Geronto: The Key to Understanding Old Age in Language and Science
Discover the significance of the root "Geronto," derived from the Greek word "gerōn," meaning "old man" or "elderly." From gerontology to geriatric, this root plays a vital role in the study and care of aging populations, emphasizing its importance across disciplines.
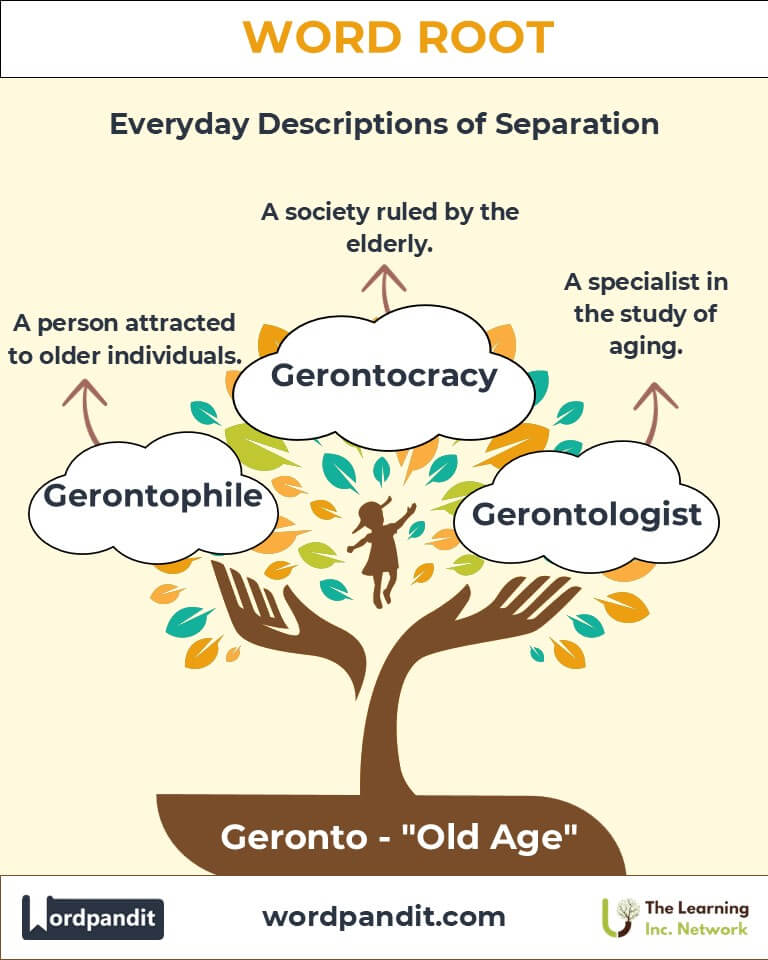
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Wisdom of Geronto
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Geronto
- Common Geronto-Related Terms
- Geronto Through Time
- Geronto in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Geronto in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Geronto Root
- The Geronto Family Tree
- FAQs about the Geronto Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Geronto Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Geronto
Introduction: The Wisdom of Geronto
When you hear the words geriatric or gerontology, what comes to mind? Likely, the wisdom and care associated with aging and the elderly. The root "Geronto" stems from the Greek word gerōn, meaning "old man" or "elderly." This root has shaped many terms that delve into the biology, psychology, and social aspects of aging, making it a cornerstone in fields like medicine, sociology, and even ethics.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word root "Geronto" originates from ancient Greek, where gerōn symbolized respect and reverence for elders. In classical times, aging was often associated with wisdom and experience, a perspective reflected in many languages. Over time, as societies became more industrialized, the term gained a scientific and medical focus, leading to the development of fields like gerontology (the study of aging) and geriatrics (medical care for the elderly).
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Geronto
Picture an elder surrounded by books, each representing a lifetime of wisdom and stories. Their gray hair symbolizes experience, and the books reflect the study and care encompassed by "Geronto."
Mnemonic Device: "Geronto is the elder’s guide, helping us study the aged far and wide."
Common Geronto-Related Terms
- Gerontology (jer-on-tol-uh-jee):
- Definition: The scientific study of aging and its effects on individuals and societies.
- Example: "She chose gerontology as her major to understand how to improve the quality of life for older adults."
- Geriatric (jer-ee-a-trik):
- Definition: Pertaining to the healthcare of elderly people.
- Example: "The hospital opened a new geriatric ward to provide specialized care for older patients."
- Gerontocracy (jer-on-tok-ruh-see):
- Definition: A system of governance where elders hold power.
- Example: "Some critics argued that the political system resembled a gerontocracy, dominated by senior leaders."
- Gerontophobia (jer-on-toe-foe-bee-uh):
- Definition: An irrational fear or dislike of aging or the elderly.
- Example: "The documentary shed light on how gerontophobia affects societal attitudes toward the aging population."
- Gerontologist (jer-on-tol-uh-jist):
- Definition: A specialist in the study of aging.
- Example: "As a gerontologist, Dr. Smith focuses on promoting active aging and combating age-related stereotypes."
Geronto Through Time
- Ancient Greece: Gerōn was a term of respect, symbolizing wisdom and the role of elders in guiding society.
- Middle Ages: Elders were valued in agrarian communities for their knowledge and experience, but aging was often seen as a period of decline.
- Modern Era: The advent of medical science and social programs brought new focus to aging, leading to the formalization of geriatrics and gerontology in the 20th century.
Geronto in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Term: Geriatric Medicine
- Relevance: Focuses on preventing and managing diseases in older adults, including dementia and osteoporosis.
- Sociology:
- Term: Gerontological Sociology
- Relevance: Examines the role of aging populations in shaping social policies and cultural attitudes.
- Psychology:
- Term: Geropsychology
- Relevance: Studies mental health and cognitive changes in aging individuals.
- Technology:
- Term: Gerontechnology
- Relevance: Designs innovations to improve the lives of older adults, such as mobility aids and smart homes.
Illustrative Story: Geronto in Action
Sophie, a gerontologist, worked tirelessly to design programs for active aging. One day, she met Mr. Clark, an 82-year-old former teacher struggling with loneliness. Sophie introduced him to a community center offering art classes for seniors. Not only did Mr. Clark rediscover his passion for painting, but he also formed friendships that enriched his life. Through her dedication, Sophie demonstrated the profound impact of gerontology in fostering dignity and joy during old age.
Cultural Significance of the Geronto Root
Across cultures, aging has been viewed with reverence, skepticism, or fear. In Asian traditions, elders are often celebrated as keepers of wisdom, while in Western societies, there’s a growing awareness of ageism and its impact. The root "Geronto" encapsulates these varied perceptions, offering a lens through which we can explore and address the challenges and opportunities of aging.

The Geronto Family Tree
- Sen- (Latin: "old"):
- Senile: Relating to old age, often used negatively.
- Senator: Originally, an elder in Roman governance.
- Arch- (Greek: "ruler, leader"):
- Monarch: A single ruler, often aged and experienced.
- Patriarch: A male elder leading a family or group.
- Chron- (Greek: "time"):
- Chronology: The study of time and its sequences.
- Chronic: Long-lasting, often associated with age-related conditions.
FAQs About the "Geronto" Root
Q: What does "Geronto" mean?
A: "Geronto" comes from the Greek root gerōn, meaning "old man" or "elderly." It serves as the foundation for words related to aging, the elderly, and their care, symbolizing the respect and study devoted to this stage of life.
Q: What is the focus of gerontology?
A: Gerontology is the interdisciplinary study of aging. It examines biological, psychological, and social aspects of aging, aiming to improve the quality of life for older adults and prepare society for the challenges of an aging population.
Q: What’s the difference between gerontology and geriatrics?
A: While both relate to aging, gerontology studies the broader impacts of aging on individuals and society, including social policies, mental health, and cultural implications. Geriatrics, on the other hand, focuses specifically on the medical care of elderly individuals, addressing age-related diseases and conditions.
Q: What is gerontophobia?
A: Gerontophobia is an irrational fear or dislike of aging or elderly people. It can manifest as ageism, a societal prejudice against older adults, which may hinder their inclusion in social, economic, and cultural spheres. Addressing gerontophobia is vital for creating a more equitable society.
Q: Why is gerontechnology important?
A: Gerontechnology combines aging research with technology to improve seniors' quality of life. Innovations like fall-detection devices, smart home systems, and telemedicine enable independence, enhance safety, and provide access to care, fostering dignity and convenience for aging populations.
Test Your Knowledge: Geronto Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Geronto" signify?
2. Which term refers to the fear of aging?
3. What does a gerontologist study?
4. Which field focuses on medical care for the elderly?
5. Why is gerontechnology important?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Geronto
The root "Geronto" is a testament to humanity’s enduring engagement with aging. From medical breakthroughs to sociocultural shifts, it reflects our evolving understanding of what it means to grow old. As global populations age, "Geronto" will continue to guide efforts in fostering dignity, care, and innovation for the elderly, ensuring a brighter future for generations to come.












