Mov, Mot: The Dynamic Roots of Movement and Motion
Discover the linguistic vibrancy of the roots "mov" and "mot," derived from the Latin "movere," meaning "to move." These roots animate words like "motion" and "remove," illustrating dynamic concepts in language, science, and everyday communication.
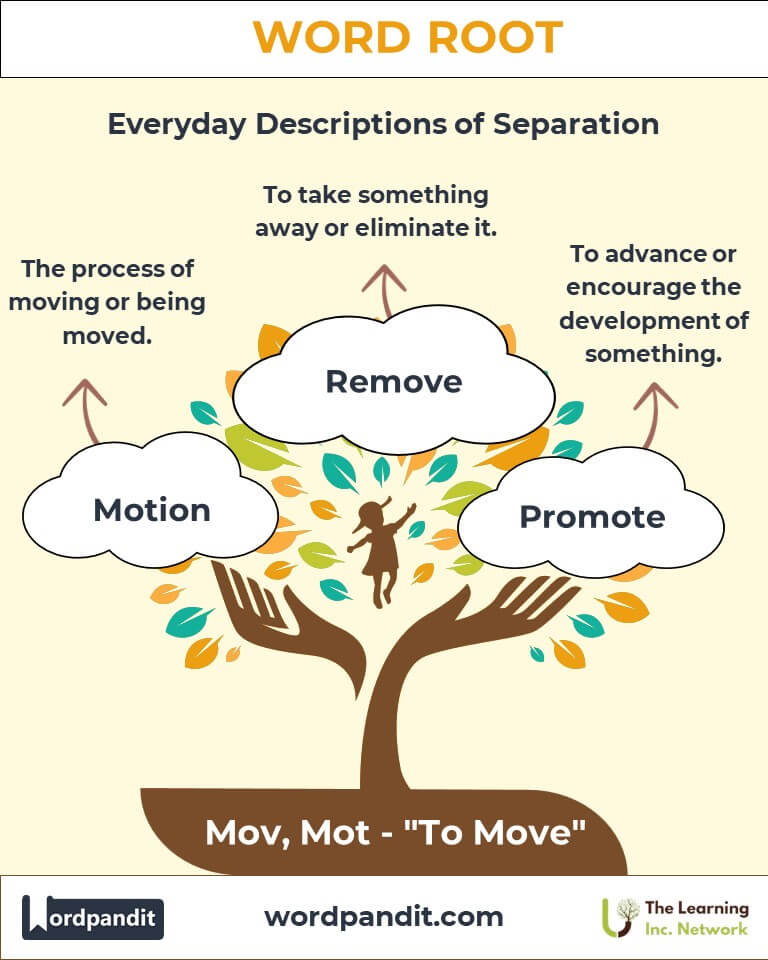
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Momentum of Mov and Mot
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mov and Mot
- Common Mov- and Mot-Related Terms
- Mov and Mot Through Time
- Mov and Mot in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Mov and Mot in Action
- Cultural Significance of Mov and Mot
- The Mov and Mot Family Tree
- FAQs About the Mov and Mot Word Roots
- Test Your Knowledge: Mov and Mot Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Momentum of Mov and Mot
Introduction: The Momentum of Mov and Mot
The roots "mov" (pronounced "moov") and "mot" (pronounced "moht") carry the essence of movement and change. Whether in "motion," symbolizing kinetic activity, or "motivate," capturing internal drive, these roots highlight how motion connects human activity, natural phenomena, and technological progress.

Etymology and Historical Journey
Originating from the Latin word movere, meaning "to move," these roots evolved through Old French and Middle English into modern forms. Their integration into English during the Middle Ages was heavily influenced by the Renaissance, a time when Latin and Greek roots revitalized technical and artistic vocabulary.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Mov and Mot
Visualize a car in motion, its engine labeled "MOV," fueled by "MOT-ivation." The continuous movement embodies the dynamic nature of these roots.
Mnemonic Device:
“Mov and Mot keep the world in motion, from motivation to removal.”
Common Mov- and Mot-Related Terms
- Motion (moh-shun):
Definition: The process of moving or being moved.
Example: "The motion of the planets is governed by gravitational forces." - Remove (ree-moov):
Definition: To take something away or eliminate it.
Example: "The workers removed the debris after the storm." - Motivation (moh-tuh-vay-shun):
Definition: The reason or drive behind an action.
Example: "Her motivation to succeed inspired her peers." - Promote (proh-moht):
Definition: To advance or encourage the development of something.
Example: "The company promotes sustainable practices." - Automobile (aw-toh-moh-beel):
Definition: A self-powered vehicle for transportation.
Example: "The automobile revolutionized personal travel."
Mov and Mot Through Time
- Ancient Context: In Roman philosophy, "movere" was metaphorically used to describe emotional and intellectual shifts, beyond mere physical motion.
- Modern Innovations: The Industrial Revolution popularized terms like "locomotive," linking movement with technology, while psychology embraced "motivation" to explore human behavior.
Mov and Mot in Specialized Fields
- Physics:
Motion: Central to Newton's laws of mechanics, describing changes in an object's position over time. - Psychology:
Motivation: Examines the drives behind human behavior, such as the desire for achievement. - Transportation:
Locomotive: Refers to engines powering trains, showcasing the root's adaptability in engineering.
Illustrative Story: Mov and Mot in Action
Maya, a young engineer, struggled with motivation after a failed project. During a train ride, observing the locomotive's motion inspired her. She realized that, like the train, her progress required consistent effort and small steps. This renewed perspective helped Maya remove doubts and promote innovation, leading to her groundbreaking designs.
Cultural Significance of Mov and Mot
In culture and language, "motion" is symbolic of life's constant change. From dance movements expressing emotion to motivational speeches driving social progress, these roots weave motion and inspiration into the human narrative.

The Mov and Mot Family Tree
- Kine (Greek: "movement"):
Examples: Kinetic, cinema. - Act (Latin: "do, act"):
Examples: Action, activate. - Tract (Latin: "draw, pull"):
Examples: Tractor, attract.
FAQs About the "Mov" and "Mot" Word Roots
Q: What do "mov" and "mot" mean?
A: The roots "mov" and "mot" originate from the Latin word movere, meaning "to move." They form the basis of many words that describe physical, emotional, or conceptual movement, connecting various aspects of life and language.
Q: How do "motion" and "motivation" differ?
A: "Motion" refers to physical movement or activity (e.g., the motion of planets), while "motivation" describes an internal drive or reason behind an action (e.g., her motivation to excel in school). One deals with external actions, and the other focuses on inner intent.
Q: Why is "motion" important in physics?
A: In physics, "motion" describes how objects change position over time. Newton's laws of motion explain how forces act on objects to cause motion, making this root essential to understanding mechanics and the principles of movement.
Q: What does "remove" signify, and how does it relate to the root?
A: "Remove" means to take something away or eliminate it. The prefix "re-" means "back" or "again," so "remove" combines with "mov" to signify moving something out of its place, such as removing clutter to create order.
Q: How is "motivate" connected to motion?
A: "Motivate" stems from "mot," implying movement or action. To motivate someone means to stimulate them into action or movement, whether physically (e.g., motivating an athlete) or mentally (e.g., motivating students to study).
Test Your Knowledge: Mov and Mot Mastery Quiz
1. What is the meaning of the root "mov"?
2. Which term means to advance something?
3. What field uses "motion" to describe object movement?
4. What does "automobile" signify?
5. Which word relates to emotional drive?
Conclusion: The Enduring Momentum of Mov and Mot
The roots "mov" and "mot" illustrate the intrinsic energy of movement, whether physical, emotional, or intellectual. Their application spans disciplines, shaping language and thought. By exploring these roots, we uncover the fundamental role of motion in life’s endless progression.












