Mem: The Root of Remembrance and Memory
Delve into the root "mem," originating from the Latin word memor, meaning "mindful" or "to remember." From foundational words like memory and memorial to more intricate applications in technology and science, "mem" is the cornerstone of language centered on remembrance and recognition.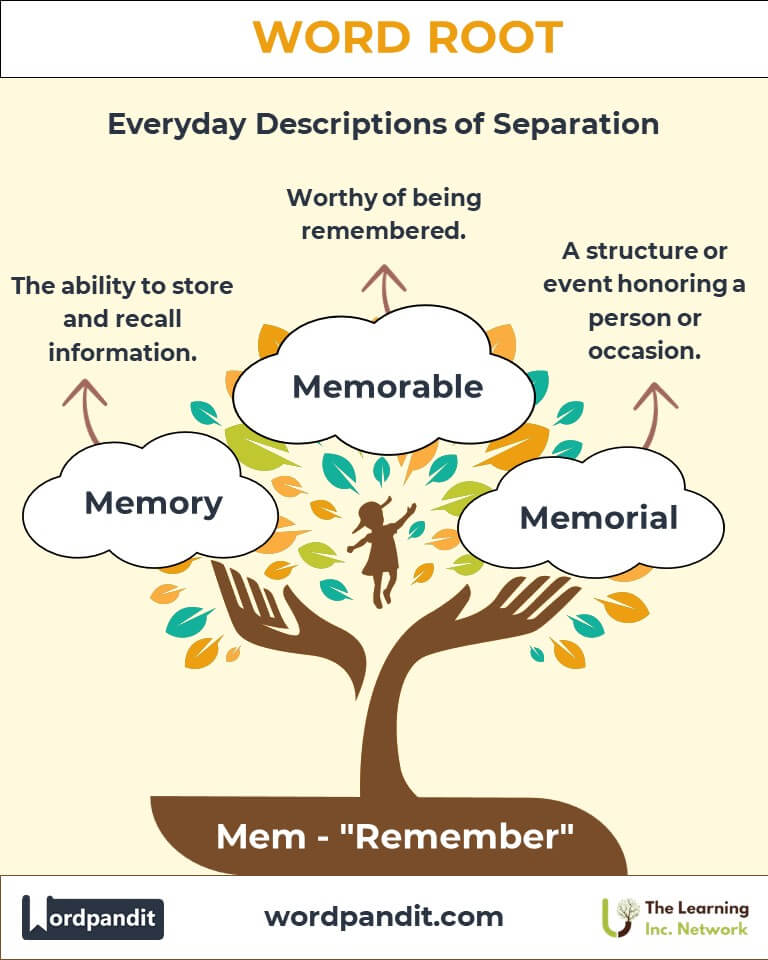
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Mem
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mem
- Common Mem-Related Terms
- Mem Through Time
- Mem in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Mem in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Mem Root
- The Mem Family Tree
- FAQs About the Mem Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Mem Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Mem
Introduction: The Essence of Mem
Memory is the anchor of human experience, shaping our identities and understanding of the world. The root "mem" (pronounced mem) encapsulates this essence, signifying "to remember." It derives from the Latin memor, a term rich in history and relevance across languages and disciplines. Whether discussing personal recollections, historical memorials, or modern memory storage, "mem" binds the past to the present.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "mem" traces its origins to the Latin memor (mindful). The Roman emphasis on oral tradition and historical recordkeeping ensured that "mem" became central to words associated with remembering and commemorating. With the spread of Latin into English during the medieval period, "mem" retained its meaning, evolving into terms like memory and memorial. Over centuries, its applications expanded, from storytelling to digital memory systems.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mem
To internalize the root "mem," imagine a glowing photograph album labeled "MEM," filled with snapshots of cherished moments. Just as the album preserves memories, "mem" anchors the concept of remembering.
Mnemonic Device: "Mem holds the mind's moments—memory, memorials, and more."
Common Mem-Related Terms
- Memory (mem-or-ee): The faculty by which the mind stores and recalls information.
- Example: "Her vivid memory of childhood painted a nostalgic picture."
- Memorable (mem-uh-ruh-bul): Worthy of being remembered.
- Example: "The concert was a memorable experience for all who attended."
- Memorial (mem-o-ree-uhl): Something established to remind people of a person or event.
- Example: "The war memorial honors those who sacrificed their lives."
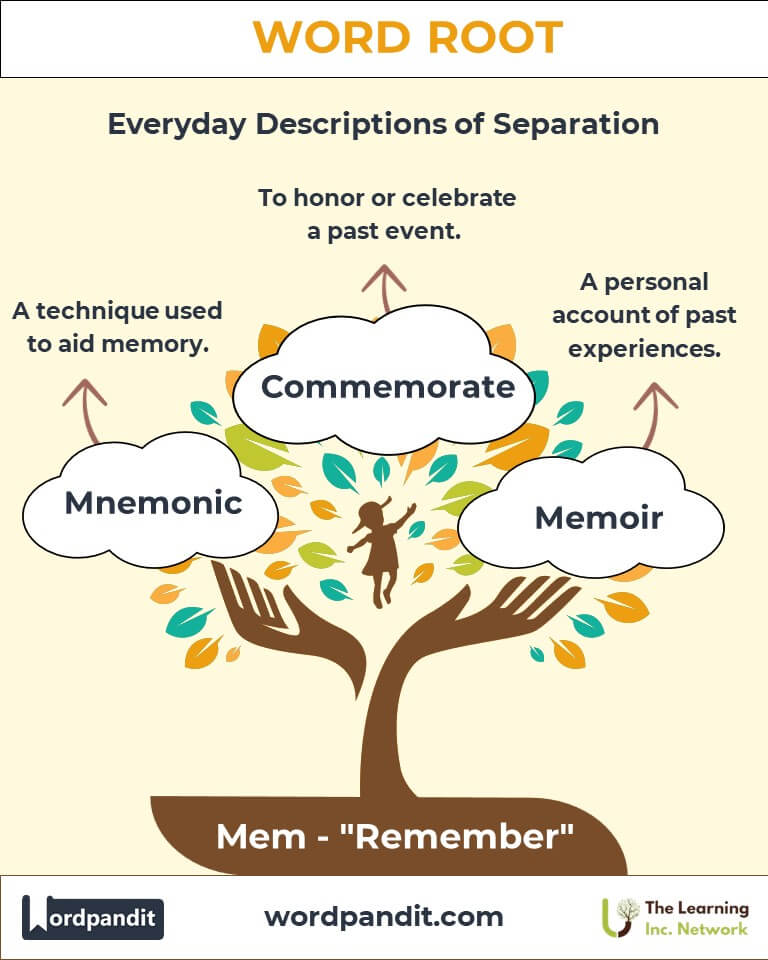
- Commemorate (kuh-mem-uh-reyt): To honor the memory of someone or something.
- Example: "A ceremony was held to commemorate the historic event."
- Memoir (mem-wahr): A written account of personal experiences.
- Example: "Her memoir offered a candid look at life during the war."
- Mnemonic (nih-mon-ik): A device or technique used to aid memory.
- Example: "Using acronyms is a common mnemonic technique."
Mem Through Time
Memory: From ancient oral traditions to written records, memory has been the foundation of cultural continuity. Early societies relied on skilled storytellers to preserve their histories, with memory as the tool.
Commemorate: While initially tied to religious rituals, the term has grown to encompass secular and global events, reflecting societal values of remembrance and reflection.
Mem in Specialized Fields
Psychology
- Episodic Memory: Focuses on personal experiences and specific events.
- Application: Essential in understanding disorders like amnesia.
Technology
- Memory Storage: Refers to devices like RAM (Random Access Memory) in computers.
- Relevance: Critical for data storage and processing in the digital age.
Medicine
- Memory Care: Focuses on treating memory-related disorders like Alzheimer’s.
- Importance: Provides therapies to improve cognitive functions.
Literature
- Memoirs: Serve as historical documents and personal reflections.
- Impact: Offer intimate glimpses into individual and collective histories.
Illustrative Story: Mem in Action
Lila, a history teacher, wanted her students to appreciate the importance of memory in shaping identity. She organized a field trip to a local war memorial, where they commemorated soldiers’ bravery. Inspired, one student began writing a memoir of her family’s immigrant journey, showcasing how remembering the past helps build a meaningful future.
Cultural Significance of the Mem Root
The root "mem" underscores the universal value of remembrance. From ancient memorials like the Pyramids to modern digital archives, societies have sought ways to preserve knowledge and honor legacies. Cultural traditions like storytelling and commemorative ceremonies highlight the root’s enduring role in connecting generations.

The Mem Family Tree
Explore related roots and their meanings:
- Mon (warn/remind): Admonish (to warn), Monitor (to keep in mind).
- Ment (mind): Mental (related to the mind), Mention (to bring to mind).
- Re (again): Recall (to bring back to memory), Remember.
FAQs About the "Mem" Word Root
Q: What does "mem" mean, and what is its origin?
A: "Mem" signifies "to remember" and originates from the Latin root memor, meaning "mindful" or "to be aware." It appears in words like memory, memorial, and memoir, emphasizing human cognition and cultural preservation.
Q: How is "mem" used in psychology?
A: In psychology, "mem" forms the basis of terms related to memory, such as episodic memory (recollections of personal experiences) and procedural memory (skills like riding a bike). It also applies to studying memory disorders like amnesia or Alzheimer’s.
Q: Why is "memorial" significant in culture?
A: Memorials honor individuals or events, serving as symbolic reminders of the past. Examples include the Vietnam Veterans Memorial or Remembrance Day ceremonies, which preserve legacies for future generations.
Q: What is a mnemonic, and how is it helpful?
A: A mnemonic is a memory aid, such as a rhyme, acronym, or visualization. For example, the acronym HOMES helps recall the Great Lakes (Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior). Mnemonics make learning easier and improve recall.
Q: How is the root "mem" relevant in technology?
A: In technology, "mem" appears in terms like memory storage, which refers to devices that save and retrieve data, such as RAM or SSDs. These systems emulate human memory, bridging cognition and computation.
Test Your Knowledge: Mem Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "mem" signify?
2. Which word means "worthy of being remembered"?
3. What does "commemorate" involve?
4. What is a mnemonic used for?
5. Which field uses "memory storage"?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Mem
The root "mem" serves as a bridge between past and present, reminding us of the importance of memory in shaping identity, culture, and innovation. As technology evolves and our understanding of the mind deepens, the root will continue to inspire how we remember, honor, and connect with the world. Embrace "mem" as a reminder to cherish the moments that define us.
Meta Description: Explore the root "mem," meaning "to remember," and its relevance in words like memory, memorial, and technology. Discover its cultural and practical applications.
Suggested uggested URL: /mem-root-meaning-memory












