Flu, Flux: The Flow of Language and Meaning
Byline: Explore the root "flu" and "flux," meaning "flow," and their significance in words that describe movement, change, and influence. From "fluid" to "influx," these roots reflect the dynamic nature of life and language.

Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Flu and Flux
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Flu and Flux
- Common Flu/Flux-Related Terms
- Flu and Flux Through Time
- Flu and Flux in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Flu and Flux in Action
- Cultural Significance of Flu and Flux
- The Flu and Flux Family Tree
- FAQs about the Flu/Flux Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Flu and Flux Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Ever-Flowing Influence of Flu and Flux
1. Introduction: The Essence of Flu and Flux
The roots "flu" (pronounced "floo") and "flux" (pronounced "fluhks") originate from Latin, meaning "flow." These roots are found in words that describe states of movement, transformation, and change. Whether it’s the fluidity of water or the influx of ideas, "flu" and "flux" enrich our vocabulary with expressions of continuity and adaptation.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The roots "flu" and "flux" trace back to the Latin verb fluere, meaning "to flow," and the noun fluxus, meaning "a flow" or "discharge." These terms entered English through Old French during the Middle Ages. Over time, they became integral in describing both physical phenomena, such as the flow of liquids, and abstract concepts, like the ebb and flow of fortunes or ideas.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Flu and Flux
Picture a river flowing effortlessly, carrying water downstream. Each wave symbolizes movement and continuity, much like the words derived from "flu" and "flux."
Mnemonic Device: “Flu and flux flow through life, bringing change and connection.”
4. Common Flu/Flux-Related Terms
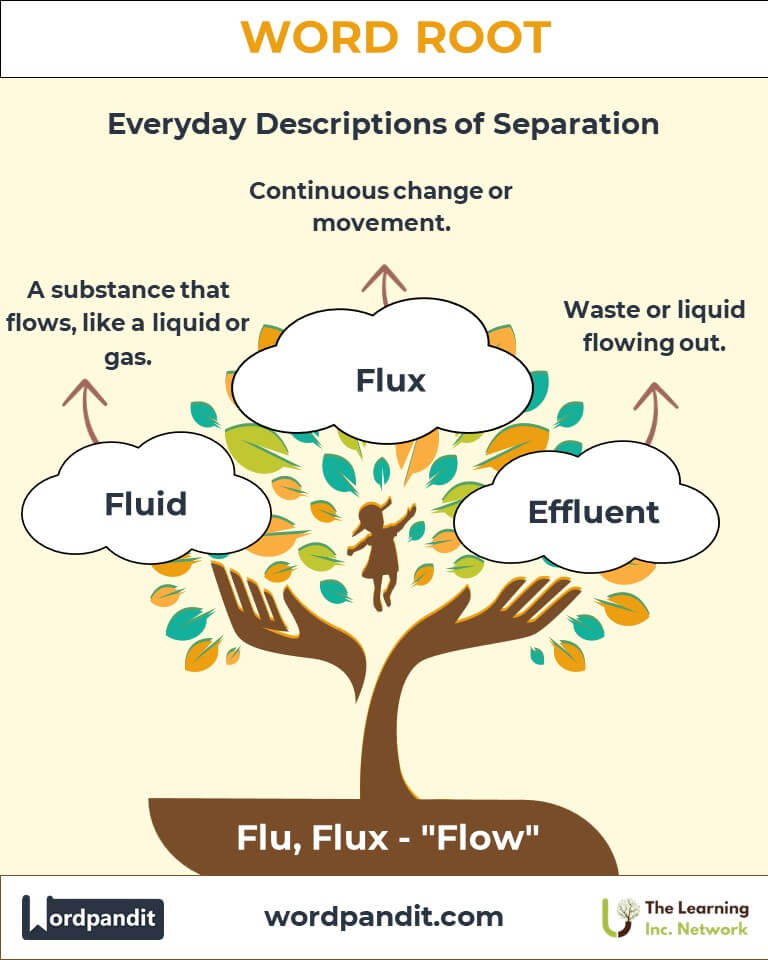
- Fluid (floo-id):
- Meaning: A substance that flows, such as liquid or gas.
- Example: "Water is a fluid that adapts to any container it fills."
- Influx (in-fluhks):
- Meaning: An arrival or flow of large amounts of something.
- Example: "The city experienced an influx of tourists during the festival."
- Fluctuate (fluhk-choo-ayt):
- Meaning: To rise and fall irregularly in number or amount.
- Example: "Stock prices tend to fluctuate daily."
- Effluent (ef-loo-uhnt):
- Meaning: Liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea.
- Example: "The factory reduced its effluent to comply with environmental laws."
- Reflux (ree-fluhks):
- Meaning: The backward flow of liquid in a system, often used in medicine or chemistry.
- Example: "Gastroesophageal reflux can cause discomfort after meals."
5. Flu and Flux Through Time
- Flux (Early Usage):
- Historically used to describe the process of melting metals or the flow of substances during alchemical transformations.
- Fluctuate (Modern Evolution):
- Initially linked to physical waves, it now commonly refers to variations in data or circumstances.
6. Flu and Flux in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Influenza: Derived from the root "flu," this word refers to a viral infection once believed to be influenced by astral "flows."
- Physics:
- Magnetic Flux: Refers to the measure of magnetic field flow through a given area.
- Economics:
- Cash Flow: Describes the movement of money within a business, emphasizing financial health.
7. Illustrative Story: Flu and Flux in Action
Maya, a marine biologist, observed how ocean currents influenced the migration of fish. She marveled at the fluid movements of the schools, likening their patterns to the ebb and flow of life. Her research on fluxes in marine ecosystems inspired innovative conservation methods, demonstrating the powerful role of "flu" and "flux" in nature.
8. Cultural Significance of Flu and Flux
The concepts of flow and movement resonate deeply across cultures. From the Taoist principle of "wu wei" (effortless flow) to the Western idea of "going with the flow," these roots embody adaptability and transformation. In literature, metaphors of rivers and tides often symbolize change and continuity.

9. The Flu and Flux Family Tree
- Flow (Old English):
- Meaning: To move in a steady and continuous stream.
- Example: "The river flows gently through the valley."
- Fluency (Latin):
- Meaning: The ability to express oneself easily and articulately.
- Example: "Her fluency in Spanish amazed the locals."
- Confluence (Latin):
- Meaning: The junction of two rivers or an assembly of ideas.
- Example: "The confluence of cultures created a vibrant cityscape."
- Influence (Latin):
- Meaning: The capacity to have an effect on others.
- Example: "Her influence on the team was transformative."
10. FAQs About the Flu/Flux Word Root
Q: What do the roots "flu" and "flux" mean?
A: The roots "flu" and "flux" come from the Latin fluere, meaning "to flow." They are used in words that describe movement, change, or influence, such as the flow of water, ideas, or energy.
Q: How is "flu" different from "flux"?
A: "Flu" generally appears in words describing a continuous or steady flow (e.g., "fluid" or "influence"). In contrast, "flux" often denotes a state of change or instability, as seen in phrases like "in flux," meaning undergoing change.
Q: What does "fluid" mean in everyday usage?
A: A "fluid" is any substance that flows, such as liquids and gases. Metaphorically, it also describes something adaptable or not fixed, such as "fluid plans."
Q: What is the meaning of "influx"?
A: "Influx" refers to the arrival or flow of large amounts of something, often used for people, money, or ideas entering a system or place.
Q: What does "fluctuate" mean?
A: "Fluctuate" means to vary irregularly, like the rise and fall of stock prices or changes in weather patterns. The term emphasizes unpredictability in movement or amounts.
Q: What is "reflux," and where is it used?
A: "Reflux" describes a backward flow of liquid, commonly used in medicine (e.g., acid reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus) or chemistry (e.g., controlled liquid flow in a reaction).
Q: What is "effluent," and why is it significant?
A: "Effluent" refers to liquid waste or sewage discharged into natural water bodies. It's a key term in environmental science, as managing effluent is essential for reducing pollution.
Q: Why is "flux" associated with change?
A: "Flux" signifies continuous movement or transformation, highlighting the idea that nothing remains constant. For example, saying "life is in flux" suggests it's undergoing significant changes.
Q: What is "magnetic flux"?
A: Magnetic flux measures the total magnetic field passing through a specific area. It's a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in electromagnetism, and is critical for understanding electric generators and transformers.
Q: What is the connection between "flu" and "influence"?
A: "Influence" originates from the idea of an invisible force "flowing" into or affecting something, like how ideas or emotions can flow between people.
11. Test Your Knowledge: Flu and Flux Mastery Quiz
1. What do the roots "flu" and "flux" mean?
2. Which word refers to a backward flow of liquid?
3. What does "fluctuate" mean?
4. Which term describes the arrival of something in large amounts?
5. What is "effluent"?
12. Conclusion: The Ever-Flowing Influence of Flu and Flux
The roots "flu" and "flux" symbolize movement, change, and influence. From the fluid dynamics of nature to the influx of ideas in culture, these roots remind us of the power of flow in shaping our world. As life continues to evolve, so does the language of "flu" and "flux," carrying their legacy forward.












