Varic: The Root of Dilated Pathways in Language and Medicine
Byline: Discover the fascinating significance of "Varic," derived from Latin and Greek roots meaning "dilated." From "varicose veins" to specialized medical terms like "varicocele," this root highlights the intricate relationship between structure and function in anatomy and medicine.
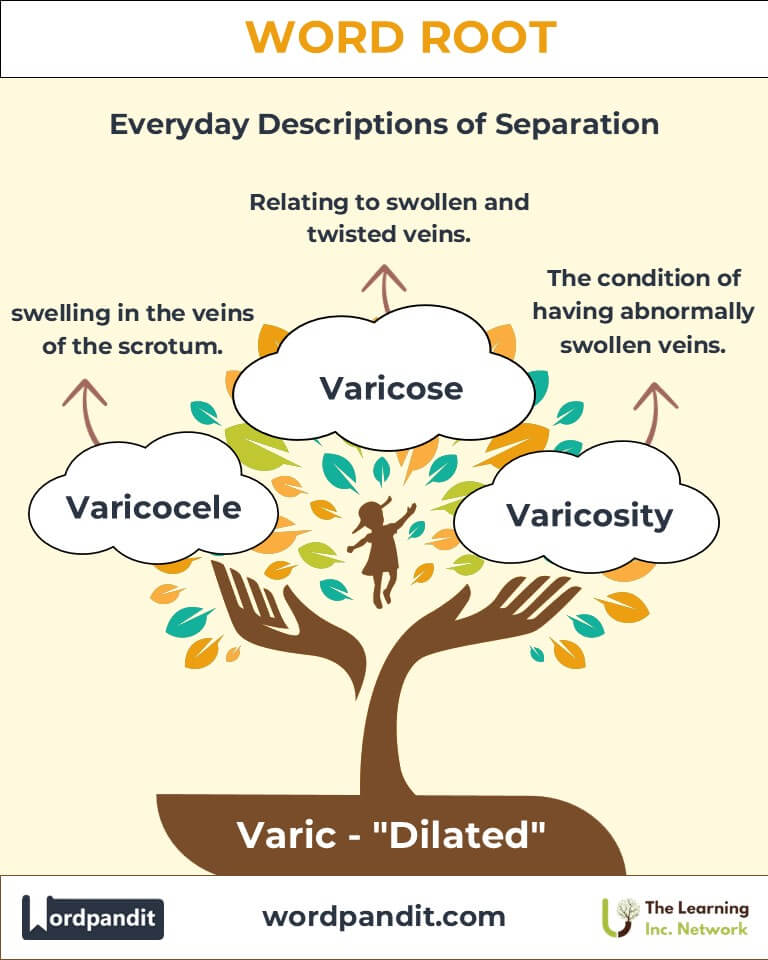
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Varic
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Varic
- Common Varic-Related Terms
- Varic Through Time
- Varic in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Varic in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Varic Root
- The Varic Family Tree
- FAQs about the Varic Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Varic Word Root Quiz
- The Expanding Legacy of Varic
1. Introduction: The Essence of Varic
The word root "Varic," pronounced as "VAIR-ik," originates from Latin varix, meaning "swollen" or "twisted." It also connects to Greek influences in medical terminology. Varic captures the essence of dilation or swelling, often in anatomical structures like veins. Commonly seen in terms such as "varicose" and "varicocele," this root underscores the delicate balance between structure and function in human physiology. Its relevance extends beyond medicine, symbolizing expansion and distortion in various contexts.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Varic" traces back to Latin varix, with its plural form varices, describing swollen veins. Its usage in Greek (varikos) further emphasized its medical implications, particularly in anatomy. Ancient physicians like Galen documented varicose veins as early as 150 AD, associating them with prolonged standing and physical labor. Over centuries, "Varic" evolved into a cornerstone of medical lexicon, forming terms that describe pathological dilations.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Varic
To remember the meaning of "Varic," visualize a swollen river winding through a valley, mirroring the twisted and enlarged veins associated with this root.
Mnemonic Device: "Varic winds and swells, like veins in valleys and rivers in spells."
4. Common Varic-Related Terms
- Varicose (VAIR-ih-kohs):
Definition: Relating to veins that are abnormally swollen and twisted.
Example: "Her varicose veins developed due to prolonged hours of standing." - Varicocele (VAIR-ih-koh-seel):
Definition: A swelling in the veins within the scrotum, often affecting fertility.
Example: "The varicocele was treated with a minimally invasive surgical procedure." - Varicosity (VAIR-ih-KOSS-ih-tee):
Definition: The condition of being abnormally swollen, especially veins.
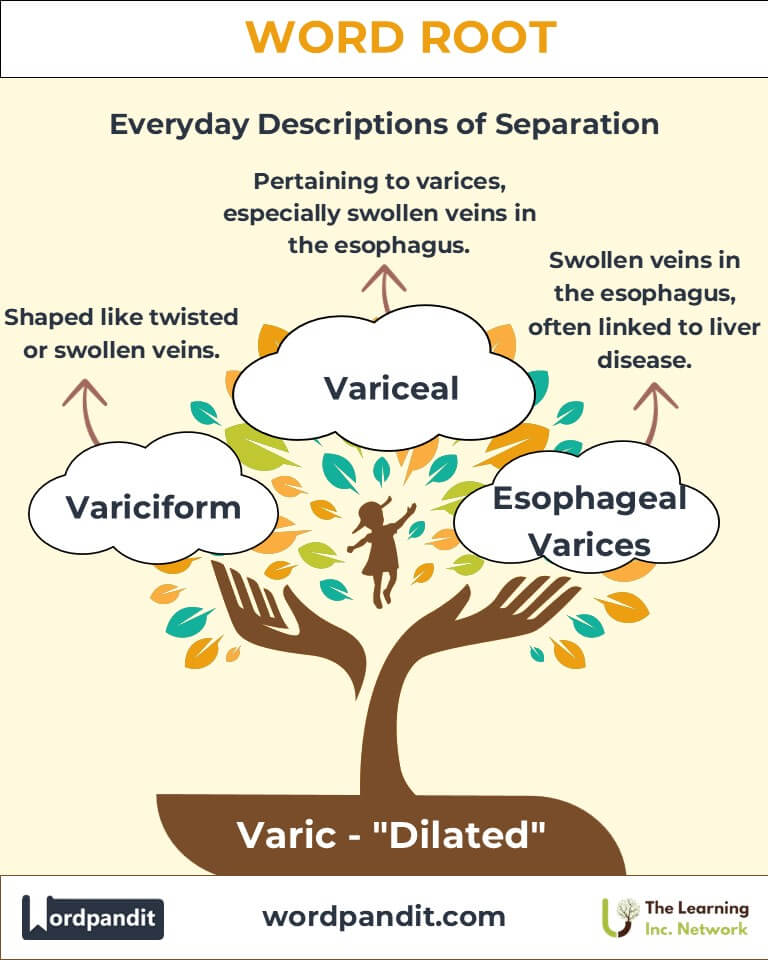
Example: "Varicosity can lead to discomfort and reduced blood flow in the lower limbs." - Variceal (VAIR-ih-seel):
Definition: Pertaining to varices, especially swollen veins in the esophagus.
Example: "Esophageal variceal bleeding is a serious complication of liver disease." - Variciform (VAIR-ih-sih-form):
Definition: Shaped like a twisted or swollen vein.
Example: "The variciform pattern of the river resembled the twisted nature of varicose veins."
5. Varic Through Time
- Antiquity: Galen and Hippocrates recognized varicose veins as early markers of venous disease.
- 19th Century Medicine: Advances in vascular surgery led to the development of techniques like vein stripping for treating varicosities.
- Modern Era: Innovations like laser therapy and sclerotherapy have refined the treatment of varicose veins, emphasizing minimally invasive methods.
6. Varic in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Varicocele: Associated with male infertility and venous insufficiency, treated through embolization or surgery.
- Radiology:
- Variceal Imaging: Advanced techniques like Doppler ultrasound allow visualization of varicose veins and varices.
- Gastroenterology:
- Esophageal Varices: Swollen veins in the esophagus linked to liver disease, requiring endoscopic intervention.
7. Illustrative Story: Varic in Action
Dr. Helen, a vascular surgeon, specialized in treating varicose veins. One day, she encountered a patient, Mark, whose swollen veins caused severe discomfort. Mark’s condition stemmed from prolonged hours as a teacher. Using advanced laser therapy, Dr. Helen treated the veins, restoring blood flow and Mark’s mobility. Mark’s gratitude reflected the profound impact of understanding the root "Varic" in both diagnosis and treatment.
8. Cultural Significance of the Varic Root
The concept of dilation and swelling extends metaphorically into cultural contexts. Swelling rivers signify fertility in ancient myths, while twisted paths are seen as symbolic of life's challenges. The root "Varic," though rooted in anatomy, reflects broader narratives of transformation and resilience.

9. The Varic Family Tree
- Angio (vessel):
Example: Angioplasty—surgical repair of blood vessels. - Phleb (vein):
Example: Phlebitis—inflammation of a vein. - Vas (vessel):
Example: Vasodilation—widening of blood vessels.
10. FAQs About " Varic "
Q: What does the root "Varic" mean?
A: The root "Varic" means "dilated" or "swollen." It is commonly used in medical terms to describe twisted or enlarged structures, particularly veins, such as in "varicose veins." The root reflects abnormal expansion, which can affect circulation and functionality in anatomy.
Q: What are varicose veins, and why do they occur?
A: Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that commonly appear in the legs. They occur when vein walls weaken, and valves inside veins fail to regulate blood flow properly. This causes blood to pool, leading to swelling and visible distortion. Contributing factors include genetics, prolonged standing, obesity, and pregnancy.
Q: What is a varicocele, and how does it affect health?
A: A varicocele is the swelling of veins in the scrotum, similar to varicose veins. It can lead to discomfort, testicular pain, or reduced sperm production, which may affect fertility. Treatments, including surgical correction or embolization, are available to alleviate symptoms and restore reproductive function.
Q: How are varicose veins treated?
A: Treatments range from lifestyle changes, such as exercise and compression stockings, to medical procedures like sclerotherapy (injection of a solution to collapse veins) and laser therapy. In severe cases, surgical removal of veins (vein stripping) may be necessary to improve circulation and appearance.
Q: What are esophageal varices, and why are they dangerous?
A: Esophageal varices are swollen veins in the esophagus, often caused by liver disease, particularly cirrhosis. These veins can rupture, leading to severe internal bleeding. Immediate medical intervention, such as endoscopic therapy, is critical to prevent life-threatening complications.
Q: Can varicose veins be prevented?
A: While genetics play a significant role, prevention strategies include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, and using compression stockings. These measures help reduce vein pressure and improve circulation.
Q: Are varicose veins purely cosmetic, or do they pose health risks?
A: Varicose veins are not just a cosmetic concern. They can lead to pain, swelling, itching, and skin ulcers. In some cases, they may contribute to blood clots (deep vein thrombosis) or chronic venous insufficiency, where blood flow in veins becomes severely impaired.
11. Test Your Knowledge: " Varic " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Varic" signify?
2. What condition involves swollen veins in the esophagus?
3. Which modern treatment targets varicose veins?
4. What does varicocele affect?
5. Which root relates to "vein"?
12. The Expanding Legacy of Varic
The root "Varic" illuminates the dynamics of dilation and swelling in both anatomical and metaphorical contexts. From its Latin origins to modern medical applications, it continues to shape our understanding of structural and functional transformations. As treatments evolve, "Varic" remains a vital part of medical terminology, bridging history, science, and human resilience.












