🌱 Sustainable Development: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
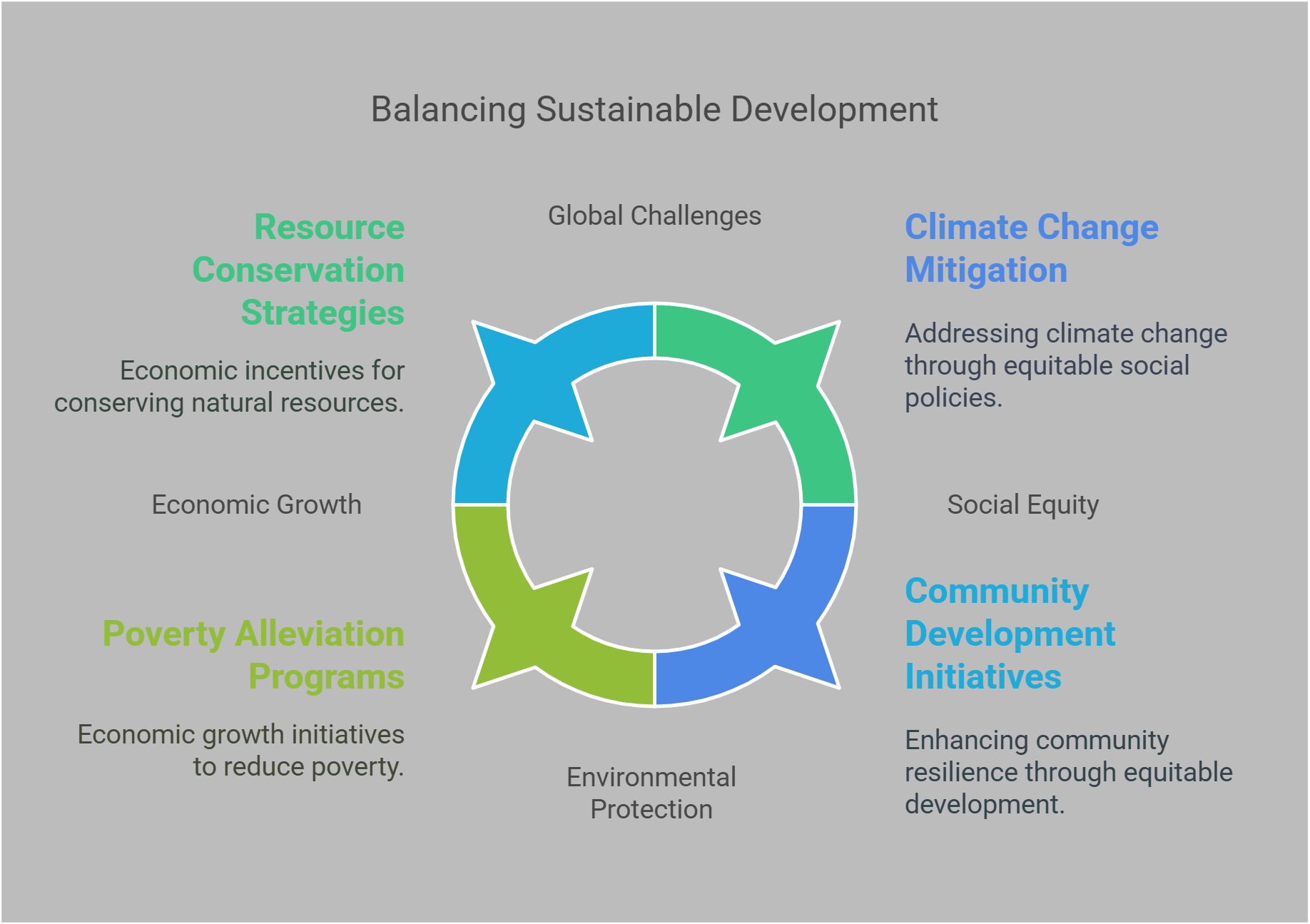
Sustainable development refers to meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This concept balances economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity. RC passages on sustainable development often discuss global challenges like climate change, resource conservation, and poverty alleviation. Understanding these concepts is essential for evaluating arguments about sustainability and interpreting solutions for a better future.
📋 Overview
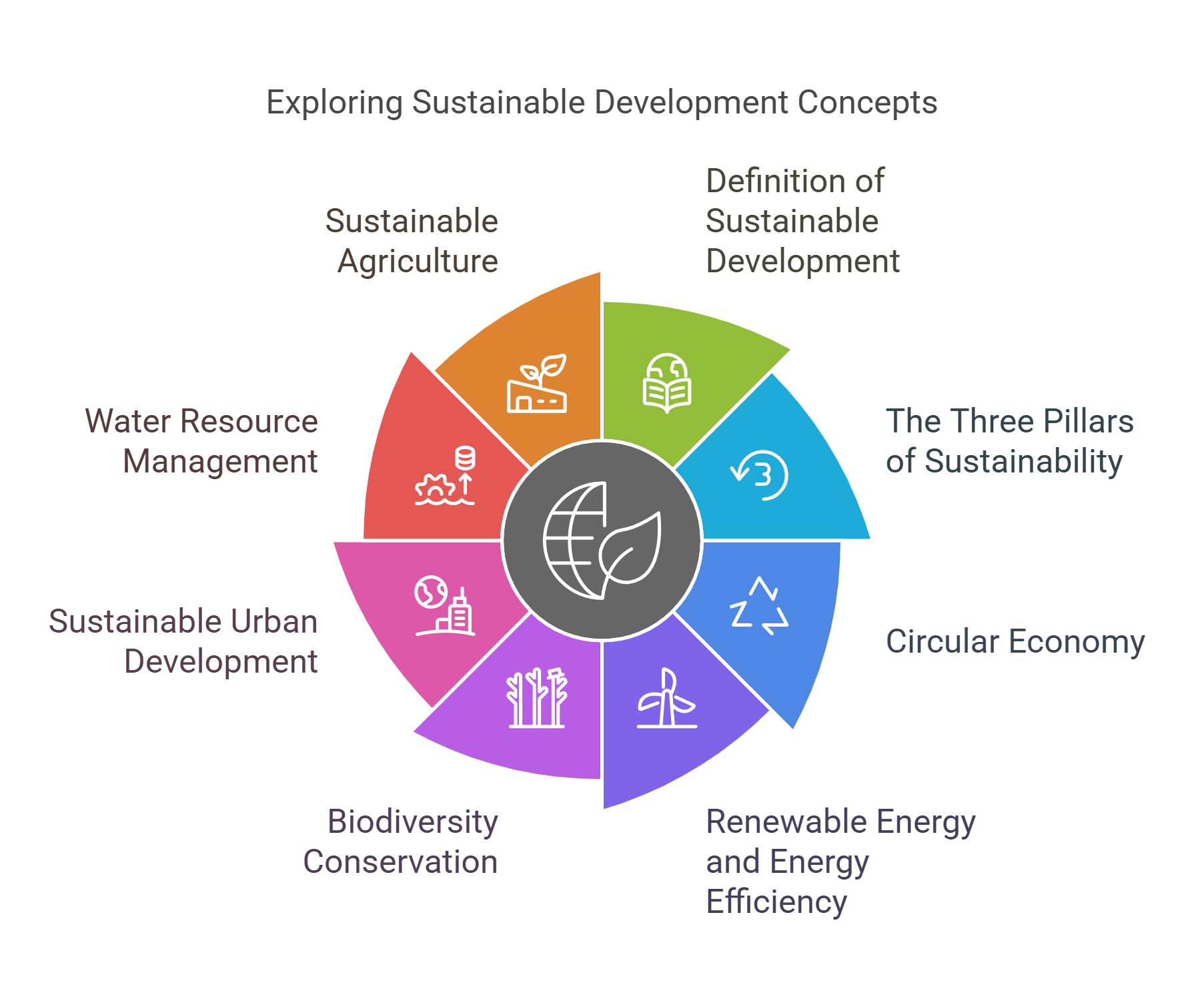
This guide will explore the following essential sustainable development concepts:
- Definition of Sustainable Development
- The Three Pillars of Sustainability
- Circular Economy
- Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency
- Biodiversity Conservation
- Sustainable Urban Development
- Water Resource Management
- Sustainable Agriculture
- Global Goals and Agreements
- Challenges and Barriers to Sustainability
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. Definition of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is a framework that seeks to achieve long-term economic, environmental, and social goals. It emphasizes intergenerational equity, ensuring that resources are available for future generations while addressing current challenges.
- Core Principle: Balancing economic growth with environmental and social needs.
- Example: Developing renewable energy projects to reduce carbon emissions while creating jobs.
- Global Impact: Influences policy-making, corporate strategies, and individual behavior.
Explained Simply: Sustainable development is like planning a family budget that ensures today’s expenses are met while saving for tomorrow’s needs.
2. The Three Pillars of Sustainability
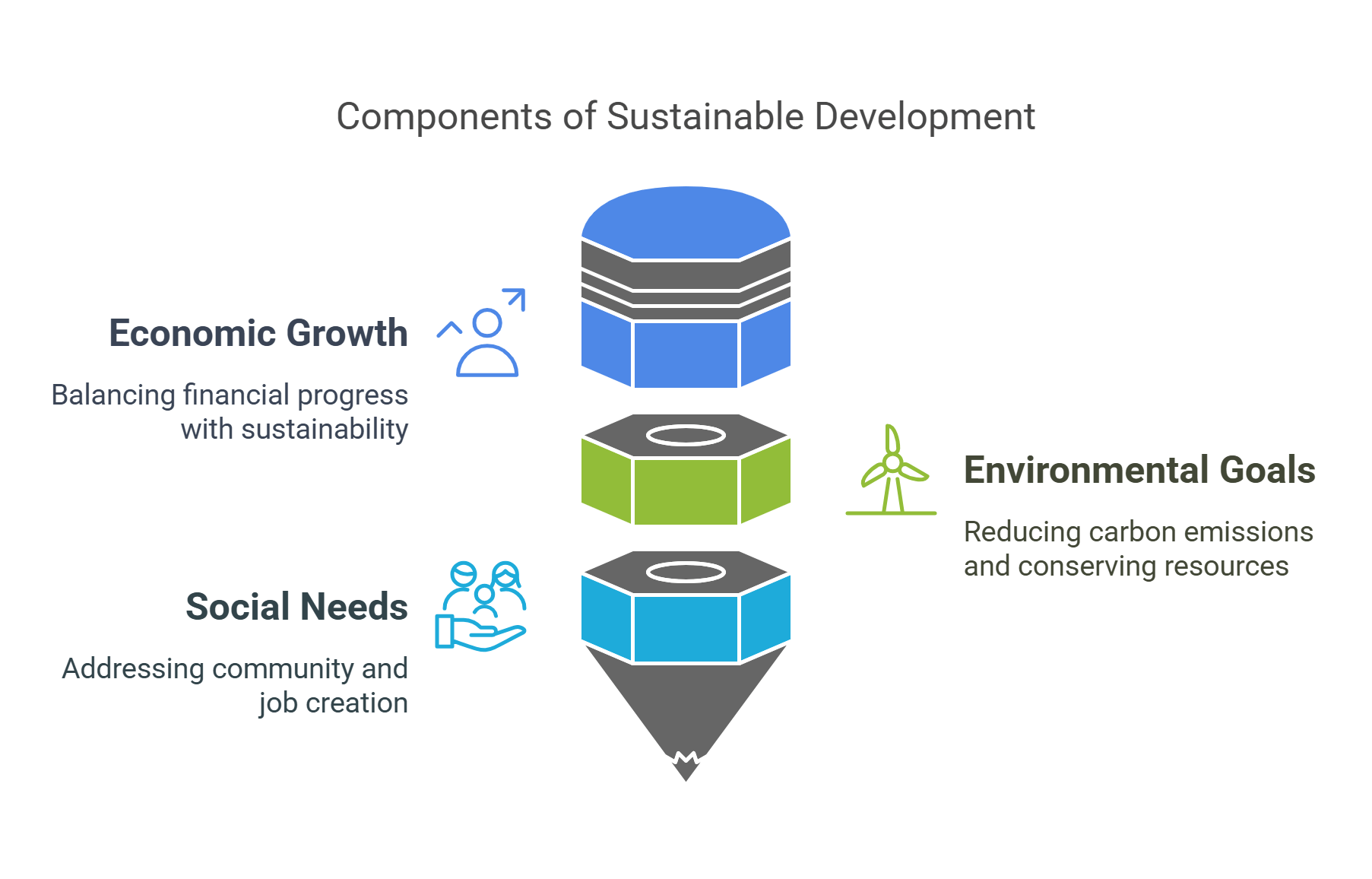
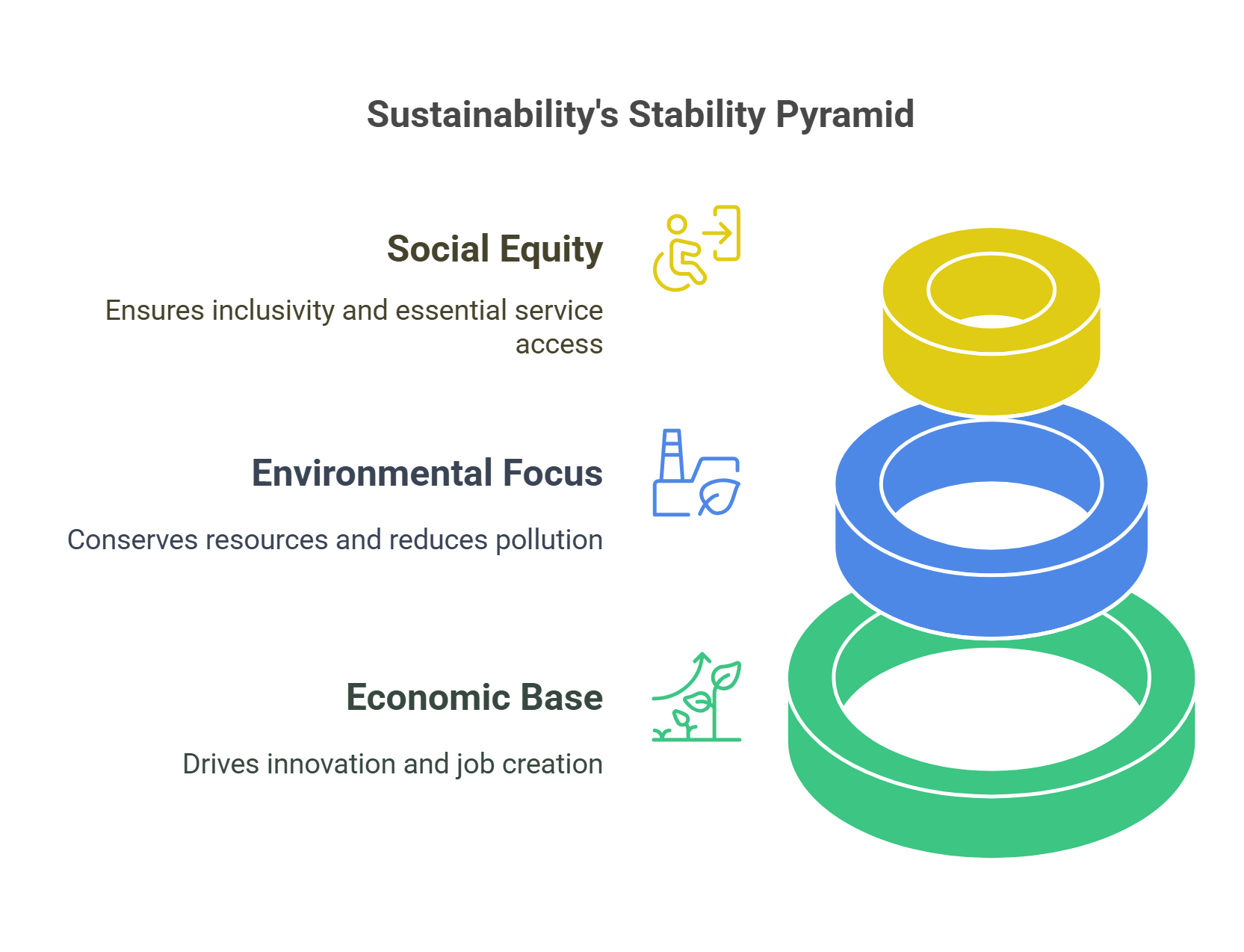
Sustainability rests on three interconnected pillars: economic, environmental, and social sustainability. Together, they form the foundation for achieving sustainable development.
- Economic: Promotes innovation, job creation, and economic stability.
- Environmental: Focuses on conserving natural resources and reducing pollution.
- Social: Ensures equity, inclusivity, and access to essential services.
- Example: A community project that builds eco-friendly housing, provides jobs, and enhances local living conditions.
Explained Simply: The three pillars are like the legs of a stool—all three are needed for stability.
3. Circular Economy
A circular economy minimizes waste and makes the most of resources by reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials.
- Principles: Reduce, reuse, and recycle to close resource loops.
- Examples: Companies using recycled materials in manufacturing, such as Patagonia’s recycled fleece clothing.
- Benefits: Reduces environmental impact and creates sustainable business opportunities.
Explained Simply: A circular economy is like turning yesterday’s trash into tomorrow’s treasure.
4. Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency
Renewable energy and energy efficiency are key to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
- Renewable Sources: Solar, wind, geothermal, and hydro energy.
- Energy Efficiency: Technologies like LED lighting and energy-efficient appliances reduce energy consumption.
- Example: Denmark’s reliance on wind power as a major energy source demonstrates a commitment to renewables.
Explained Simply: Renewable energy is like harnessing the sun and wind instead of burning limited resources.
5. Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity conservation protects the variety of life on Earth, ensuring ecosystems remain healthy and resilient.
- Importance: Biodiversity supports food security, clean water, and climate regulation.
- Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
- Example: Protected areas like national parks conserve wildlife and ecosystems.
Explained Simply: Conserving biodiversity is like keeping every piece of a puzzle intact to maintain the full picture of life.
6. Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainable urban development focuses on creating cities that are livable, equitable, and environmentally friendly.
- Smart Cities: Use technology to manage resources efficiently.
- Public Transport: Promotes low-emission travel and reduces congestion.
- Example: Curitiba, Brazil, is renowned for its sustainable urban planning, including an efficient bus rapid transit system.
Explained Simply: Sustainable urban development is like designing a city where everyone can thrive without harming the planet.
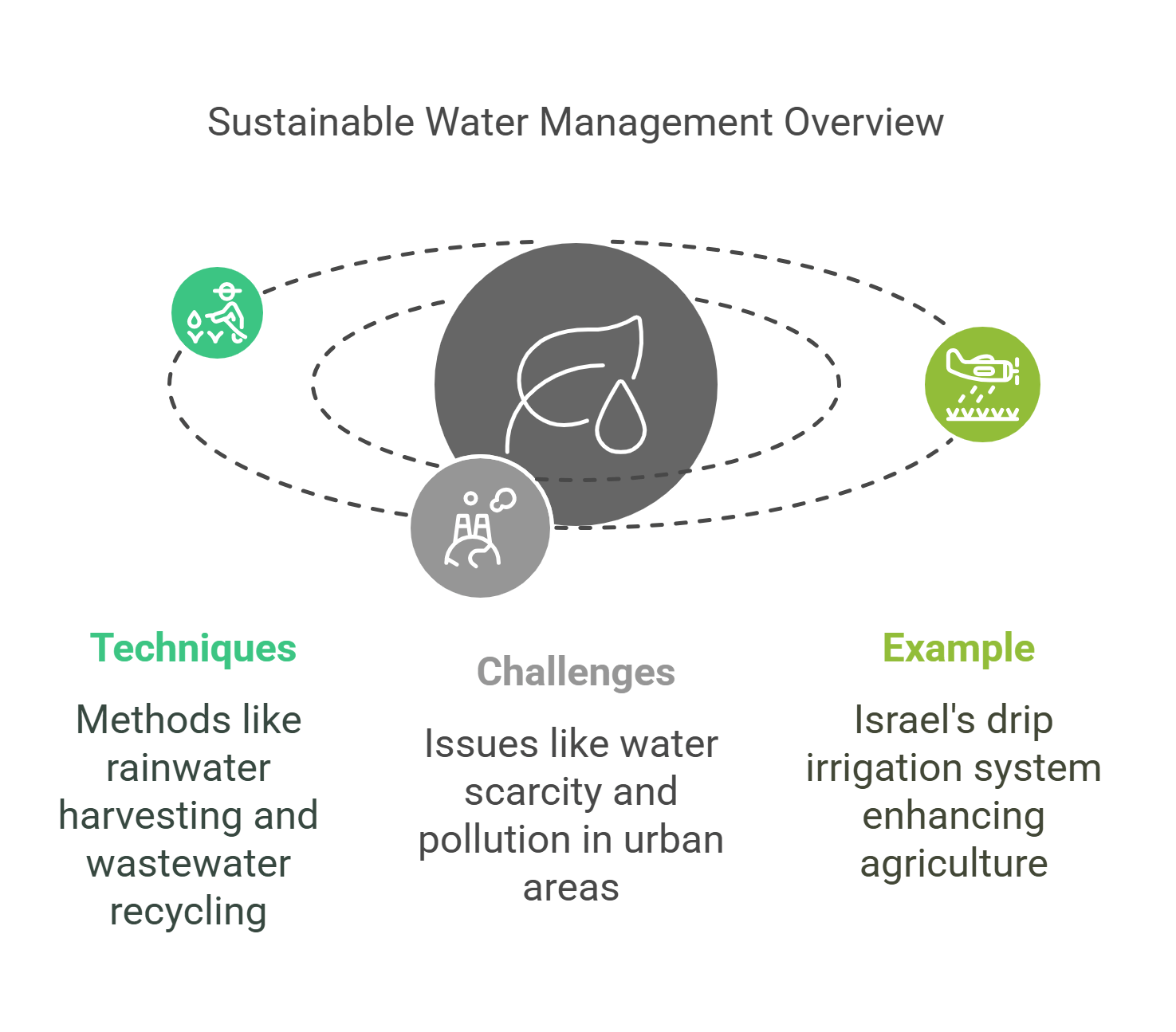
7. Water Resource Management
Sustainable water resource management ensures the availability and quality of water for future generations.
- Techniques: Rainwater harvesting, wastewater recycling, and efficient irrigation.
- Challenges: Addressing water scarcity and pollution in densely populated areas.
- Example: Israel’s drip irrigation systems conserve water while boosting agricultural productivity.
Explained Simply: Managing water sustainably is like making sure there’s enough clean water for everyone, now and in the future.
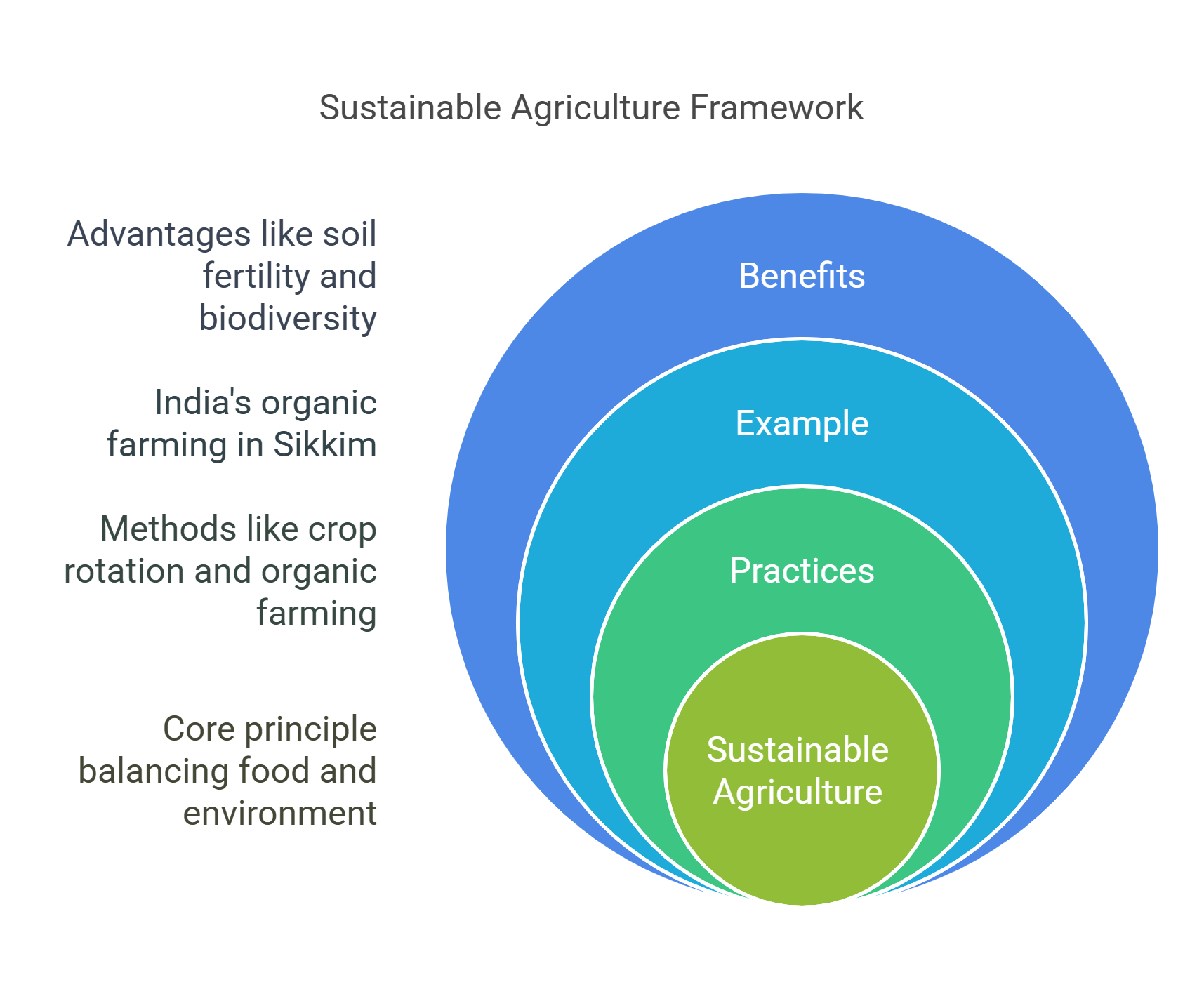
8. Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture balances food production with environmental health and economic viability.
- Practices: Crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry.
- Example: India’s adoption of organic farming methods in Sikkim, the first 100% organic state.
- Benefits: Enhances soil fertility, reduces chemical use, and supports biodiversity.
Explained Simply: Sustainable agriculture is like growing food today while ensuring the land stays fertile for tomorrow.
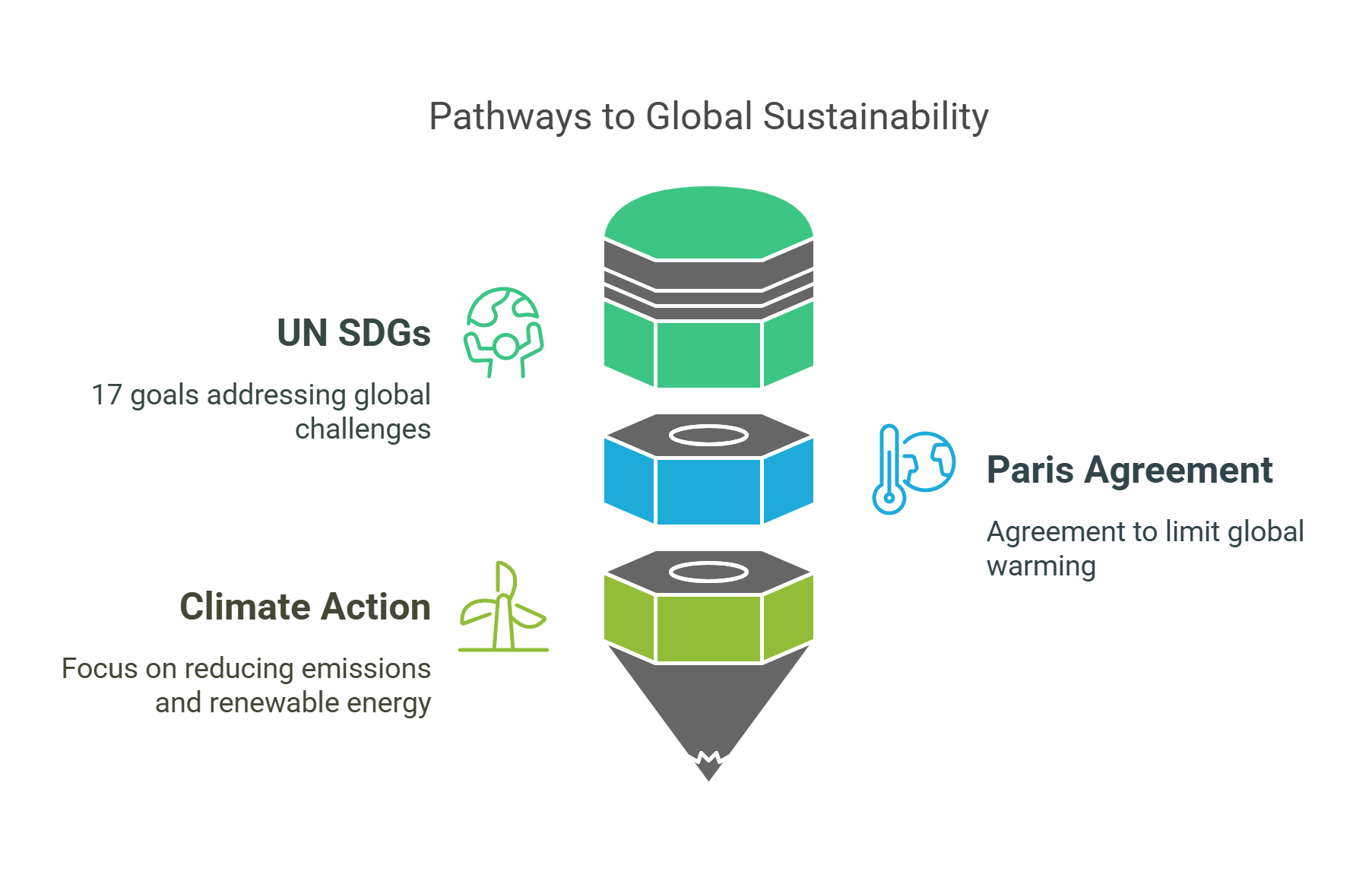
9. Global Goals and Agreements
International initiatives guide sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): 17 goals targeting poverty, inequality, and environmental protection.
- Paris Agreement: Focuses on limiting global warming to below 2°C.
- Example: Goal 13 of the SDGs emphasizes climate action, urging countries to reduce emissions and adopt renewable energy.
Explained Simply: Global goals are like a roadmap guiding the world toward a sustainable future.
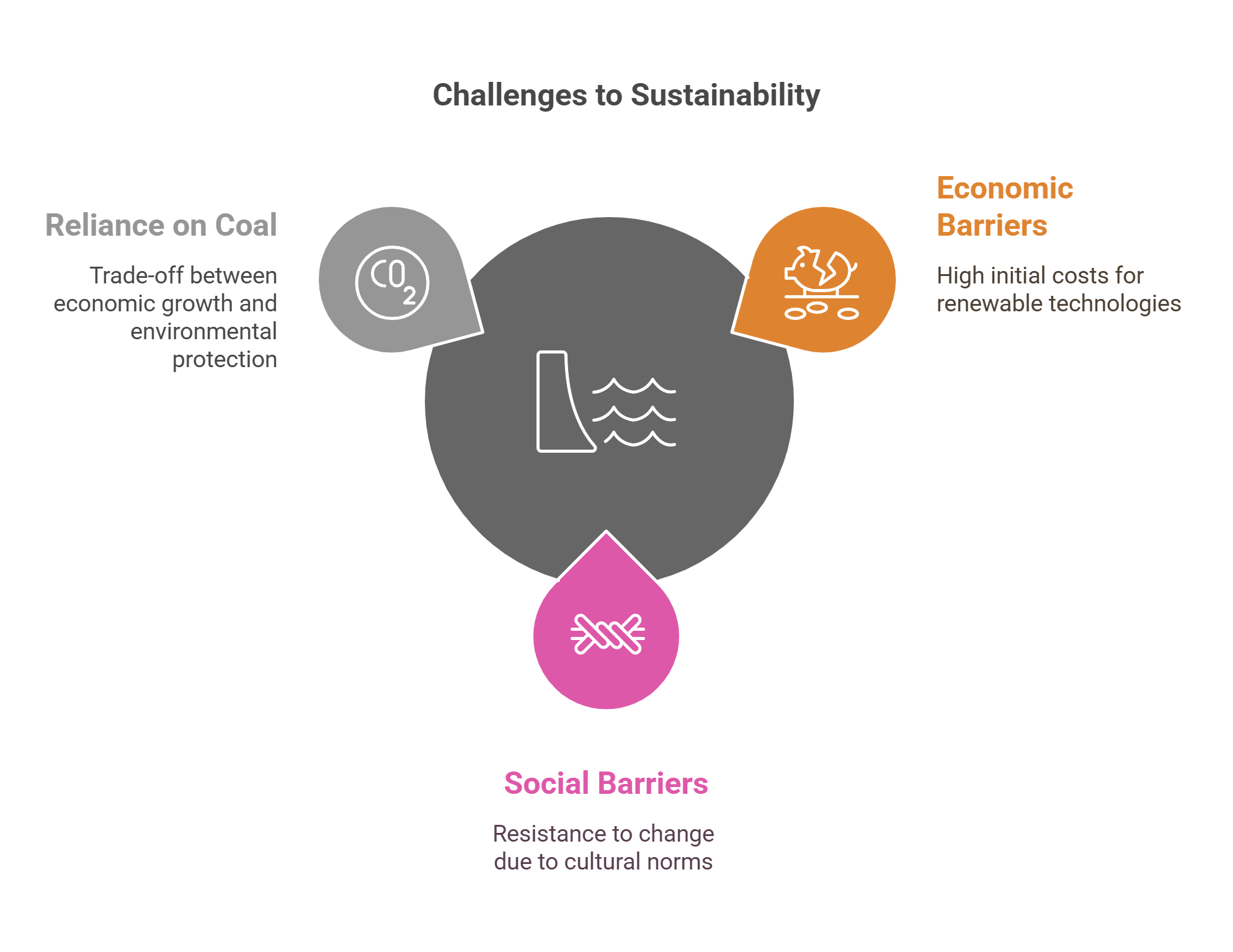
10. Challenges and Barriers to Sustainability
Achieving sustainability faces numerous obstacles, from economic constraints to political resistance.
- Economic Barriers: High initial costs for renewable technologies.
- Social Barriers: Resistance to change due to cultural or behavioral norms.
- Example: The reliance on coal in developing countries highlights the trade-off between economic growth and environmental protection.
Explained Simply: Challenges to sustainability are like hurdles on a race track—they can be overcome with effort and innovation.
✨ Conclusion
Sustainable development offers a blueprint for balancing human needs with environmental health and social equity. By mastering concepts like renewable energy, circular economy, and global goals, readers can better analyze RC passages on this critical topic. Understanding sustainability equips us to address the challenges of today while preserving resources for future generations. 🌱












