Cyano: Exploring the Blue Depths of Language and Science
Dive into the vibrant world of the root "Cyano," derived from the Greek word kyanos, meaning "dark blue." From its presence in medical terms like cyanosis to its foundational role in microbiology with cyanobacteria, "Cyano" paints a rich linguistic and scientific tapestry that connects language with the natural world.
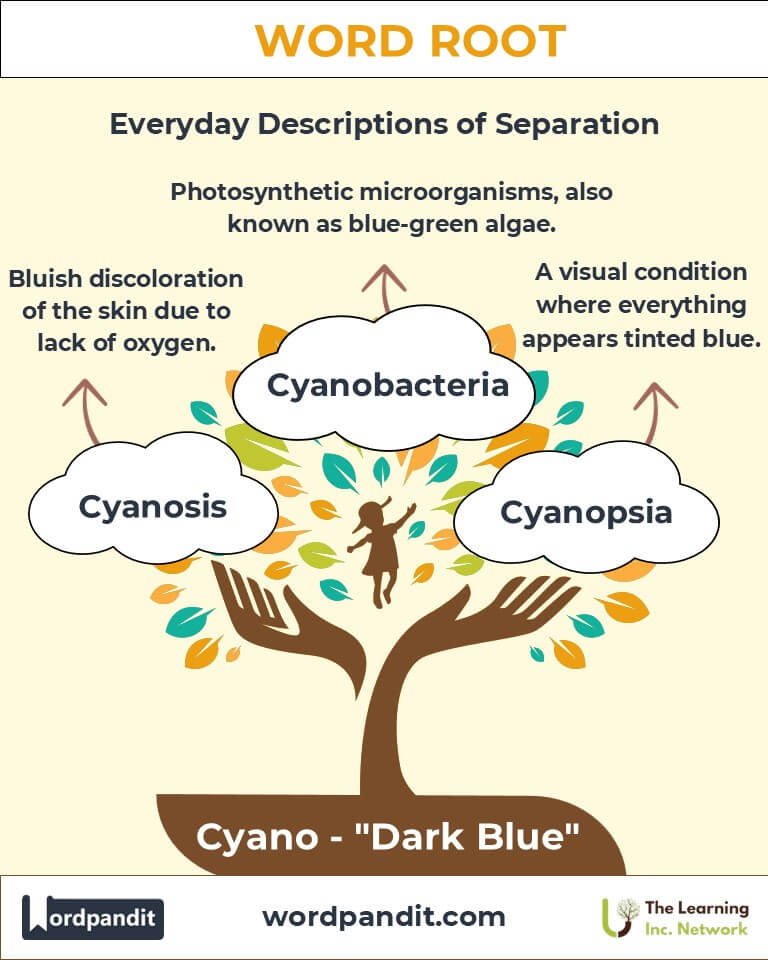
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Vibrant World of "Cyano"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cyano"
- Common "Cyano"-Related Terms
- "Cyano" Through Time
- "Cyano" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Cyano" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Cyano" Root
- The "Cyano" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Cyano" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Cyano" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of "Cyano"
Introduction: The Vibrant World of "Cyano"
The term "Cyano" evokes imagery of the deep blue sea and a breath of fresh air. Pronounced "sigh-a-no," this root originates from the Greek word kyanos (dark blue) and symbolizes the richness of the color in various contexts. In science and medicine, it plays a vital role in describing phenomena tied to the color blue, such as cyanosis (bluish skin due to oxygen deprivation) and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae crucial for Earth’s ecosystems).

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Cyano" traces its roots to ancient Greek, where kyanos referred to both the color dark blue and substances such as lapis lazuli. Over time, the root transitioned into Latin and subsequently English, becoming part of scientific nomenclature. The term gained prominence in the 19th century with advancements in chemistry and microbiology, marking its significance in describing blue-hued phenomena.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Cyano"
To remember "Cyano," visualize a breathtaking tropical lagoon, its waters shimmering in brilliant shades of blue.
Mnemonic Device: "Cyano paints the world blue—from skies to seas and science too."
Common "Cyano"-Related Terms
- Cyanosis (sigh-a-no-sis): A bluish discoloration of the skin due to lack of oxygen.
Example: "The doctor diagnosed cyanosis in the patient with severe asthma." - Cyanobacteria (sigh-a-no-bak-teer-ee-uh): Photosynthetic microorganisms often called blue-green algae.
Example: "Cyanobacteria are crucial for producing oxygen on Earth." - Cyanide (sigh-a-nide): A chemical compound containing the cyano group, known for its toxicity.
Example: "Cyanide compounds are handled with extreme caution in laboratories." - Cyanotype (sigh-a-no-type): A photographic printing process producing blue images.
Example: "The artist used the cyanotype technique to create stunning prints." - Cyanopsia (sigh-a-nop-see-uh): A visual condition where everything appears tinted blue.
Example: "After cataract surgery, the patient experienced mild cyanopsia."
"Cyano" Through Time
- Cyanide in History: Derived from cyanogen (blue-producing), cyanide was first isolated in the 18th century during studies of dye production. Despite its toxic nature, it played a role in industrial advancements.
- Cyanobacteria's Evolutionary Impact: Dating back billions of years, cyanobacteria revolutionized life on Earth by generating oxygen through photosynthesis, paving the way for complex organisms.
"Cyano" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Cyanosis indicates oxygen deprivation, essential in diagnosing respiratory or circulatory issues.
- Microbiology: Cyanobacteria are integral to understanding ecological systems and the origins of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- Art and Photography: Cyanotype is a unique method to create monochromatic art, showcasing blue hues.
- Chemistry: Cyanide is widely studied for its reactivity, despite its association with toxicity.
Illustrative Story: "Cyano" in Action
Dr. Marina, a marine biologist, studied cyanobacteria’s role in combating climate change. While conducting research on a coral reef, she observed how these microorganisms restored oxygen levels in degraded ecosystems. Meanwhile, an artist nearby used the cyanotype method to document the reef's recovery, demonstrating how "Cyano" bridges science and art.
Cultural Significance of the "Cyano" Root
Blue has long been a color of mystique and depth in human culture, symbolizing trust, tranquility, and introspection. From its role in ancient dyes like lapis lazuli to modern applications in art and science, "Cyano" encapsulates humanity’s fascination with the hue of the heavens and oceans.

The "Cyano" Family Tree
- Chloro- (Green):
Example: Chlorophyll: A green pigment vital for photosynthesis. - Leuko- (White):
Example: Leukocyte: White blood cell crucial for immunity. - Erythro- (Red):
Example: Erythrocyte: Red blood cell responsible for oxygen transport.
FAQs About the Cyano Word Root
Q: What does "Cyano" mean?
A: "Cyano" comes from the Greek word kyanos, meaning "dark blue." It signifies the color blue and is used to describe terms linked to blue pigmentation, oxygen-related medical phenomena, or certain chemical compounds like cyanide.
Q: Why is cyanosis a critical medical condition?
A: Cyanosis occurs when the blood lacks sufficient oxygen, causing a bluish tint in the skin, lips, or nails. This condition is critical because it signals underlying problems such as heart disease, respiratory distress, or hypothermia, all requiring immediate attention.
Q: How do cyanobacteria benefit the environment?
A: Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, produce oxygen through photosynthesis and play a crucial role in carbon cycling and nitrogen fixation. These processes support ecosystems and help combat climate change by regulating atmospheric gases.
Q: Why is cyanide toxic, yet used in industries?
A: Cyanide inhibits cellular respiration, preventing cells from using oxygen to produce energy, which makes it highly toxic. However, its chemical properties make it useful in industries like mining (for gold and silver extraction) and manufacturing (for plastics and dyes). When handled safely, it has practical applications despite its toxicity.
Q: What role does the cyanotype process play in art and photography?
A: Cyanotype is a photographic technique that produces prints in striking shades of blue. Invented in the 19th century, it is still used by artists for its unique aesthetic. The process involves coating a surface with light-sensitive chemicals and exposing it to ultraviolet light.
Test Your Knowledge: Cyano Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Cyano" signify?
2. What are cyanobacteria?
3. What does cyanosis indicate?
4. Which field uses cyanotypes?
5. Why are cyanobacteria considered vital?
Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of "Cyano"
The root "Cyano" serves as a reminder of the beauty and significance of the color blue in science, art, and culture. From life-sustaining cyanobacteria to diagnostic cyanosis, its influence spans disciplines, enriching our understanding of the natural world.












