Osteo: The Foundation of Bone in Language and Science
Byline:
Explore the world of "osteo," a Greek-derived root meaning "bone," and its applications in medicine, science, and everyday language. From osteoporosis to osteology, "osteo" connects us to the vital structures that support and shape our bodies.
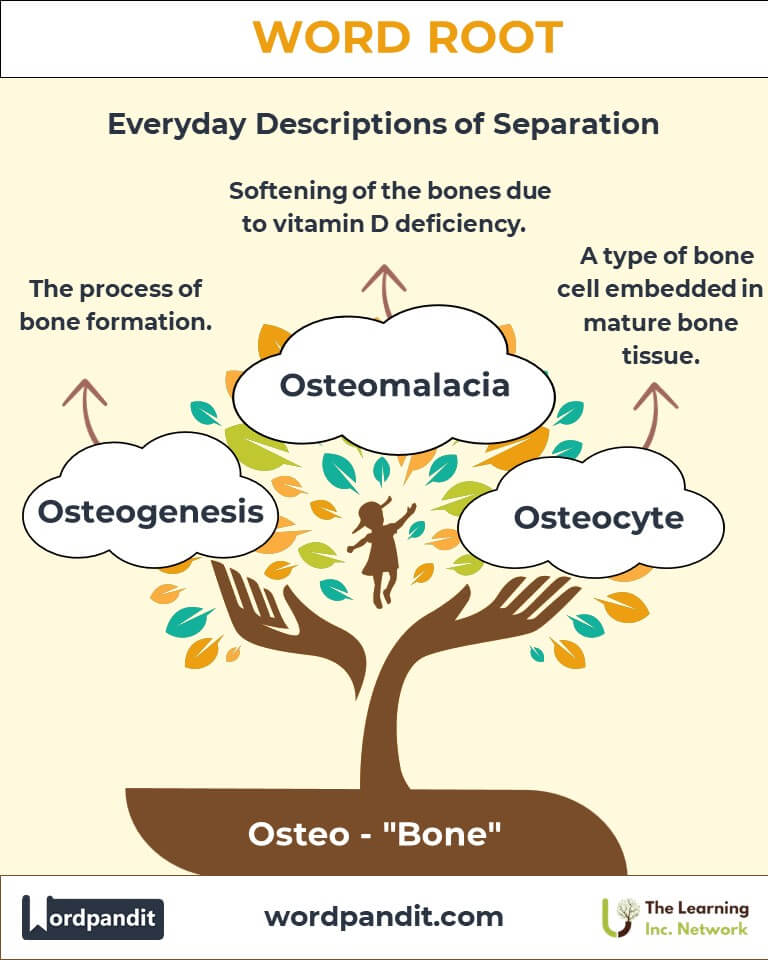
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Strength in "Osteo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Osteo"
- Common Osteo-Related Terms
- Osteo Through Time
- Osteo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Osteo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Osteo"
- The Osteo Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Osteo" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Osteo" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Strength of "Osteo"
Introduction: The Strength in "Osteo"
Bones are the scaffolding of life, holding us upright and connecting us to the ancient past through fossils. The root "osteo" (pronounced os-tee-oh) comes from the Greek word osteon, meaning bone. This root is foundational in medical terminology, offering insight into skeletal health, diseases, and the study of bones, or osteology. Whether you're exploring biology or understanding osteoporosis, "osteo" highlights the importance of bone structure across disciplines.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The Greek root osteon provided a basis for numerous terms in classical and modern medicine. Early anatomists used "osteo" to describe bone diseases and conditions, such as osteitis (bone inflammation). Over time, this root merged into English through Latin, gaining prominence in anatomy, pathology, and anthropology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Osteo"
Imagine a bridge made entirely of bones, symbolizing strength and connection. The word osteo serves as the foundation, supporting the entire structure.
Mnemonic Device: "Osteo is the backbone of strength, from osteology to osteoporosis."
Common Osteo-Related Terms
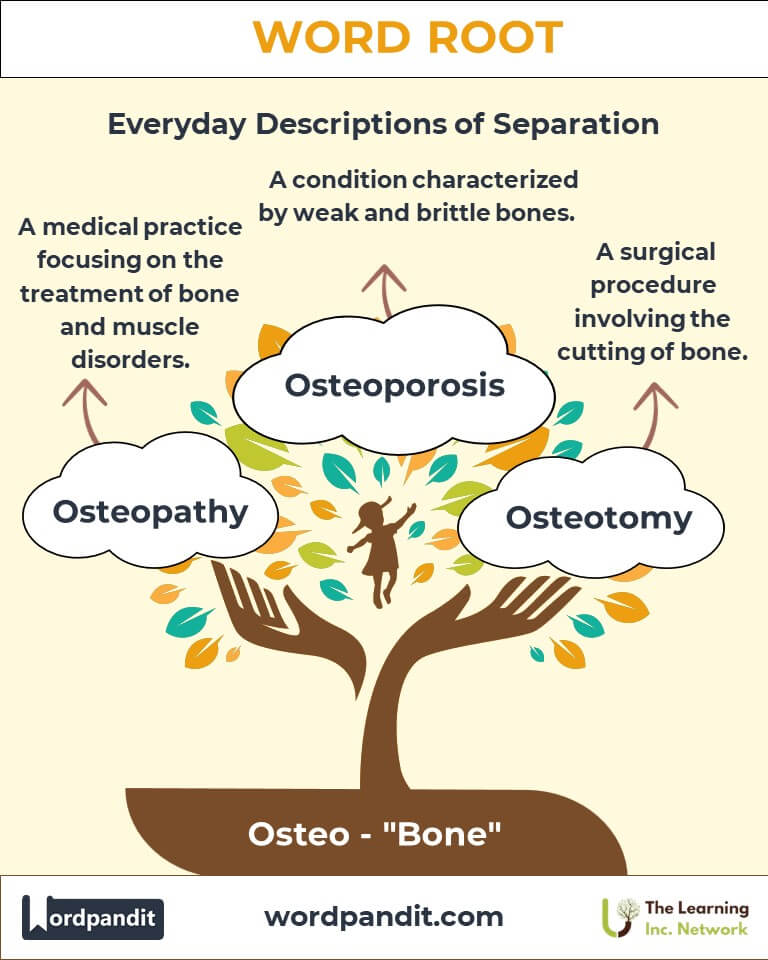
- Osteoporosis: A condition characterized by weakened bones, making them prone to fractures.
Example: “Calcium supplements help prevent osteoporosis in older adults.” - Osteology: The scientific study of bones.
Example: “Osteology helps archaeologists understand ancient species.” - Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease involving cartilage and bone.
Example: “Regular exercise alleviates symptoms of osteoarthritis.” - Osteotomy: A surgical procedure to cut and reshape bones.
Example: “An osteotomy corrected the patient’s bone deformity.” - Osteogenesis: The process of bone formation.
Example: “Osteogenesis occurs during early development and fracture repair.”
Osteo Through Time
- Osteopath (19th Century): A practitioner focusing on musculoskeletal manipulation to promote healing.
- Osteoporosis (20th Century): Once rare, this term became more common with advancements in understanding age-related bone loss.
Osteo in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Osteomyelitis (bone infection): A critical condition requiring antibiotics or surgery.
Example: “Osteomyelitis requires immediate treatment to prevent bone damage.” - Archaeology: Osteometry (measurement of bones): Key in studying skeletal remains.
Example: “Osteometry helps reconstruct ancient lifestyles and populations.” - Biotechnology: Osteoblasts (bone-forming cells): Used in regenerative medicine.
Example: “Osteoblast research pioneers advancements in bone tissue engineering.”
Illustrative Story: "Osteo" in Action
Dr. Elena Martinez, an osteologist, unearthed ancient human remains in a remote desert. By studying the skeleton's osteological features, she identified signs of osteoporosis, offering clues about the individual’s diet and lifestyle. This discovery shed light on how historical societies managed nutritional challenges, connecting "osteo" to both past and present.
Cultural Significance of "Osteo"
Bones hold a deep symbolic meaning in cultures worldwide. From Day of the Dead celebrations to bone-based artistic carvings, "osteo" reflects humanity’s reverence for life’s structure. It also inspires idiomatic expressions, such as “bone of contention,” emphasizing its linguistic versatility.

The Osteo Family Tree
- Oss (Latin: "bone"):
- Ossify: To harden or turn into bone.
- Ossuary: A container for storing bones.
- Skelet (Greek: "dried body"):
- Skeleton: The internal framework of bones.
- Skeletal: Relating to the skeleton.
- Cranio (Greek: "skull"):
- Craniotomy: Surgical opening of the skull.
- Cranium: The skull, especially enclosing the brain.
FAQs About the "Osteo" Word Root
Q: What does "osteo" mean?
A: The root "osteo" is derived from the Greek word osteon, meaning "bone." It forms the basis of many terms related to bones, their structure, and health in both medical and scientific contexts.
Q: Is "osteo" only used in medical terms?
A: While "osteo" is commonly associated with medical terminology (e.g., osteoarthritis or osteoporosis), it also appears in fields like anthropology (osteology), archaeology (osteometry), and biotechnology.
Q: What is the difference between osteology and osteopathy?
A: Osteology is the scientific study of bones, focusing on their structure and evolution, while osteopathy is an alternative medicine branch emphasizing musculoskeletal manipulation to improve overall health.
Q: What are osteoblasts, and why are they important?
A: Osteoblasts are specialized cells responsible for forming new bone tissue. They produce a collagen-rich matrix that mineralizes into strong bone, crucial for growth, healing, and maintaining skeletal health.
Q: What causes osteoporosis?
A: Osteoporosis is caused by decreased bone density, often due to aging, hormonal changes, inadequate calcium and vitamin D, sedentary lifestyles, or medical conditions. It makes bones weak and prone to fractures.
Test Your Knowledge: "Osteo" Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "osteo" signify?
2. Which term describes the study of bones?
3. What condition involves bone weakening?
4. What are bone-forming cells called?
5. Which field uses osteometry?
Conclusion: The Enduring Strength of "Osteo"
The root "osteo" underscores the significance of bones in health, culture, and history. From scientific advancements to everyday expressions, it connects us to the structures that define our existence. As we continue to innovate and explore, "osteo" remains a cornerstone of knowledge, reminding us of the strength within.












