Systol: The Rhythmic Pulse of Contraction in Language and Science
Discover the dynamic significance of the root "Systol," derived from the Greek word "systole," meaning "contraction." This word root pulsates through the fields of medicine, biology, and linguistics, encapsulating the essence of rhythmic activity essential to life and expression.
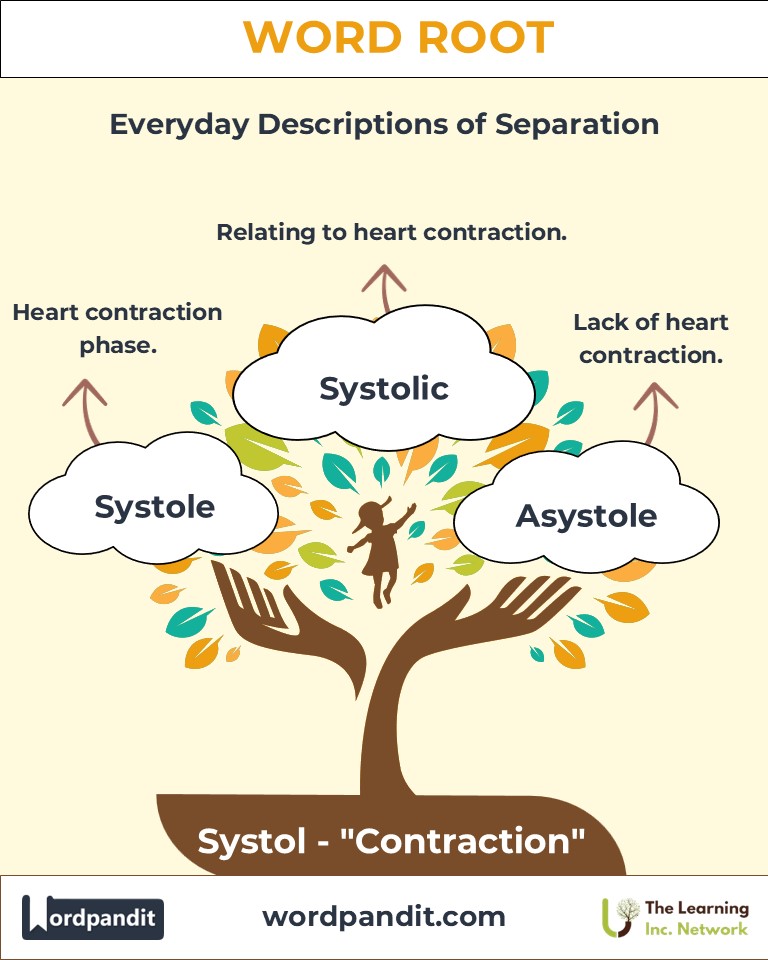
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Systol
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Systol
- Common Systol-Related Terms
- Systol Through Time
- Systol in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Systol in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Systol Root
- The Systol Family Tree
- FAQs about the Systol Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Systol Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Pulse of Systol
Introduction: The Power of Systol
Picture the rhythmic beat of a heart, contracting to pump life-giving blood throughout the body. The root "Systol" (pronounced SIS-toll) embodies this vital motion, capturing the essence of contraction and rhythmic activity. Originating from the Greek word "systole," meaning "a drawing together" or "contraction," this root forms the foundation of terms critical in medicine, physiology, and beyond.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Systol" traces back to ancient Greek, where "systole" described the act of drawing together or compressing. In the medical lexicon, it evolved to denote the contraction phase of the heart's rhythmic cycle. As the understanding of human anatomy deepened, "systole" became a cornerstone of cardiovascular terminology, underscoring the importance of contraction in sustaining life.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Systol
To remember "Systol," envision the heart squeezing in perfect rhythm, pulling life forward with every beat.
Mnemonic Device: “Systol syncs the pulse of life, contracting with purpose.”
Common Systol-Related Terms
- Systole (SIS-tuh-lee): The contraction phase of the heart’s cycle, when blood is pumped out of the chambers.
- Example: "During systole, the ventricles contract to propel blood into the arteries."
- Systolic (sis-TOL-ik): Pertaining to systole, often used to describe blood pressure during heart contractions.
- Example: "A systolic blood pressure of 120 is considered normal."
- Asystole (ay-SIS-tuh-lee): A medical condition marked by the absence of heart contractions (cardiac arrest).
- Example: "The patient was in asystole and required immediate resuscitation."
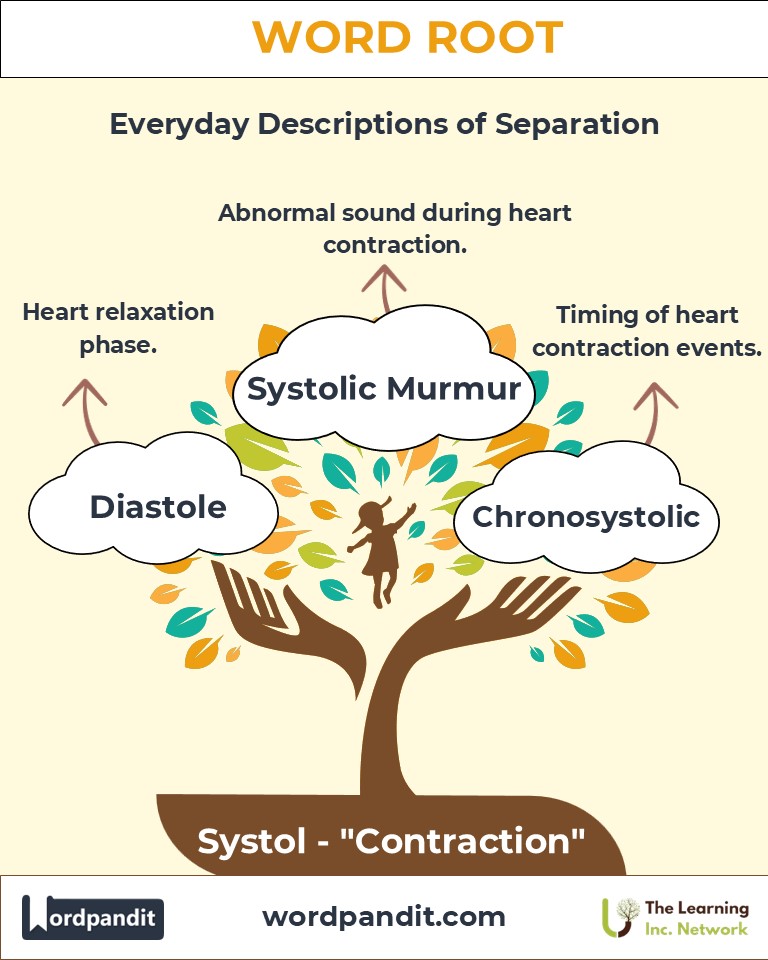
- Systolic Murmur (sis-TOL-ik MUR-mur): An abnormal heart sound occurring during systole, often indicating valve issues.
- Example: "The doctor detected a systolic murmur during the physical exam."
Systol Through Time
The term "systole" has maintained its precision across centuries, evolving from its general Greek origins to a cornerstone in modern cardiology. In the early days of medicine, physicians used the term to describe various rhythmic bodily functions, but its association with the heart has cemented its central role in cardiovascular studies.
Systol in Specialized Fields
- Cardiology:
- Systole describes the heart's contraction phase, critical in measuring blood pressure and diagnosing heart conditions.
- Example: "The systolic reading in a blood pressure measurement indicates arterial pressure during heartbeats."
- Linguistics:
- In ancient rhetoric, "systole" referred to a shortening or contraction of syllables in poetry or speech.
- Technology:
- Advanced AI in healthcare now uses systolic data for predictive modeling of heart diseases.
Illustrative Story: Systol in Action
Dr. Elena Rivera, a cardiologist, was faced with a patient suffering from dangerously high systolic blood pressure. Through careful monitoring and the use of AI technology analyzing systolic patterns, she identified an underlying issue—a valve defect. A successful surgery not only restored the patient’s health but highlighted the life-saving importance of understanding systolic rhythms.
Cultural Significance of the Systol Root
The rhythmic nature of "systole" resonates beyond medicine, symbolizing balance and harmony in life. Many cultures view the heartbeat as a metaphor for life's natural cycles, emphasizing contraction and expansion as universal principles.

The Systol Family Tree
- Stol (to place, send):
- Epistolary: Relating to letters or correspondence.
- Example: "Her epistolary novels showcased the beauty of handwritten communication."
- Diastol (expansion):
- Diastole: The phase of relaxation in the heart's cycle.
- Example: "Diastole complements systole, ensuring the heart's continuous rhythm."
- Chron (time):
- Chronosystolic: Pertaining to the timing of systolic events.
- Example: "Chronosystolic measurements help in detailed cardiac analysis."
FAQs About " Systol "
Q: What does "Systol" mean?
A: "Systol" comes from the Greek word "systole," meaning "contraction" or "drawing together." It refers to the act of compressing or condensing, particularly in medical and biological contexts like the contraction phase of the heart. Its linguistic versatility extends to rhetoric, where it historically described syllable shortening.
Q: What is systole in the heart?
A: In cardiology, systole is the phase of the cardiac cycle during which the heart’s ventricles contract to pump blood into the arteries. This is a vital function as it ensures that oxygen-rich blood reaches all parts of the body and supports cellular functions.
Q: How does systolic pressure differ from diastolic pressure?
A: Systolic pressure measures the force exerted on arterial walls during heart contraction (systole), whereas diastolic pressure measures the force during heart relaxation (diastole). Both readings are crucial indicators of cardiovascular health, with normal systolic values typically ranging from 90 to 120 mmHg.
Q: What does asystole mean?
A: Asystole refers to a state where the heart ceases to contract, resulting in the absence of a heartbeat. This condition, also known as cardiac arrest or "flatline," is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention to restore heart function.
Q: Why is systole significant in measuring blood pressure?
A: Blood pressure readings include systolic pressure (the top number), which reflects the maximum force exerted when the heart contracts and pumps blood. Elevated systolic pressure can indicate conditions like hypertension, which, if untreated, may lead to severe complications such as heart attack or stroke.
Test Your Knowledge: " Systol " Mastery Quiz
1. What does "systole" describe?
2. What is the normal range for systolic blood pressure?
3. What term refers to a heart condition marked by the absence of contraction?
4. What is a systolic murmur?
5. How does systole compare to diastole?
Conclusion: The Living Pulse of Systol
The root "Systol" embodies the essential act of contraction, vital to both language and life. From the rhythmic beating of the heart to its linguistic origins, it represents motion, energy, and harmony. As our understanding of this root deepens, its relevance in medicine, science, and culture continues to expand, connecting us to the timeless rhythm of life.












