Meteoro: Reaching for the Heights in Language and Science
Discover the wonder of the word root "meteoro," derived from the Greek word "meteoros," meaning "high" or "lofty." From the study of atmospheric phenomena in meteorology to the exploration of celestial bodies like meteorites, this root connects us to the skies and beyond.
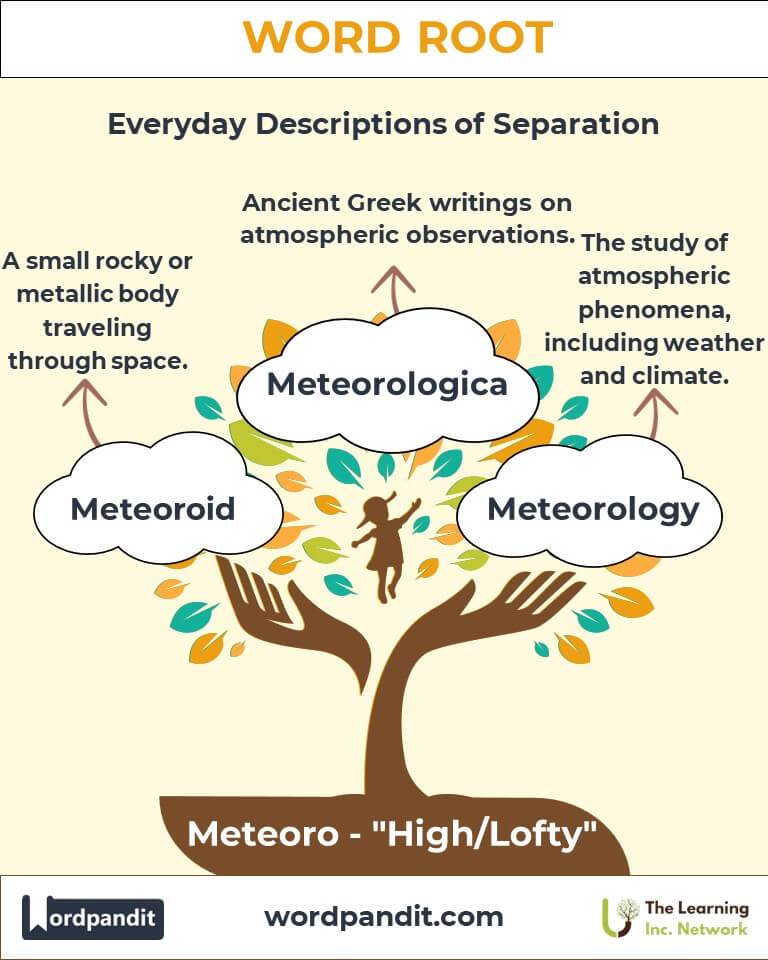
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Meteoro
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meteoro
- Common Meteoro-Related Terms
- Meteoro Through Time
- Meteoro in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Meteoro in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Meteoro Root
- The Meteoro Family Tree
- FAQs about the Meteoro Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Meteoro Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Meteoro
Introduction: The Essence of Meteoro
What do shooting stars, weather patterns, and celestial science have in common? They all stem from the word root "meteoro." Pronounced mee-tee-or-oh, this root originates from the Greek word "meteoros," meaning "high" or "raised up." It has become the foundation for terms that explore lofty realms, from Earth's atmosphere to outer space. In science, "meteoro" bridges the study of weather and astronomy, highlighting humanity’s enduring fascination with the heavens.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "meteoro" traces its origins to the Greek word metéōros, meaning "high in the air" or "lofty." In ancient Greece, it was used to describe phenomena that occurred in the atmosphere, such as weather patterns or celestial events. Over time, the term evolved, and in the Middle Ages, it became central to the study of weather, eventually forming the word "meteorology." The study of meteors expanded during the Enlightenment, as scientific exploration of space deepened humanity’s understanding of objects from the sky.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meteoro
To remember the root "meteoro," imagine a shooting star streaking across the night sky, leaving behind a sense of wonder and loftiness.
Mnemonic Device: "Meteoro takes you high—into the air and beyond the sky!"
Common Meteoro-Related Terms
- Meteorology (mee-tee-or-ol-uh-jee):
Definition: The study of atmospheric phenomena, including weather and climate.
Example: "Meteorology helps us predict storms and understand climate change." - Meteorite (mee-tee-or-ite):
Definition: A fragment of a meteoroid that survives its journey through the atmosphere and lands on Earth.
Example: "The meteorite displayed in the museum was part of a larger asteroid." - Meteor (mee-tee-or):
Definition: A small celestial body that burns brightly upon entering Earth's atmosphere, commonly called a "shooting star."
Example: "We watched the meteor shower under the clear night sky." - Meteoric (mee-tee-or-ik):
Definition: Relating to meteors or something rapid and spectacular in rise.
Example: "Her meteoric rise to fame surprised everyone." - Meteoroid (mee-tee-or-oid):
Definition: A small rocky or metallic body traveling through space.
Example: "Before becoming a meteor, a meteoroid travels millions of miles through space."
Meteoro Through Time
- Ancient Greece: Early philosophers like Aristotle studied "meteoros" as part of their inquiries into natural phenomena.
Key term: "Meteorologica" referred to writings on atmospheric observations. - Modern Science: During the 18th and 19th centuries, advancements in meteorology allowed for more accurate weather predictions, while the discovery of meteorites led to significant developments in astronomy.
Meteoro in Specialized Fields
- Astronomy:
• Meteorites offer valuable insights into the composition of the solar system.
Example: Studying meteorites helps scientists understand planetary formation. - Meteorology:
• Essential for climate science and weather prediction.
Example: Meteorological models guide disaster preparedness and resource management. - Geology:
• Impact craters formed by meteorites reveal Earth’s geological history.
Example: The Chicxulub crater provides evidence of the meteorite impact that caused the dinosaur extinction.
Illustrative Story: Meteoro in Action
On a quiet summer night, Alex and his grandfather sat under the stars, watching a meteor shower. As Alex wished on a shooting star, his grandfather explained the science behind meteors and how some fragments become meteorites. Years later, inspired by that night, Alex became a meteorologist, studying hurricanes to save lives. The "meteoro" root not only shaped his career but also connected his passion for the skies with his desire to make a difference on Earth.
Cultural Significance of the Meteoro Root
The "meteoro" root has inspired art, literature, and traditions across cultures. Meteors have often been viewed as omens or signs, while meteorology has guided agricultural practices for centuries. The fascination with celestial phenomena continues to shape humanity’s curiosity and imagination.

The Meteoro Family Tree
- Aero (air):
• Aerodynamics: The study of how air interacts with objects.
• Aeronautics: The science of flight. - Astro (star):
• Astronomy: The study of celestial objects.
• Astrophysics: The physics of the universe. - Strato (layer):
• Stratosphere: The atmospheric layer above the troposphere.
• Stratocumulus: A type of cloud formation.
FAQs About " Meteoro "
Q: What does "meteoro" mean?
A: The root "meteoro" means "high" or "lofty," originating from the Greek word metéōros. It was historically used to describe things in the sky or elevated above the ground, such as celestial phenomena or weather events.
Q: What is the difference between a meteor and a meteorite?
A: A meteor is a streak of light produced when a meteoroid burns up upon entering Earth’s atmosphere, often called a "shooting star." A meteorite, on the other hand, is the solid fragment of the meteoroid that survives the atmospheric journey and lands on Earth.
Q: What does meteorology study?
A: Meteorology is the scientific study of atmospheric phenomena, such as weather, climate, and other processes in Earth’s atmosphere. Meteorologists analyze patterns to forecast weather and understand long-term climate behavior.
Q: What is a meteoroid?
A: A meteoroid is a small rock or particle traveling through space. If it enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns up, it becomes a meteor. If it survives and lands on Earth, it’s known as a meteorite.
Q: Why is a meteoric rise associated with rapid success?
A: The term "meteoric rise" comes from the rapid and brilliant appearance of meteors in the sky. It metaphorically represents a quick, spectacular ascent to fame or success, much like a meteor streaking brightly across the night sky.
Q: Are meteor showers predictable?
A: Yes, meteor showers are predictable because they occur when Earth passes through the debris left by comets or asteroids. Famous examples include the Perseids and Leonids, which occur annually.
Q: How are meteorites useful for scientific research?
A: Meteorites provide invaluable insights into the composition of the solar system. They often contain ancient materials formed during the early stages of planetary development, helping scientists study the origins of the planets and other celestial bodies.
Q: How does meteorology differ from astronomy?
A: Meteorology focuses on the study of Earth’s atmosphere, including weather and climate. Astronomy, however, deals with celestial objects and phenomena beyond Earth’s atmosphere, such as stars, planets, and galaxies.
Test Your Knowledge: " Meteoro " Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "meteoro" mean?
2. Which of the following is studied in meteorology?
3. What is a meteoroid?
4. What is the term for a meteor fragment that lands on Earth?
5. What does "meteoric rise" refer to?
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Meteoro
The root "meteoro" lifts our language and imagination to new heights, connecting the mysteries of the atmosphere and outer space. From the science of weather to the wonders of shooting stars, it continues to inspire curiosity and exploration. Embrace the legacy of "meteoro" as a reminder to always reach for the skies.












