds up the process of finding new treatments by analyzing vast datasets.
Explained Simply: AI in healthcare is like having a super-intelligent assistant helping doctors diagnose and treat patients faster and more accurately.
9. AI in Autonomous Systems
Detailed Explanation: Autonomous systems use AI to operate independently, making decisions without human intervention.
- Examples: Self-driving cars navigate roads and avoid obstacles using AI.
- Drones: Perform tasks like delivering packages or monitoring crops in agriculture.
- Challenges: Include ensuring safety and reliability in complex, unpredictable environments.
Explained Simply: AI in autonomous systems is like giving machines the ability to think and act on their own in real-time.
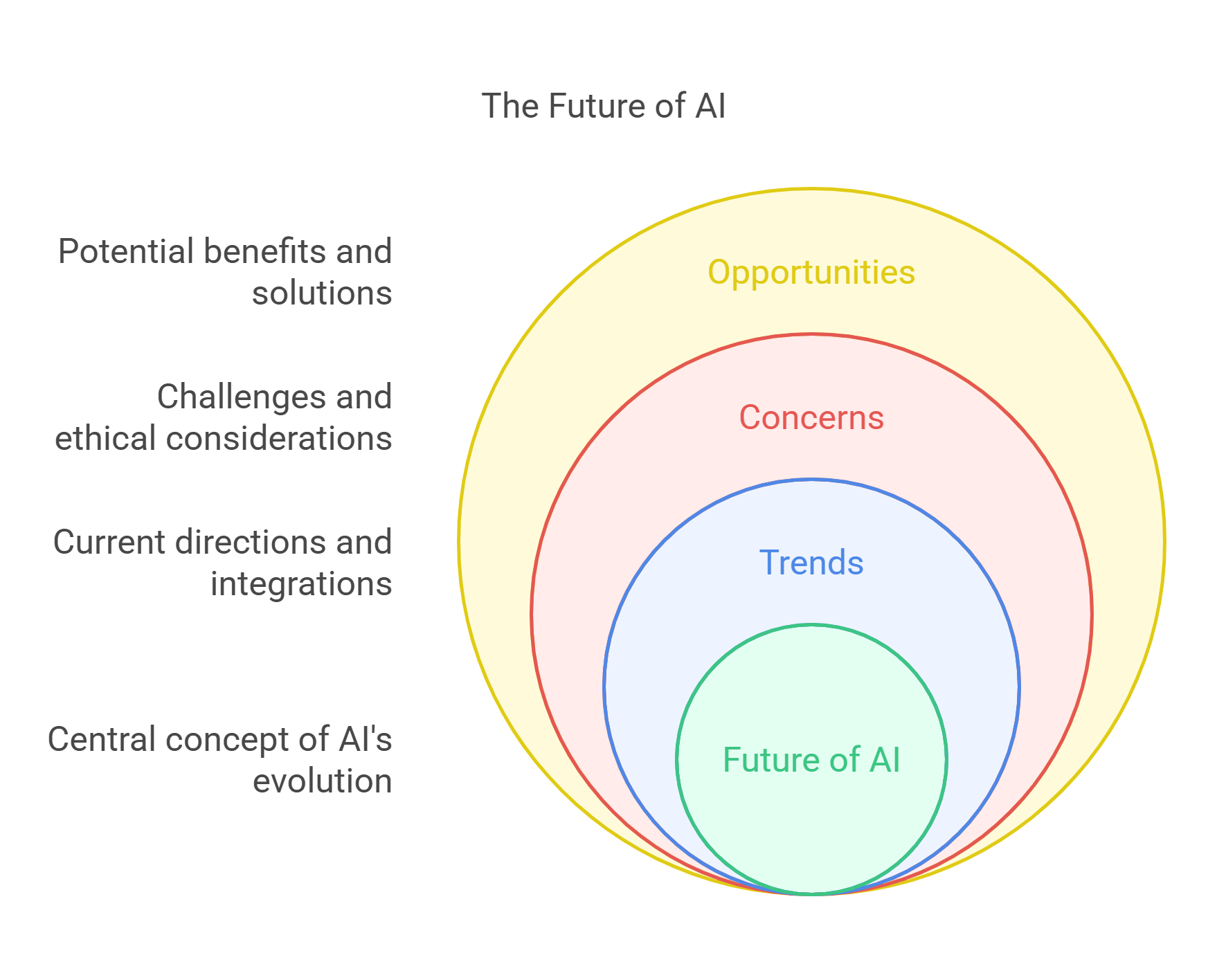
10. The Future of AI
Detailed Explanation: The future of AI involves advancements in technology, expanding its applications and addressing challenges.
- Trends: Include AI integration in education, energy management, and climate change solutions.
- Concerns: Addressing job displacement and ensuring ethical AI development.
- Opportunities: Harnessing AI for global good, such as eradicating diseases or improving sustainability.
Explained Simply: The future of AI is like opening a toolbox of endless possibilities to solve some of the world’s biggest challenges.
✨ Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping industries and transforming daily life. By mastering concepts like machine learning, robotics, and ethics, readers will be better prepared to analyze RC passages on this dynamic topic. Understanding the potential and pitfalls of AI enables informed discussions about technology’s role in shaping our future.












