Terato: The Monstrous Root of Anomalies in Science and Medicine
Discover the fascinating origin and applications of the root "Terato," derived from the Greek word for "monster." This root underpins words that describe anomalies, wonders, and marvels in the fields of biology, medicine, and beyond. From teratology, the study of congenital abnormalities, to teratogens, substances causing developmental anomalies, "Terato" continues to intrigue scientists and scholars alike.
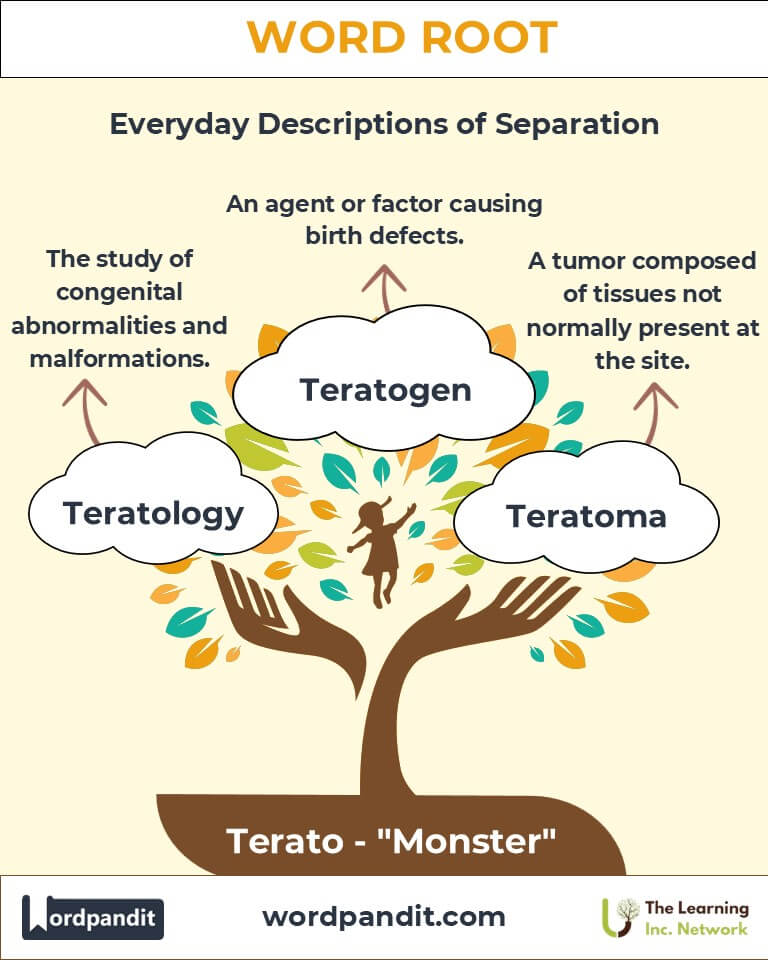
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Terato
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Terato
- Common Terato-Related Terms
- Terato Through Time
- Terato in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Terato in Action
- Cultural Significance of Terato
- The Terato Family Tree
- FAQs about the Terato Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Terato Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Terato
Introduction: The Essence of Terato
The root Terato, pronounced teh-rah-toh, derives from the Greek word teras, meaning "monster" or "marvel." While its initial connotation referred to mythical creatures and extraordinary phenomena, in modern contexts, "Terato" has come to signify abnormalities, particularly in medicine and biology. It forms the basis of terms like teratology (the study of congenital malformations) and teratogen (an agent causing birth defects), emphasizing its relevance in scientific discovery and healthcare.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The journey of "Terato" begins in ancient Greece, where teras referred to signs, portents, or mythical monstrosities. Over time, it transitioned into medical terminology, particularly during the Renaissance, as scholars began to systematically study anomalies in humans and animals. By the 19th century, "Terato" became central to embryology and pathology, marking its place in scientific inquiry.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Terato
To remember Terato, visualize a mythical beast guarding a library of medical knowledge. Its imposing form symbolizes extraordinary phenomena and rare anomalies.
Mnemonic Device: "Terato reveals the marvels and monsters of biological anomalies."
Common Terato-Related Terms
- Teratology (teh-rah-tol-uh-jee): The study of congenital abnormalities and developmental malformations.
- Example: "Advances in teratology have helped identify environmental factors causing birth defects."
- Teratogen (teh-rah-toh-jen): An agent or factor that causes malformations in embryos.
- Example: "Exposure to certain drugs during pregnancy can act as teratogens."
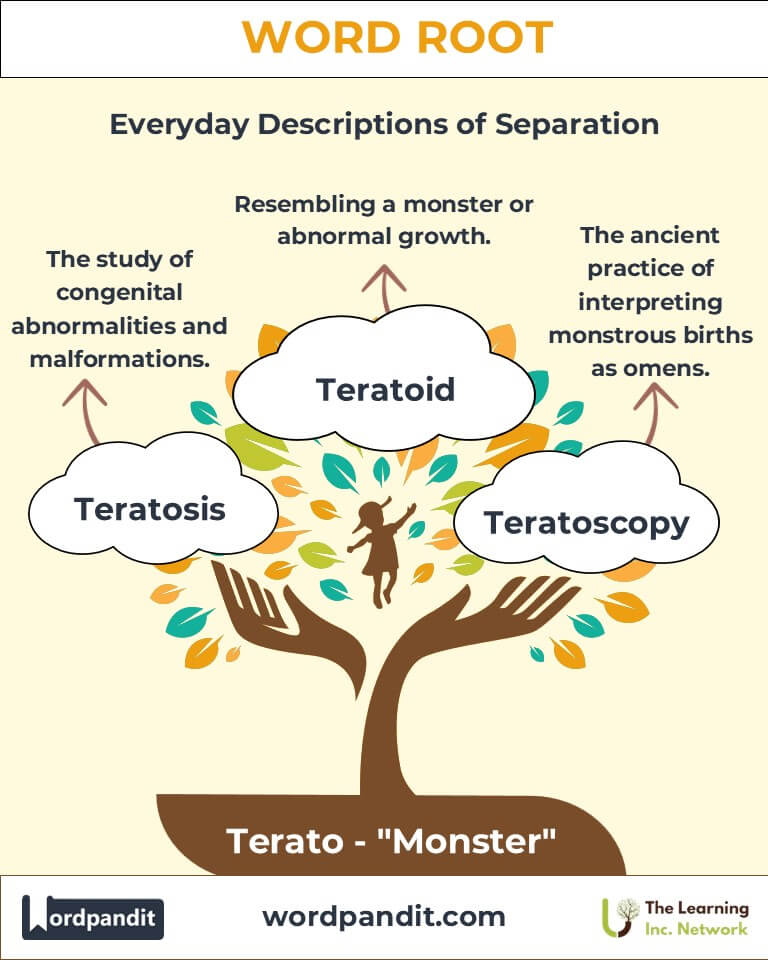
- Teratoid (teh-rah-toid): Resembling a monster or abnormal growth.
- Example: "The tumor had a teratoid structure, containing multiple tissue types."
- Teratosis (teh-rah-toh-sis): A condition involving congenital malformations.
- Example: "The physician specialized in treating teratosis cases in neonates."
- Teratoma (teh-rah-toh-mah): A type of tumor composed of tissues not normally present at the site.
- Example: "The surgeons successfully removed a teratoma from the patient’s abdomen."
Terato Through Time
- Teratoscopy (Historical): The practice of interpreting monstrous births or anomalies as omens.
- Shift in Usage: Ancient superstition gave way to scientific study with the advent of teratology.
- Teratogen Identification (Modern): Research in the 20th century pinpointed substances like thalidomide as teratogens, revolutionizing public health policies and prenatal care.
Terato in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Teratology: Informs understanding and prevention of congenital disabilities.
- Application: Identifying environmental teratogens to reduce risks during pregnancy.
- Pharmacology:
- Research: Shapes drug safety regulations.
- Example: The banning of harmful medications during pregnancy.
- Oncology:
- Teratomas: Challenge surgeons and pathologists due to their complexity.
- Example: Advances in imaging have improved teratoma diagnosis and treatment.
Illustrative Story: Terato in Action
Dr. Elena Vasquez, a teratologist, faced a puzzling case: a newborn with a rare teratosis. Through meticulous research and collaboration, her team identified a previously unknown teratogen in the mother’s environment—a contaminated water source. Her findings prompted community-wide changes, preventing future cases and showcasing the vital role of Terato-focused science in safeguarding public health.
Cultural Significance of Terato
The concept of "monsters" has fascinated humanity across cultures, from Greek mythology’s hydras to modern medical mysteries. Terato symbolizes both fear and wonder, bridging ancient superstitions with contemporary scientific exploration. It reminds us that anomalies, once feared as omens, now drive innovation and understanding.

The Terato Family Tree
- Morph- (Shape, form):
- Morphology: Study of form and structure.
- Example: Morphology aids in classifying teratoid growths.
- Gen- (Origin, birth):
- Genetics: The study of heredity and variation.
- Example: Genetic research uncovers hereditary teratosis causes.
- Patho- (Disease):
- Pathology: Study of diseases.
- Example: Pathologists investigate teratomas for diagnostic insights.
FAQs About " Terato "
Q: What does "Terato" mean, and where does it originate?
A: "Terato" comes from the Greek word teras, meaning "monster" or "marvel." Originally used to describe extraordinary or monstrous phenomena in mythology and nature, it now applies to anomalies or abnormalities, especially in medical and biological contexts.
Q: What is teratology, and why is it important?
A: Teratology is the study of congenital abnormalities and malformations. This field is crucial for understanding how genetic, environmental, or chemical factors can affect embryonic development, allowing for advancements in prenatal care, early diagnosis, and prevention of birth defects.
Q: What is a teratogen, and how does it affect development?
A: A teratogen is any substance or environmental factor that can disrupt normal embryonic or fetal development, causing malformations. Examples include certain drugs (e.g., thalidomide), alcohol, and infections like rubella. Understanding teratogens helps in formulating guidelines to protect pregnant individuals and their babies.
Q: What is a teratoma, and why is it significant?
A: A teratoma is a type of tumor that contains tissues or organs like hair, teeth, or muscle, not typical for its site. Its significance lies in its developmental origins, as it can provide insights into cellular differentiation and early embryonic processes.
Q: What is the difference between a congenital anomaly and a teratoid condition?
A: A congenital anomaly refers to any abnormality present at birth, such as cleft palate or heart defects. A teratoid condition, however, typically involves abnormalities resembling a "monstrous" or multi-tissue structure, such as a teratoma.
Q: How has the concept of teratogens evolved in medicine?
A: Historically, the understanding of teratogens was limited. With advancements in science, substances like alcohol, certain drugs, and environmental toxins have been identified as teratogens. This evolution has led to stricter regulations and better prenatal care to minimize exposure to these harmful factors.
Q: What role does genetics play in teratology?
A: Genetics plays a significant role in teratology, as some congenital anomalies stem from genetic mutations or inherited conditions. Advances in genetic testing help identify predispositions to anomalies and aid in early intervention.
Test Your Knowledge: " Terato " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Terato" mean?
2. What does teratology study?
3. Which of the following is a teratogen?
4. What is a teratoma?
5. Teratoscopy is...
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Terato
The root Terato bridges the mythical and scientific, transforming our understanding of anomalies from superstition to systematic study. Its applications in medicine, pharmacology, and oncology underscore its enduring relevance. By exploring Terato, we gain insights into the extraordinary facets of life, inspiring us to seek solutions and marvel at the complexities of existence.












