Sphinct: The Root of Control and Constriction
Byline: Explore the root "sphinct," from its Greek origin meaning "bind" or "tighten." This root forms the basis of terms in biology and medicine, such as "sphincter" and "sphingomyelin," illustrating its importance in physiology and cellular structure.
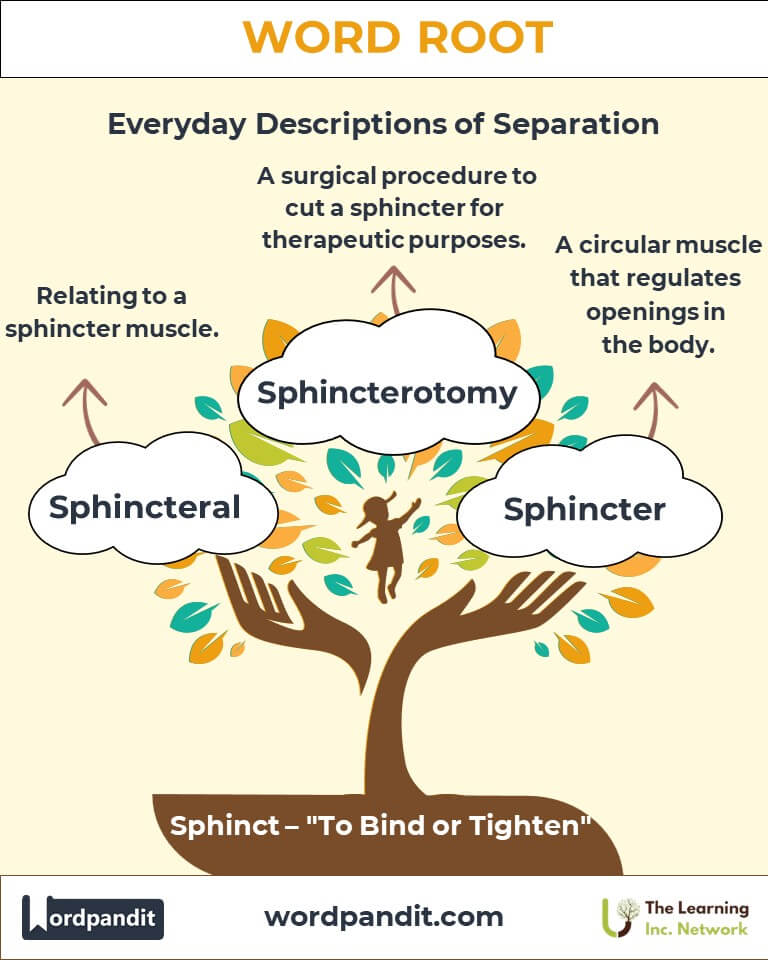
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Sphinct
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sphinct
- Common Sphinct-Related Terms
- Sphinct Through Time
- Sphinct in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Sphinct in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Sphinct Root
- The Sphinct Family Tree
- FAQs about the Sphinct Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Sphinct Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Sphinct
Introduction: The Essence of Sphinct
The word root "sphinct," pronounced as "sfinkt," originates from the Greek word sphingo, meaning "to bind or constrict." It is most commonly associated with the sphincter muscles, crucial to bodily control by regulating the flow of substances through passageways. Beyond anatomy, the root is also integral to cellular biology, as seen in "sphingomyelin," a lipid critical to cell membranes.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "sphinct" has its roots in Ancient Greek, where sphingo described tightening or constriction. This concept transitioned into Latin and later into modern medical terminology. In early anatomy studies, sphincters symbolized the body's natural mechanisms of control, echoing the ancient understanding of balance and restraint.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Sphinct
Picture a tightly tied drawstring bag: when loosened, it releases its contents, and when tightened, it secures them. This image embodies the essence of "sphinct," which regulates and controls flow.
Mnemonic Device: "Sphinct is the body's drawstring—tightening to hold and loosening to release."
Common Sphinct-Related Terms
- Sphincter (sfink-ter):
- Definition: A circular muscle that regulates the opening and closing of bodily passageways.
- Example: "The lower esophageal sphincter prevents stomach acid from entering the esophagus."
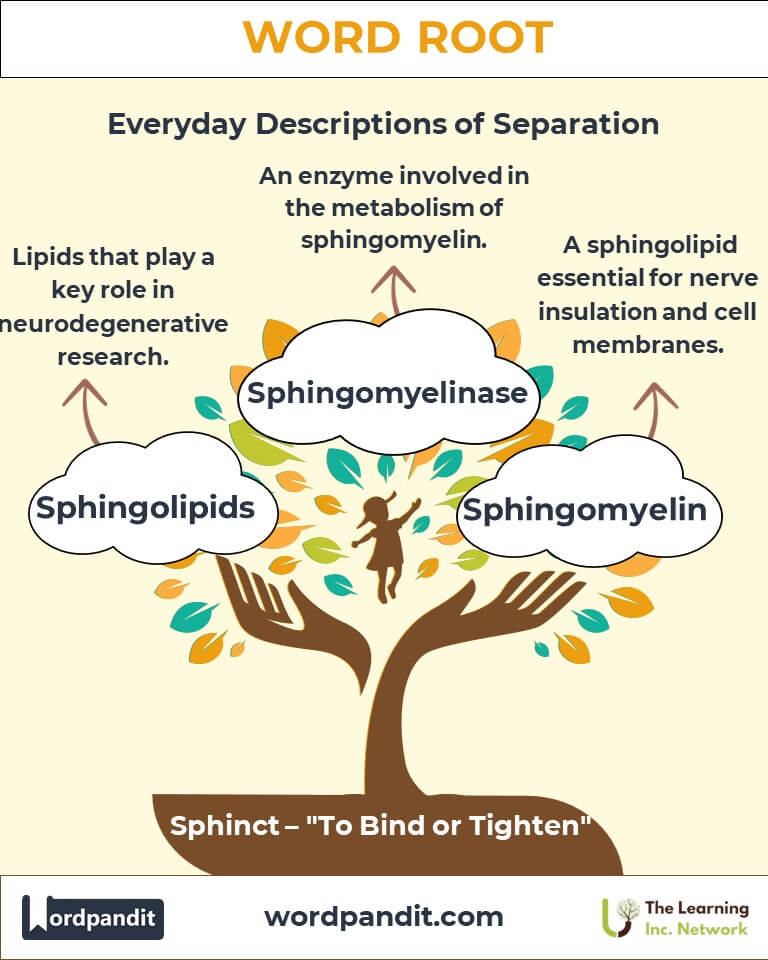
- Sphingomyelin (sfing-oh-my-eh-lin):
- Definition: A type of sphingolipid essential to cell membranes and nerve insulation.
- Example: "Sphingomyelin is vital for forming the protective myelin sheath around neurons."
- Sphincteral (sfink-ter-uhl):
- Definition: Pertaining to a sphincter muscle.
- Example: "The sphincteral function is crucial in urinary continence."
- Sphincterotomy (sfink-ter-ot-uh-mee):
- Definition: A surgical procedure to cut a sphincter muscle for therapeutic purposes.
- Example: "A sphincterotomy can relieve symptoms of anal fissures."
Sphinct Through Time
- Classical Understanding: The term "sphincter" was first applied by ancient anatomists to describe muscles that resembled circular bands.
- Modern Expansion: In the 20th century, cellular biology introduced "sphingolipids," linking the root to molecular structures, broadening its scope beyond gross anatomy.
Sphinct in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Sphincter Dysfunction: Disorders like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) involve the failure of sphincters to close effectively.
- Surgical Interventions: Procedures like sphincteroplasty aim to restore function.
- Cellular Biology:
- Sphingomyelin: Found in the nervous system, it contributes to signal transmission and cellular integrity.
- Neuroscience:
- Sphingolipids: Pivotal in neurodegenerative research, particularly in conditions like multiple sclerosis.
Illustrative Story: Sphinct in Action
Meet Dr. Maria Gomez, a researcher studying the role of sphingomyelin in nerve regeneration. When a patient, Tim, suffered nerve damage after an accident, Dr. Gomez’s groundbreaking work on sphingolipids helped design a treatment to repair his myelin sheath. Tim's recovery showcased the profound impact of "sphinct"-based science, transforming lives through molecular innovation.
Cultural Significance of the Sphinct Root
Ancient cultures revered the body’s ability to regulate itself, often symbolizing control and discipline. In modern times, "sphinct" represents scientific advancements, particularly in medicine and biology, underscoring humanity's pursuit of understanding and control over health.

The Sphinct Family Tree
- Constric- (Latin: bind or tighten):
- Constrict: To make narrower by pressure.
- Constriction: The action of tightening or narrowing.
- Myo- (Greek: muscle):
- Myopathy: Muscle disease.
- Myology: The study of muscles.
- Phleb- (Greek: vein):
- Phlebotomy: Drawing blood from a vein.
- Phlebology: The study of veins.
FAQs About the "Sphinct" Root
Q: What does "sphinct" mean?
A: The root "sphinct" originates from the Greek word sphingo, meaning "to bind or constrict." It is associated with the concept of tightening or controlling flow, fundamental in anatomy and biology.
Q: What is a sphincter muscle, and why is it important?
A: A sphincter is a ring-like muscle that controls the opening and closing of bodily passageways, playing critical roles in processes like digestion and excretion.
Q: What is sphingomyelin, and how is it related to "sphinct"?
A: Sphingomyelin is a lipid found in cell membranes, particularly in the myelin sheath of nerve cells. Its name reflects its binding and constricting role in forming stable cell membranes.
Q: What disorders are associated with sphincter dysfunction?
A: Disorders like GERD, urinary incontinence, and anal fissures are caused by sphincter dysfunction. Treatments range from lifestyle changes to surgeries like sphincterotomy.
Q: Are sphingolipids and sphincter muscles connected?
A: While they share the same linguistic root, sphingolipids regulate cellular structure, and sphincter muscles control physiological flow. Both involve regulation and binding, creating a conceptual link.
Q: What is a sphincterotomy, and when is it performed?
A: A sphincterotomy is a surgical procedure to cut or relax a sphincter muscle. It is performed to relieve conditions like anal fissures or bile duct obstructions.
Test Your Knowledge: Sphinct Mastery Quiz
1. What does "sphinct" mean?
2. Which term describes a circular muscle controlling flow in the body?
3. What is sphingomyelin?
4. Which field studies the role of sphingolipids?
5. What surgical procedure involves cutting a sphincter muscle?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Sphinct
The root "sphinct" underscores the balance of control and release, essential to life processes. From the regulation of bodily functions to breakthroughs in cellular biology, this root remains a testament to the complexity and elegance of natural systems. As science advances, "sphinct" continues to inspire innovation, offering deeper insights into the mechanisms that bind us together—literally and figuratively.












