Botryo: The Clustered Significance in Nature and Science
Byline:
Delve into the fascinating world of the root Botryo, derived from the Greek word "botrys," meaning "cluster" or "bunch of grapes." This root plays a pivotal role in scientific terminology, symbolizing clustered formations in biology, medicine, and beyond.
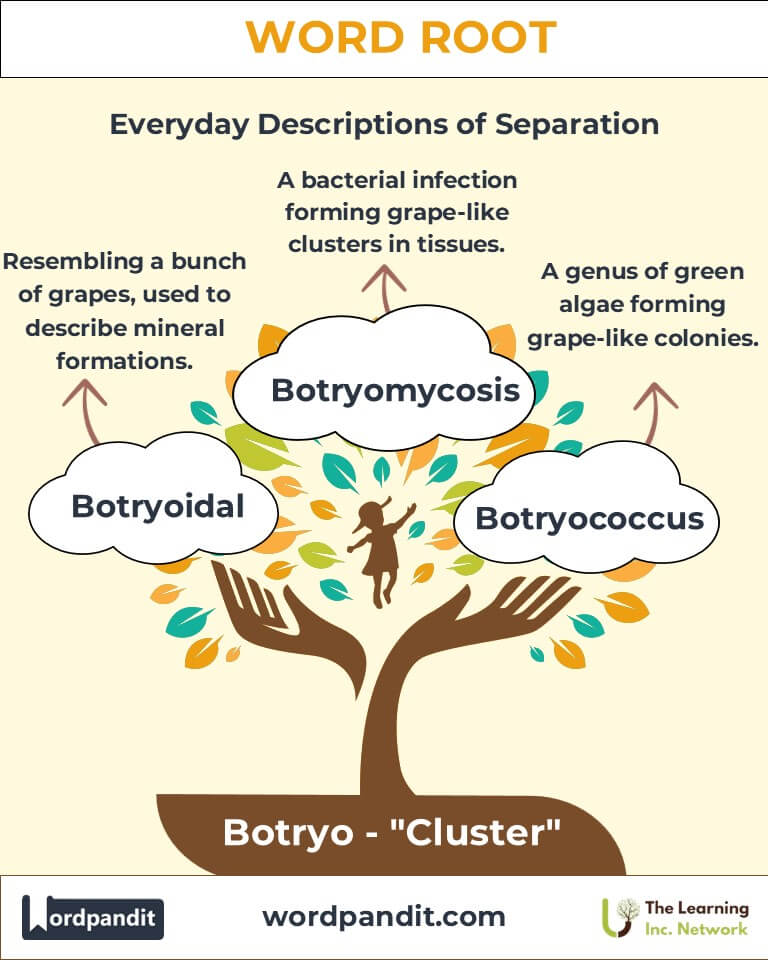
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Botryo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Botryo
- Common Botryo-Related Terms
- Botryo Through Time
- Botryo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Botryo in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Botryo Root
- The Botryo Family Tree
- FAQs about the Botryo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Botryo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of Botryo
Introduction: The Essence of Botryo
The word root Botryo evokes imagery of natural clusters, whether it's a bunch of grapes or microorganisms grouped together. Pronounced "bot-ree-oh," this root signifies grouping and interconnectedness. From botryoidal minerals to medical conditions like botryomycosis, Botryo illustrates how clustering is fundamental in both natural forms and scientific concepts.
Etymology and Historical Journey
The root Botryo originates from the Greek word botrys, meaning "bunch of grapes." Ancient Greek naturalists used this term to describe grape clusters and similar formations in nature. With the evolution of language and science, Botryo became integral to terms in biology, geology, and medicine, emphasizing clustered or aggregated structures.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Botryo
Imagine a luscious grapevine, each bunch representing a unique cluster of concepts tied to Botryo. The clusters symbolize unity and natural formation.
Mnemonic Device:
"Botryo bundles life's formations, from grapes to medical conditions."
Common Botryo-Related Terms
- Botryoidal (bot-ree-oid-uhl): Resembling a bunch of grapes, often used to describe certain mineral formations.
Example: "The botryoidal malachite displayed an intricate, grape-like surface." - Botryomycosis (bot-ree-oh-my-ko-sis): A rare bacterial infection causing grape-like clusters of granules in tissues.
Example: "The patient was diagnosed with botryomycosis, a condition affecting the skin." - Botrytis (bot-rye-tis): A fungal genus known for infecting plants, especially grapes.
Example: "The vineyard suffered a botrytis outbreak, affecting wine production." - Botryococcus (bot-ree-oh-kok-us): A genus of green algae forming grape-like colonies.
Example: "Botryococcus braunii is studied for its potential in biofuel production."
Botryo Through Time
- Botryoidal Minerals: The term emerged in the 18th century, describing rounded, grape-like mineral surfaces.
- Botrytis in Winemaking: Known as the "noble rot," it historically contributed to the production of sweet wines like Sauternes.
- Medical Evolution: Botryomycosis was first identified in the late 19th century in humans and animals.
Botryo in Specialized Fields
- Geology: Botryoidal formations describe minerals like malachite and hematite, prized for their unique, aesthetic shapes.
- Agriculture: Botrytis cinerea plays a dual role, as a destructive plant pathogen and a catalyst in producing high-quality sweet wines.
- Medicine: Botryomycosis offers insights into bacterial infections and immune responses, aiding advances in treatment.
- Bioenergy: Botryococcus braunii is a promising algae for renewable energy due to its lipid-rich composition.
Illustrative Story: Botryo in Action
In a small vineyard nestled in the French countryside, winemaker Jacques faced a challenge: a botrytis outbreak. Instead of despairing, he recognized its potential for creating sweet, complex wines. By carefully managing the rot, Jacques produced a world-renowned vintage, proving that even grape-like clusters of fungi can lead to brilliance. Meanwhile, his son studied botryococcus in a laboratory, dreaming of a future where algae-powered vehicles roamed the streets. Together, their passion for Botryo bridged tradition and innovation.
Cultural Significance of the Botryo Root
The grapevine, a literal representation of Botryo, is a universal symbol of abundance, fertility, and celebration. In mythology, grapes were sacred to Dionysus, the Greek god of wine and revelry. Today, Botryo-related terms in science and agriculture echo this cultural reverence for clustering and growth.
The Botryo Family Tree
- Ampelo- (Greek: grapevine): Example: Ampelography – The study of grapevine varieties.
- Myco- (Greek: fungus): Example: Mycology – The study of fungi, including botrytis.
- Cocco- (Greek: berry): Example: Coccus – A spherical bacterium, often appearing in clusters.
FAQs About the Brachio Root
Q: What does "Brachio" mean?
A: "Brachio" originates from the Greek word brachion, meaning "arm." It refers to the upper limb of the body or arm-like structures in biology, zoology, and robotics, emphasizing movement, strength, and connection.
Q: What is the significance of the brachial artery?
A: The brachial artery is a major blood vessel in the upper arm, carrying oxygenated blood to the muscles and bones. It plays a crucial role in medical diagnostics, such as measuring blood pressure through the arm.
Q: Why is the Brachiosaurus named after "Brachio"?
A: The dinosaur Brachiosaurus is named for its long, arm-like front legs, which were much longer than its hind legs. This unique feature allowed it to reach high vegetation, making it a standout in its ecological niche.
Q: What are brachiopods, and why are they important?
A: Brachiopods are marine animals with arm-like appendages used for feeding. Fossils of brachiopods are significant in paleontology as they help scientists understand the evolution and biodiversity of ancient marine ecosystems.
Q: How is "Brachio" used in robotics?
A: In robotics, "Brachio" inspires the design of mechanical arms, often referred to as robotic brachia. These devices mimic the human arm’s structure and functionality, enabling precision tasks in surgery, manufacturing, and exploration.
Q: What is the antebrachium, and how does it differ from the brachium?
A: The antebrachium refers to the forearm, the section between the elbow and wrist, while the brachium refers to the upper arm, located between the shoulder and elbow. Both terms emphasize the functional divisions of the arm.
Q: What is the brachial plexus, and why is it important?
A: The brachial plexus is a complex network of nerves located in the shoulder, controlling movement and sensation in the arm and hand. Damage to the brachial plexus can result in significant impairments, including paralysis.
Q: How does "Brachio" connect to paleontology?
A: In paleontology, "Brachio" features prominently in names like Brachiosaurus, highlighting physical characteristics such as long, arm-like legs. This term provides insight into ancient creatures’ anatomy and their adaptation to their environments.
Q: Can "Brachio" refer to something outside anatomy or biology?
A: Yes, "Brachio" can also describe arm-like structures in engineering, particularly in robotics. Robotic brachia are designed for precision tasks, combining biology-inspired mechanics with cutting-edge technology.
Test Your Knowledge: Brachio Mastery Quiz
1. What does "Brachio" signify?
2. Which animal has "Brachio" in its name due to its unique front limbs?
3. What does the brachial plexus primarily control?
4. What is the antebrachium?
5. What are brachiopods most known for?
Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of Botryo
The root Botryo beautifully intertwines nature, science, and culture, symbolizing the power of clustering in both tangible and abstract forms. Whether through mineral formations, fungal interactions, or algae's promise for a sustainable future, Botryo remains a testament to the interconnectedness of life. Let it inspire you to see the beauty in clusters and their boundless possibilities.













