Tryp: The Root of Boring Through Nature and Science
Byline: Delve into the fascinating world of the word root "Tryp," derived from the Greek word trypan, meaning "to bore" or "to drill." From life-saving enzymes like trypsin to the notorious trypanosome, a parasitic organism, "Tryp" drills its way through diverse fields, connecting biology, medicine, and beyond.
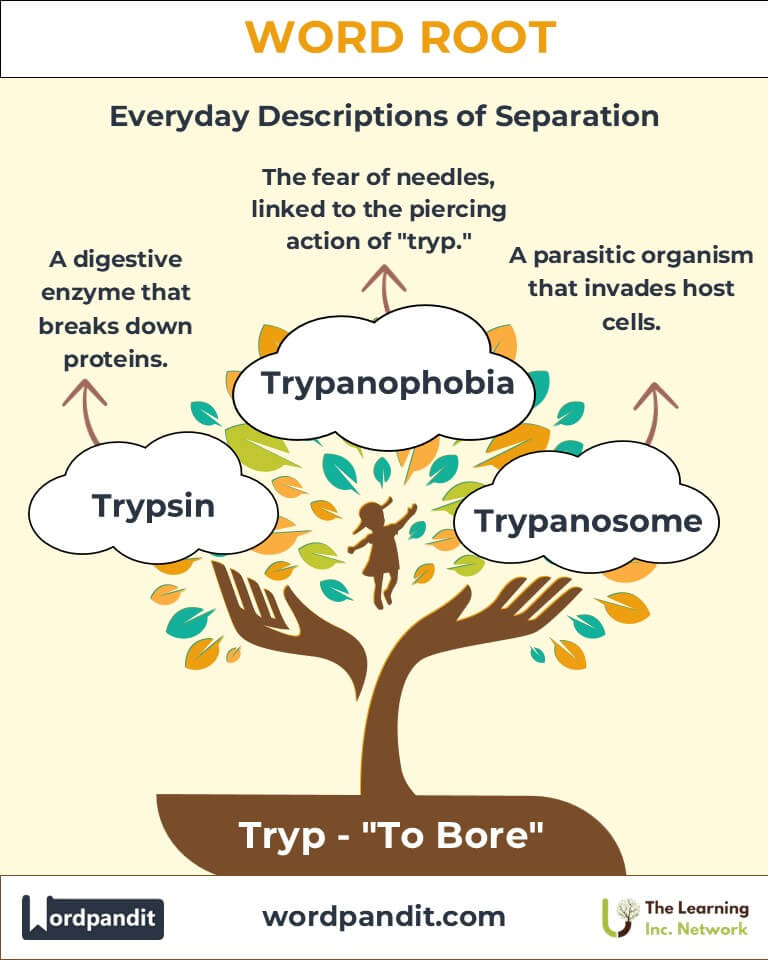
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Tryp
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Tryp
- Common Tryp-Related Terms
- Tryp Through Time
- Tryp in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Tryp in Action
- Cultural Significance of Tryp
- The Tryp Family Tree
- FAQs about the Tryp Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Tryp Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Tryp
1. Introduction: The Essence of Tryp
The root Tryp (pronounced "trip") means "to bore" or "to drill." Originating from Greek, this root is central to terms describing piercing actions or processes, both in biological mechanisms and in nature. "Tryp" finds its way into critical scientific concepts, such as the enzyme trypsin, which bores through proteins to facilitate digestion, and trypanosome, a microscopic parasite known for "boring" into host cells. Through these examples, the root illustrates how nature employs precision drilling for both constructive and destructive purposes.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root Tryp traces back to the Greek term trypan, which means "to drill" or "to pierce." This imagery of boring evolved into scientific contexts during the 19th century, particularly in the naming of biological entities and processes. For example, trypsin was coined to describe a digestive enzyme breaking down proteins, while trypanosome—named for its spiral, drilling motion—became infamous in discussions of tropical diseases. The root reflects a dynamic interplay between mechanical action and biological function.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Tryp
Picture a carpenter’s drill piercing wood. Now imagine the drill representing the root "Tryp," penetrating barriers to achieve a goal—whether digesting proteins or invading host cells.
Mnemonic Device: “Tryp drills through life—digesting proteins, boring through cells, and spinning stories in science.”
4. Common Tryp-Related Terms
- Trypsin (trip-sin):
Definition: A digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins in the small intestine.
Example: "Trypsin is essential for converting complex proteins into absorbable amino acids." - Trypanosome (trip-uh-noh-sohm):
Definition: A parasitic protozoan known for causing diseases such as African sleeping sickness.
Example: "The trypanosome parasite evades the immune system through antigenic variation." - Trypanophobia (trip-an-oh-foh-bee-uh):
Definition: The fear of needles or injections, linked metaphorically to the piercing action of "tryp."
Example: "Overcoming trypanophobia is essential for patients requiring regular injections." - Trypanosomiasis (trip-uh-noh-suh-my-uh-sis):
Definition: A disease caused by trypanosome parasites, such as sleeping sickness or Chagas disease.
Example: "Efforts to control tsetse flies aim to reduce cases of trypanosomiasis." - Triptych (trip-tik):
Definition: Although not biologically related, this term originates from a folding panel design often pierced with hinges, echoing the action of "boring."
Example: "The medieval triptych displayed intricate carvings connected by drilled hinges."
5. Tryp Through Time
- Ancient Origins: Early Greek craftsmen used trypan tools for drilling, symbolizing precision and efficiency.
- 19th Century Medicine: The discovery of trypsin as a critical digestive enzyme expanded the root’s biological applications.
- Modern Parasitology: The naming of trypanosome highlighted the root’s enduring relevance, reflecting the parasite’s ability to bore into hosts.
6. Tryp in Specialized Fields
- Biology:
- Trypsin: Plays a vital role in digestion by breaking down proteins into peptides and amino acids.
- Parasitology:
- Trypanosome parasites: Key to understanding vector-borne diseases like African sleeping sickness and Chagas disease.
- Medicine:
- Overcoming trypanophobia (needle fear) has improved vaccine compliance worldwide.
- Engineering and Technology:
- Although metaphorical, "Tryp" principles inspire mechanical drilling techniques for precision cutting.
7. Illustrative Story: Tryp in Action
Dr. Elena, a parasitologist, studied the lifecycle of trypanosomes to develop a vaccine for sleeping sickness. Meanwhile, her colleague, a biochemist, researched trypsin inhibitors to combat digestive disorders. Together, they discovered a link between the parasite's drilling mechanism and digestive enzyme pathways, paving the way for novel treatments. Their efforts showcased how "Tryp" bridges biology, medicine, and innovation.
8. Cultural Significance of Tryp
The root Tryp symbolizes both creation and destruction, reflecting humanity's dual relationship with tools of piercing and drilling. From ancient crafting techniques to modern medical breakthroughs, "Tryp" serves as a reminder of how precision actions shape life and technology.

9. The Tryp Family Tree
- Trep (Greek: twist, bore):
- Trepanation: A surgical procedure involving the drilling of a hole in the skull.
- Trepan: A drilling tool used in construction.
- Perfor (Latin: bore through):
- Perforate: To make a hole through something.
- Perforation: A pierced or punctured area.
- Fur (Latin: dig, furrow):
- Furrow: A groove or trench in a surface.
- Furcifer: A metaphorical "digger" or scoundrel.
10. FAQs About " Tryp "
Q: What does the root "Tryp" mean?
A: The root "Tryp" comes from the Greek word trypao, meaning "to bore" or "to drill." It is used in contexts involving penetration, repetitive movement, or the act of creating holes, often in science, medicine, and engineering.
Q: How is "Tryp" used in biology?
A: In biology, "Tryp" appears in terms like trypanosomes, which are parasitic protozoa known for their ability to bore into host cells. These parasites cause diseases such as sleeping sickness in humans and animals.
Q: What is tryptophan?
A: Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a role in producing serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Its name derives from the root "Tryp," reflecting its chemical processes involving molecular transformations.
Q: What does "trypophobia" mean?
A: Trypophobia is an aversion or fear of clustered holes or repetitive patterns. Although not officially recognized as a phobia in medical terms, many individuals experience discomfort or anxiety when exposed to such visual stimuli.
Q: How is "Tryp" used in technology?
A: In technology, "Tryp" is associated with drilling and perforation techniques used in construction, manufacturing, and material sciences, where precision and repetitive action are essential for creating holes or bores.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Tryp " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Tryp" signify?
2. What are trypanosomes?
3. What is tryptophan?
4. What does trypophobia describe?
5. Where is "Tryp" used in technology?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Tryp
The root "Tryp" showcases the power of boring—whether in facilitating digestion or in the invasive mechanisms of parasites. Its applications in science, medicine, and metaphorical contexts reflect humanity's intricate relationship with this drilling concept. As we uncover new applications, the legacy of Tryp continues to "bore" into our understanding of the world.












