Coelo: Exploring the Root of Hollow Spaces in Science and Nature
Discover the fascinating world of the root "coelo," derived from the Greek word "koilos," meaning hollow. From the anatomy of coelomates to the evolutionary marvel of coelacanths, this root shapes the language of biology and paleontology, unveiling the hidden mysteries of hollow spaces in life and science.
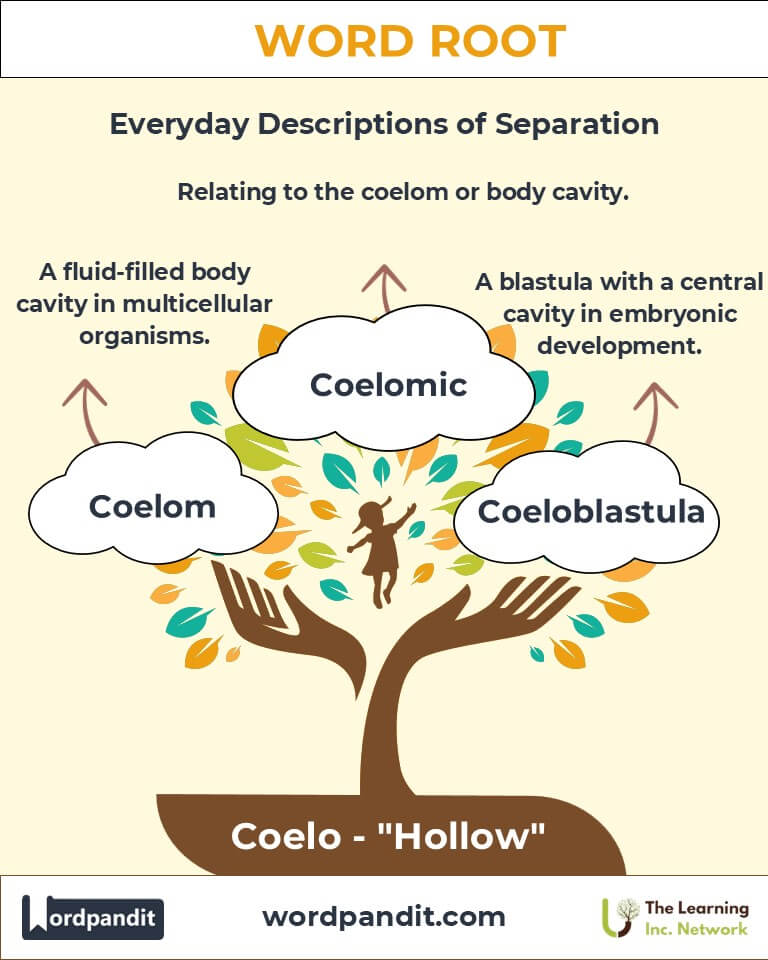
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Hollow Significance of Coelo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Coelo
- Common Coelo-Related Terms
- Coelo Through Time
- Coelo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Coelo in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Coelo Root
- The Coelo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Coelo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Coelo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Timeless Relevance of Coelo
Introduction: The Hollow Significance of Coelo
Imagine exploring an ancient fish species or studying the body cavities of complex organisms. The root "coelo," pronounced SEE-loh, encapsulates the essence of hollow spaces and cavities. Originating from Greek, it signifies "hollow" or "cavity" and has influenced a variety of scientific terms across disciplines. Its relevance spans biology, paleontology, and anatomy, illuminating the unseen structures and evolutionary functions of living beings.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "coelo" derives from the Greek word koilos, meaning hollow or concave. Initially used in ancient texts to describe physical depressions or cavities, it entered scientific lexicons through Latin translations during the Renaissance. Terms like "coelom" (body cavity) and "coelacanth" (a hollow-spined fish) showcase how the root has evolved, intertwining with discoveries in anatomy and paleontology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Coelo
To remember "coelo," picture a coelom, a hollow cavity within the body of an organism, serving as the stage for vital functions like digestion and circulation.
Mnemonic Device: "Coelo creates cavities where life thrives and ancient tales survive."
Common Coelo-Related Terms
- Coelom (SEE-luhm): A fluid-filled body cavity in many multicellular organisms, crucial for organ development and movement.
Example: "Earthworms possess a coelom that allows them to move fluidly through soil." - Coelacanth (SEE-luh-kanth): An ancient lobe-finned fish thought extinct until rediscovered in the 20th century.
Example: "The coelacanth is a living fossil, offering insights into vertebrate evolution." - Coelenteron (SEE-len-ter-on): The central digestive cavity of cnidarians, such as jellyfish and corals.
Example: "The coelenteron enables jellyfish to digest prey efficiently despite their simple anatomy." - Coelomic (SEE-loh-mik): Pertaining to the coelom or body cavity.
Example: "Coelomic fluid helps distribute nutrients in annelids." - Coeloblastula (SEE-loh-blas-too-luh): A type of blastula with a central cavity formed during embryonic development.
Example: "The coeloblastula is a key stage in the early development of many animals."
Coelo Through Time
- Coelacanth Rediscovery: Long thought extinct, the discovery of live coelacanths in 1938 redefined evolutionary history, revealing links to early tetrapods.
- The Evolution of the Coelom: From simple acoelomates to complex coelomates, the coelom illustrates how hollow spaces have facilitated organismal complexity and mobility.
Coelo in Specialized Fields
- Biology: Coelom describes fluid-filled cavities in multicellular animals, vital for organ placement and movement.
- Paleontology: Coelacanth represents evolutionary milestones, bridging aquatic and terrestrial life.
- Embryology: Coeloblastula highlights the significance of cavities in early development stages.
Illustrative Story: Coelo in Action
Dr. Aria, a marine biologist, led a deep-sea expedition to study coelacanths. She marveled at their hollow, oil-filled spines, which allowed them to survive in high-pressure environments. Meanwhile, in her lab, she examined coelomic structures in segmented worms, connecting her findings to broader evolutionary principles. Her research illuminated how coelo-derived structures enable life to adapt, thrive, and evolve.
Cultural Significance of the Coelo Root
The "coelo" root symbolizes humanity’s quest to explore the unseen. From coelacanth fossils inspiring myths of sea monsters to coeloms exemplifying life’s intricate designs, "coelo" bridges ancient wonders with modern discoveries. Its legacy underscores the beauty and utility of hollow spaces in science and storytelling.

The Coelo Family Tree
- Coeli- (Greek, hollow): Example: Coeliac (pertaining to the abdomen).
- Cavi- (Latin, hollow): Example: Cavity (a hollow space).
- Sin- (Latin, curve or hollow): Example: Sinus (a cavity in bone or tissue).
FAQs About the Coelo Word Root
Q: What does "coelo" mean, and where does it come from?
A: "Coelo" means "hollow" or "cavity" and comes from the Greek word koilos. It is a root used in scientific terminology to describe hollow structures or spaces, particularly in anatomy and biology. Its applications include describing cavities in organisms (e.g., coelom) and even hollow spines in ancient fish like coelacanths.
Q: What is a coelom, and why is it significant?
A: A coelom is a fluid-filled cavity found in many multicellular animals, situated between the outer body wall and internal organs. It allows the internal organs to move independently of the body wall, providing protection and facilitating organ growth and movement. This innovation in evolution is critical for the functionality of complex organisms.
Q: What makes the coelacanth such an important discovery?
A: Coelacanths are ancient lobe-finned fish once believed to be extinct for millions of years until they were rediscovered in 1938. Their hollow, oil-filled spines and primitive features provide a living link to early vertebrates, offering insights into the evolutionary transition from aquatic to terrestrial life.
Q: How is the coelo root used in embryology?
A: In embryology, "coelo" is used in terms like coeloblastula, which describes an early stage of embryonic development characterized by a hollow cavity. This stage is critical as it sets the foundation for the development of more complex body structures.
Q: Are coeloms found in all animals?
A: No, not all animals have a coelom. Animals are categorized based on the presence or absence of this cavity. Coelomates, such as humans and earthworms, have a true coelom, while acoelomates (e.g., flatworms) lack it entirely. Pseudocoelomates, like roundworms, have a cavity that is not fully lined with mesodermal tissue.
Q: Why are hollow structures important in biology?
A: Hollow structures, such as coeloms, coelenterons, and coeloblastulas, are essential for various biological functions. They provide space for organs to grow, facilitate efficient nutrient and waste exchange, and enable the development of complex body systems. These cavities are evolutionary adaptations that enhance survival and functionality.
Q: What is the difference between a coelom and a coelenteron?
A: A coelom is a fluid-filled cavity found in coelomates, serving as a space for internal organs and aiding in movement. A coelenteron, on the other hand, is the central digestive cavity of cnidarians (like jellyfish and corals) and is primarily involved in digestion and nutrient distribution.
Test Your Knowledge: Coelo Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "coelo" signify?
2. Which organism is associated with the term "coelacanth"?
3. What does the coelom house in animals?
4. What does "coelenteron" refer to?
5. Which field studies coelomic structures?

Conclusion: The Timeless Relevance of Coelo
The root "coelo" underscores the profound importance of hollow structures in life and science. From coeloms supporting complex organisms to the discovery of coelacanths redefining evolution, "coelo" continues to illuminate the hidden marvels of biology and paleontology. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of life, this root reminds us that even hollow spaces are filled with purpose and wonder.











