Hemero: The Essence of the Day in Language and Life
Delve into the fascinating root "Hemero," derived from Greek, meaning "day." From terms like hemeralopia (day blindness) to ephemeral (short-lived), this root encapsulates the transient nature of time, weaving through scientific, literary, and everyday contexts.
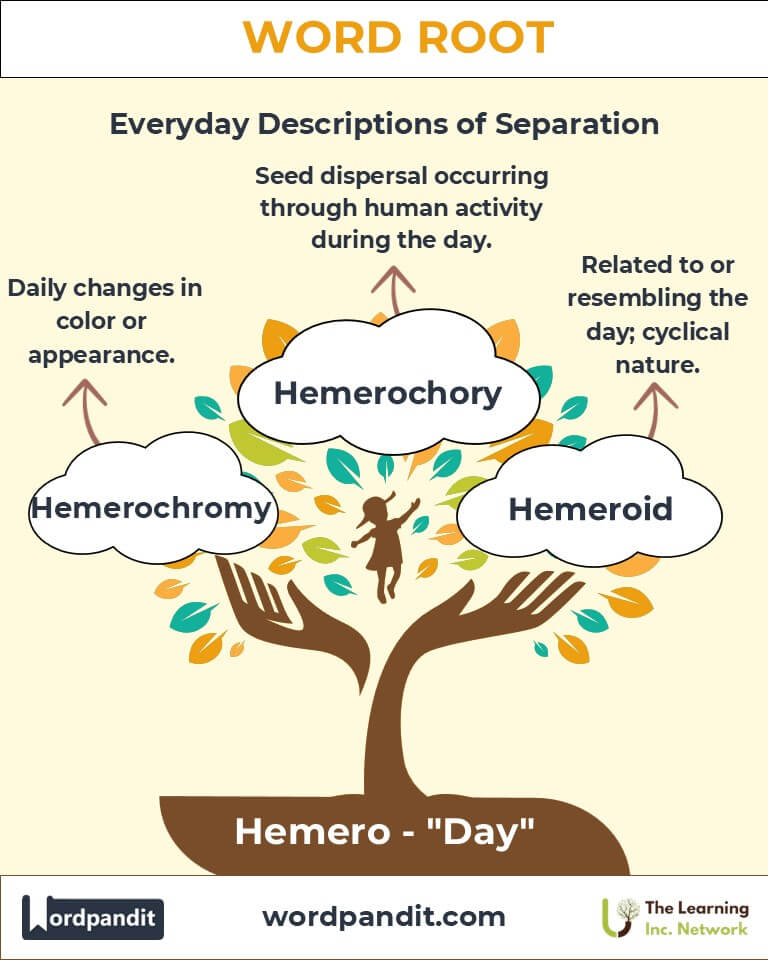
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Daily Power of Hemero
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Remembering Hemero
- Common Hemero-Related Terms
- Hemero Through Time
- Hemero in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Hemero in Action
- Cultural Significance of Hemero
- The Hemero Family Tree
- Conclusion: Hemero’s Living Legacy
Introduction: The Daily Power of Hemero
Imagine a single day, filled with light and activity, as the foundation of this Greek root. Pronounced "heh-meh-ro," Hemero signifies "day" and reflects the passage of time. Its influence spans biology, literature, and everyday expressions, highlighting the ephemeral beauty of existence.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root Hemero originates from the Greek word hēmera (day). In ancient Greece, it symbolized the cyclical nature of time. As science and language evolved, Hemero found a place in medical terminology and poetic expressions, emphasizing brevity and impermanence.
Mnemonic: Remembering Hemero
Picture a sunrise marking the start of a new day, its fleeting light reminding you of the transient nature of time.
Mnemonic: "Hemero lights the day, fleeting yet bright."
Common Hemero-Related Terms
- Hemeralopia (heh-meh-ruh-loh-pee-uh): Day blindness; difficulty seeing in bright light.
Example: "The patient’s hemeralopia made outdoor activities challenging." - Ephemeral (ih-feh-muh-rul): Lasting a very short time.
Example: "The ephemeral beauty of cherry blossoms reminds us to cherish each moment." - Ephemeris (ih-feh-muh-ris): A table listing the positions of celestial bodies for each day.
Example: "Astronomers consult the ephemeris for precise star tracking." - Hemeroid (heh-meh-royd): Related to or resembling the day.
Example: "The hemeroid cycle dictated the ancient farmer’s routines." - Hemerochromy (heh-meh-roh-kroh-mee): Daily changes in color or appearance.
Example: "Some flowers exhibit hemerochromy, altering their hues throughout the day."
Hemero Through Time
- Ephemeral: Initially used in ancient texts to describe a short-lived phenomenon, it has since gained prominence in poetic and philosophical works.
- Hemeralopia: First documented in ancient Greek medical practices, its understanding has advanced significantly in modern ophthalmology.
Hemero in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Hemeralopia identifies conditions affecting daylight vision, improving diagnostic precision.
- Astronomy: Ephemeris tables are critical for navigation and celestial event prediction.
- Literature: Ephemeral symbolizes the fleeting nature of beauty and existence in poetry and prose.
Illustrative Story: Hemero in Action
On a radiant morning, Dr. Lila, an astronomer, prepared to study a meteor shower. Using the latest ephemeris, she calculated the event’s peak. Meanwhile, her assistant, suffering from hemeralopia, struggled with the sunlight. Together, they marveled at the ephemeral beauty of the meteors, reflecting on how science and nature intertwine through the root Hemero.
Cultural Significance of Hemero
In Greek mythology, Hemera, the goddess of the day, symbolized light and renewal. Across cultures, day-centric rituals, such as sun salutations and harvest festivals, echo Hemero’s themes of impermanence and renewal.

The Hemero Family Tree
- Chrono (Greek: time):
- Chronology: The arrangement of events in time.
- Chronometer: A precise timekeeping device.
- Photo (Greek: light):
- Photography: Capturing images using light.
- Photosynthesis: Plants converting light into energy.
- Dia (Greek: through, across):
- Diary: A daily record of thoughts or events.
- Dial: A device marking the passage of hours.
FAQs About the Hemero Root
Q: What does “Hemero” mean?
A: Hemero originates from the Greek word hēmera, meaning "day." It is used in various contexts to highlight concepts related to time, transience, and daily cycles, emphasizing the brevity or regularity of events.
Q: What is Hemeralopia?
A: Hemeralopia is a medical condition characterized by difficulty seeing in bright light or during the day. It is the opposite of night blindness (nyctalopia) and often indicates underlying issues with retinal function or ocular health.
Q: How does “Ephemeral” relate to Hemero?
A: The term ephemeral is derived from Hemero and refers to something that lasts for only a short time, often just a day. Examples include ephemeral flowers that bloom briefly or fleeting moments of beauty in life.
Q: What is an Ephemeris?
A: An ephemeris is a detailed astronomical table that records the positions of celestial bodies, such as planets and stars, for each day. It is vital for astronomers, astrologers, and navigators to predict or track celestial events accurately.
Q: What does Hemerochromy refer to?
A: Hemerochromy refers to changes in color or appearance that occur daily. This phenomenon is commonly observed in nature, such as flowers that shift hues depending on the time of day, showcasing the dynamic effects of light and time.
Test Your Knowledge: Hemero Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root “Hemero” mean?
2. Which condition involves difficulty seeing in daylight?
3. What does “Ephemeral” describe?
4. What is an Ephemeris used for?
5. Which field commonly uses Hemero-based terms?
Conclusion: Hemero’s Living Legacy
The root Hemero connects us to the rhythm of daily life and the fleeting beauty of time. Whether through medical advances, literary reflections, or celestial studies, Hemero reminds us to cherish each passing day. Its enduring relevance inspires us to appreciate the transient and timeless alike.












