Post: The Root of After in Language and Expression
Byline: Discover the depth and utility of the root "post," derived from Latin, meaning "after." From everyday terms like "postpone" to more specialized ones like "posterior," this root has shaped how we articulate the concept of timing and sequence.
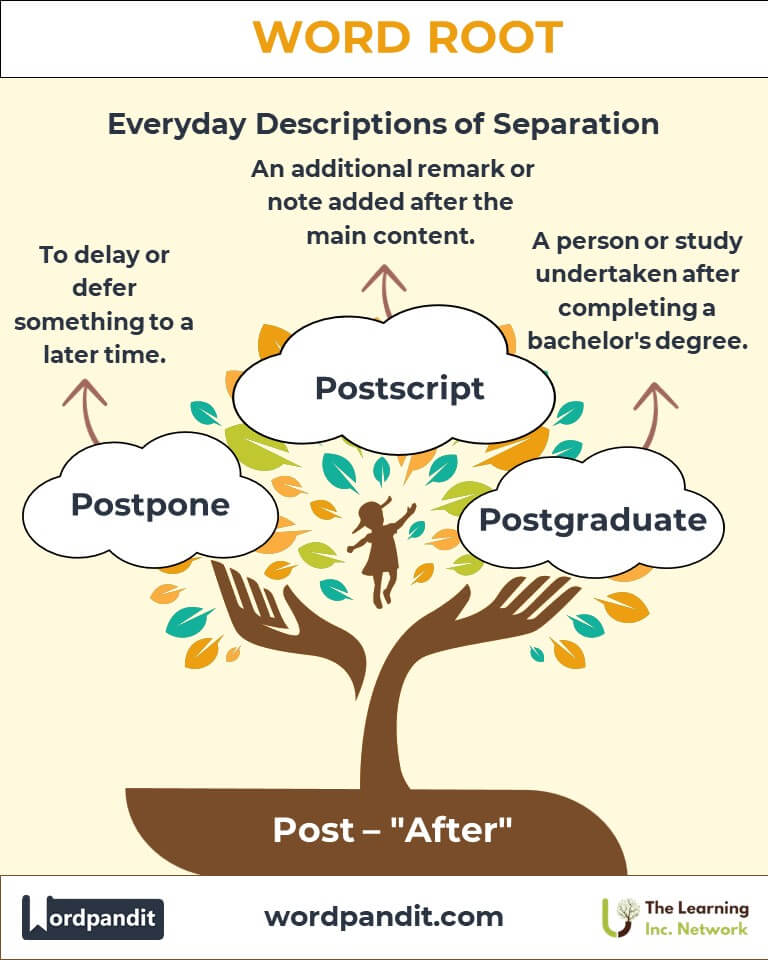
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Post
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Post
- Common Post-Related Terms
- Post Through Time
- Post in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Post in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Post Root
- The Post Family Tree
- FAQs about the Post Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Post Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Post
Introduction: The Essence of Post
The root "post," derived from Latin, simply means "after." Pronounced as "pohst," this root organizes the concept of time across countless words. From common phrases to technical vocabulary, "post" embodies progression, delay, or sequence, making it an indispensable linguistic tool.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "post" traces its origins to Latin, where it meant "after" or "behind." Emerging through classical literature and philosophy, it became foundational in organizing ideas related to time and space. Words like "posterior" were initially used in anatomical contexts before broadening into everyday speech.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Post
Picture a timeline where a bright arrow labeled "POST" points to the future. This visualization links the root to everything that follows a specific event.
Mnemonic Device: "Post always comes after—like the next chapter in a story."
Common Post-Related Terms
- Postpone: To delay or defer something to a later time. Example: "The event was postponed due to rain."
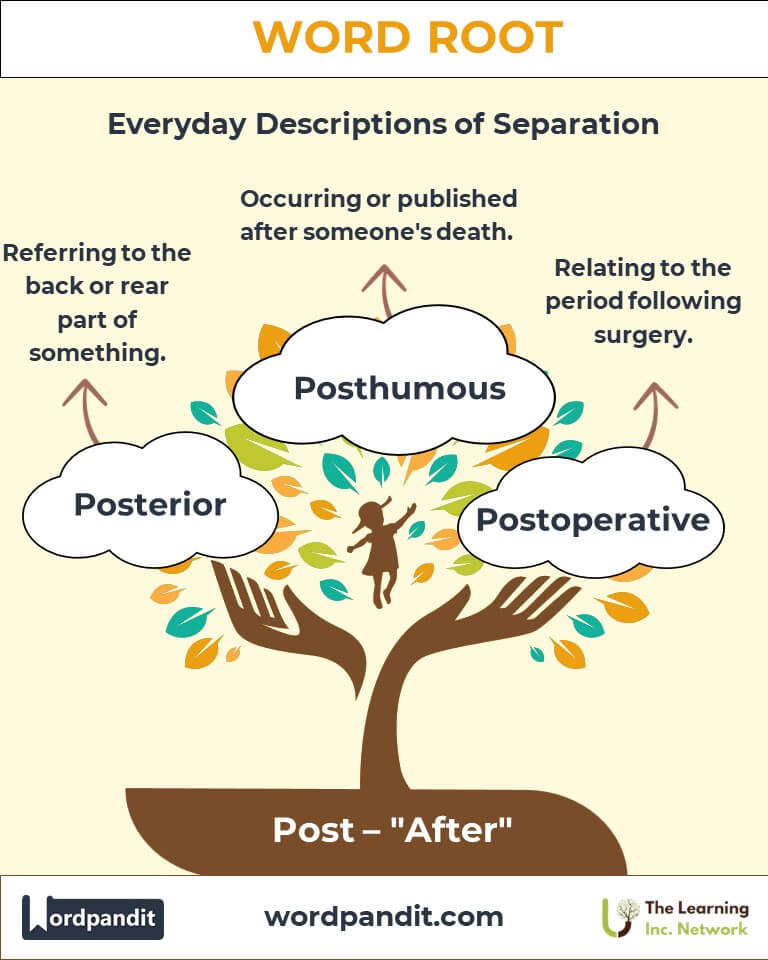
- Posterior: Referring to the back or rear part of something. Example: "The posterior view of the building offers a stunning garden."
- Posthumous: Occurring or published after someone's death. Example: "The artist’s posthumous fame far exceeded expectations."
- Postscript: An additional remark or note added after the main content, often abbreviated as P.S. Example: "She added a heartfelt postscript to her letter."
- Postgraduate: A person or study undertaken after completing a bachelor's degree. Example: "She pursued postgraduate studies in engineering."
Post Through Time
- Posthumous: From Latin posthumus, it initially meant "last-born" before taking on its modern association with events after death.
- Posterity: This term, meaning "future generations," reflects an enduring focus on what follows.
Post in Specialized Fields
- Medicine: Postoperative: Pertaining to the period following surgery. Example: "Postoperative care is critical for recovery."
- Technology: Postprocessing: Refers to enhancing or editing data or images after initial capture. Example: "The photographer spent hours on postprocessing."
- Law and Business: Postdate: To assign a later date to a document or event. Example: "The contract was postdated to align with the launch date."
Illustrative Story: Post in Action
When Emma learned her university exam was postponed, she decided to use the extra time to study more. Meanwhile, her younger brother Tim, fascinated by anatomy, explored the concept of posterior muscles in his biology class. Together, their day demonstrated how "post" connects the ordinary with the scientific.
Cultural Significance of the Post Root
The concept of "after" is central to many cultural expressions. In literature, a "postscript" adds layers of intimacy or wit. Posthumous works, from Vincent van Gogh's paintings to Emily Dickinson's poetry, remind us of the profound impact of creations released "after" their creators' lifetimes.

The Post Family Tree
- Pre- (Latin: "before"): Example: Preview – a glimpse before the main event.
- Ante- (Latin: "before"): Example: Antecedent – a thing or event that precedes.
- Retro- (Latin: "backward"): Example: Retrospect – looking back on past events.
FAQs About the "Post" Word Root
Q: What does "post" mean in Latin?
A: "Post" originates from Latin, where it means "after" or "behind." It serves as a foundation for numerous words that describe sequences or events that follow another.
Q: How is "posterior" used in anatomy?
A: In anatomy, "posterior" refers to the back or rear side of the body. For example, the posterior side of the human body includes the back, shoulder blades, and buttocks. It contrasts with "anterior," which refers to the front of the body.
Q: What is a "postscript," and where is it commonly used?
A: A postscript, often abbreviated as "P.S.," is an additional note or remark added after the main body of a letter or document. It’s commonly used to emphasize something important or add a personal touch after the main content has been concluded.
Q: What does "posthumous" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Posthumous" describes events or works occurring after a person’s death. For example, a book published after an author’s death or awards given to someone posthumously reflect this term. It highlights how their legacy continues after they are gone.
Q: What is the difference between "postpone" and "delay"?
A: Both terms involve setting something to occur later. However, "postpone" usually implies a deliberate decision to reschedule an event or action for a specific time, while "delay" can occur unintentionally, often due to unforeseen circumstances.
Q: How is "post" used in medical terminology?
A: In medicine, "post" is frequently used as a prefix to describe periods or conditions after a specific event, such as "postoperative," which refers to the recovery period following surgery.
Test Your Knowledge: Post Word Root Quiz
1. What does "post" mean?
2. What does "posterior" refer to?
3. What is a "postgraduate"?
4. Which term means "to delay"?
5. What does "posthumous" mean?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Post
The root "post" continues to guide our understanding of time, sequence, and progress. From casual usage to specialized fields, it links past, present, and future in meaningful ways.














