Cocco: The Root of Tiny Spheres in Science and Nature
Discover the significance of the root "Cocco," derived from the Greek word kokkos, meaning "berry." From microbiology to botany, "Cocco" has shaped our understanding of small, round structures in nature and their profound impact on various scientific fields.
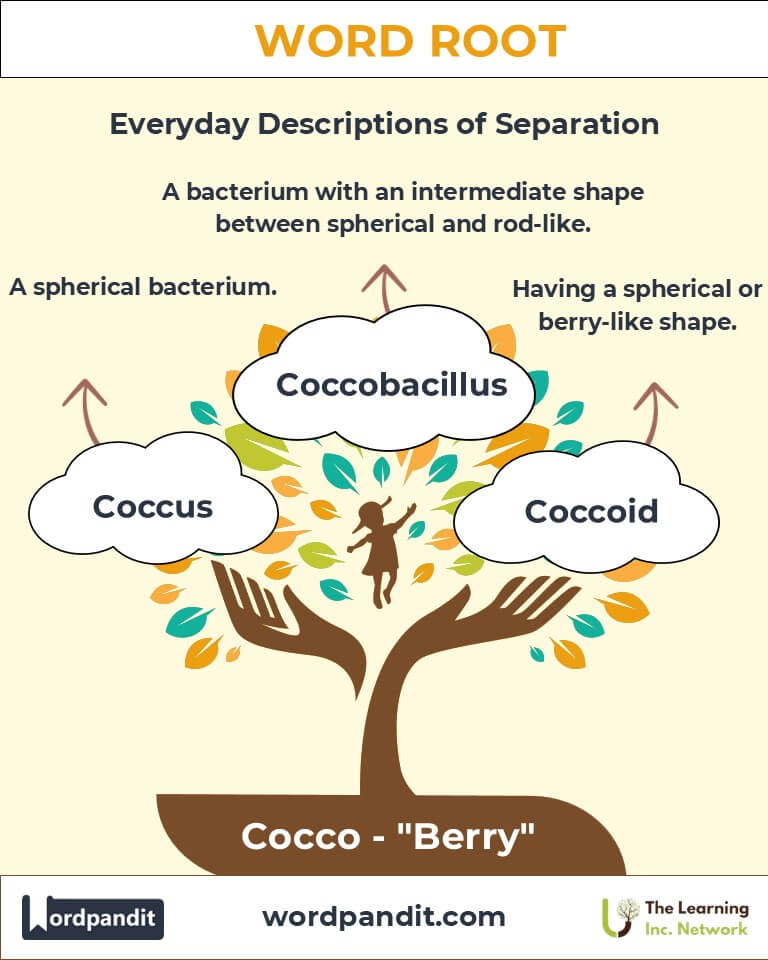
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Cocco"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cocco"
- Common Cocco-Related Terms
- "Cocco" Through Time
- "Cocco" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Cocco" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Cocco"
- The "Cocco" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Cocco" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Cocco" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Tiny Yet Mighty Legacy of "Cocco"
Introduction: The Essence of "Cocco"
Have you ever wondered why some microorganisms or plant seeds are described as "coccoid"? The root Cocco encapsulates the concept of roundness, derived from the Greek word kokkos, meaning "berry." Pronounced as "koh-koh," this root appears in a variety of scientific terms describing spherical forms. Whether in microbiology, where cocci bacteria are studied, or in everyday descriptions of tiny berries, "Cocco" connects our understanding of form, function, and nature’s design.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Cocco" traces back to ancient Greek, where kokkos referred to a small, round berry. This descriptive term migrated into Latin as "coccus," retaining its essence of roundness. Over time, it became integral in fields like microbiology, where it described spherical bacteria. The term's enduring relevance highlights its utility in categorizing and visualizing natural forms, from plant seeds to microscopic organisms.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cocco"
Picture a handful of small, round berries spilling onto a table, each perfectly spherical and uniform. These berries symbolize the essence of "Cocco."
Mnemonic Device: "Cocco clusters are tiny spheres, like berries bringing life everywhere!"
Common Cocco-Related Terms
- Coccus (koh-kus): A spherical-shaped bacterium.
Example: Staphylococcus aureus, a common coccus, can cause skin infections. - Coccoid (koh-koh-oid): Having a spherical or berry-like shape.
Example: Under the microscope, the algae appeared coccoid in form. - Coccolith (koh-koh-lith): A microscopic, calcareous plate forming part of the outer layer of coccolithophores (marine algae).
Example: Coccoliths play a crucial role in the ocean’s carbon cycle. - Coccyx (kok-siks): The small, triangular bone at the base of the human spine, named for its resemblance to a bird’s beak.
Example: Injuries to the coccyx can cause significant discomfort. - Coccobacillus (koh-koh-buh-sil-us): A bacterium with a shape intermediate between spherical and rod-like.
Example: Haemophilus influenzae is classified as a coccobacillus.
"Cocco" Through Time
- Coccus (Antiquity): Initially a general descriptor for spherical objects, the term gained precision with the advent of microbiology, classifying spherical bacteria.
Shift: The word evolved from describing fruit-like shapes to defining microscopic life forms. - Coccoliths (Modern Use): Once obscure, these microfossils are now critical to studying past climate changes and understanding marine ecosystems.
"Cocco" in Specialized Fields
- Microbiology: Coccus bacteria, such as Streptococcus, are studied for their role in health and disease.
- Marine Science: Coccolithophores, single-celled algae, produce coccoliths, contributing to marine carbon sequestration.
- Anatomy: The coccyx in humans, though vestigial, plays a role in supporting pelvic structures.
Illustrative Story: "Cocco" in Action
In a coastal research lab, Dr. Elena observed coccolithophores through a microscope. These minuscule, coccoid algae, floating in the ocean, were silently capturing carbon dioxide and forming the coccoliths that would later settle on the ocean floor. Their spherical beauty not only fascinated her but also underscored their role in mitigating climate change. Like berries of the sea, these "Cocco" forms nurtured the planet's delicate balance.
Cultural Significance of "Cocco"
The root "Cocco" often symbolizes smallness and simplicity in nature. Ancient Greeks used kokkos for seeds and berries, essential to life and sustenance. Today, "Cocco" terms remind us of the interconnectedness of microscopic and macroscopic worlds, from bacteria shaping ecosystems to berries enriching diets.

The "Cocco" Family Tree
- Bacill- (Rod-shaped): Bacillus: Rod-like bacteria.
Example: Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax. - Spher- (Sphere): Spherical: Having a round shape.
Example: A soap bubble is perfectly spherical. - Morph- (Shape): Morphology: The study of form and structure.
Example: Microbial morphology is key to identifying species.
FAQs About the Cocco Word Root
Q: What does "Cocco" mean?
A: "Cocco" comes from the Greek word kokkos, meaning "berry" or "spherical." It describes objects, shapes, or organisms that are round or berry-like, such as cocci bacteria or spherical seeds.
Q: What is a Coccus?
A: A coccus is a type of bacterium that has a spherical shape. These bacteria can exist as single cells, in pairs, chains, or clusters. Examples include Streptococcus (chain-forming cocci) and Staphylococcus (cluster-forming cocci). Their shapes are important for identification and understanding their behavior in microbiology.
Q: What are Coccoliths?
A: Coccoliths are microscopic, calcareous plates produced by single-celled algae called coccolithophores. These plates contribute to oceanic carbon cycling by sequestering carbon dioxide in the form of calcium carbonate and eventually forming chalk and limestone deposits when they settle on the seabed.
Q: Is the Coccyx related to the "Cocco" root?
A: Yes, the coccyx, or tailbone, derives its name from the Greek word for "cuckoo" (kokkyx) due to its resemblance to a bird’s beak, which aligns with the root's idea of small, curved, or berry-like shapes.
Q: What is a Coccobacillus?
A: A coccobacillus is a bacterium with a shape that is intermediate between spherical (coccus) and rod-like (bacillus). These bacteria, like Haemophilus influenzae, demonstrate how the root "Cocco" combines with others to describe subtle variations in bacterial morphology.
Q: What does "Coccoid" mean in science?
A: Coccoid refers to anything that is spherical or resembles a berry. It is often used to describe the shape of algae, bacteria, or microscopic particles.
Q: How do Coccoliths contribute to the environment?
A: Coccoliths play a vital role in the global carbon cycle. By fixing carbon dioxide into calcium carbonate, they help regulate atmospheric CO2 levels and support marine ecosystems. Their accumulation over millions of years forms chalk and limestone deposits, such as the White Cliffs of Dover.
Test Your Knowledge: Cocco Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Cocco" mean?
2. Which term describes a spherical bacterium?
3. What are Coccoliths made of?
4. What does "Coccyx" refer to?
5. Which bacterium is an example of Coccobacillus?

Conclusion: The Tiny Yet Mighty Legacy of "Cocco"
The root "Cocco" beautifully encapsulates the power of small, spherical forms in nature and science. From the microscopic bacteria that influence ecosystems to the coccoid seeds that nourish life, "Cocco" connects us to the fundamental shapes that sustain existence.











