Eco: The Root of Harmony in Nature and Living Spaces
Dive into the versatile root "eco," originating from the Greek word oikos, meaning "house" or "environment." From ecology to eco-friendly, this root forms the foundation of terms that shape how we understand and interact with the world around us.
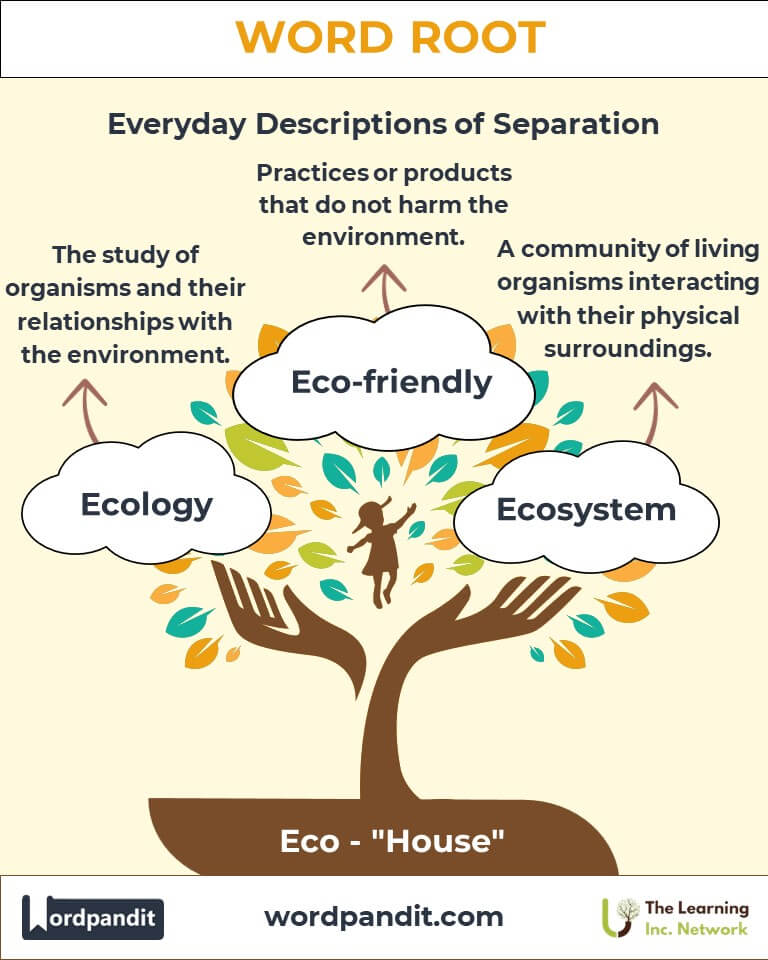
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Eco"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Eco"
- Common Eco-Related Terms
- "Eco" Through Time
- "Eco" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Eco" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Eco" Root
- The "Eco" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Eco" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Eco" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Eco"
1. Introduction: The Essence of "Eco"
What do ecology, economics, and eco-friendly have in common? They all derive from the root "eco," pronounced ee-koh, which traces its origin to the Greek word oikos, meaning "house" or "environment." This root embodies the interconnectedness of living spaces, communities, and the natural world. In an era emphasizing sustainability, "eco" has gained prominence across fields, shaping how we care for our planet and our homes.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "eco" originated in ancient Greek culture, where oikos referred to a household or family unit. Philosophers like Aristotle extended its meaning to the management of households and communities. By the 19th century, "eco" found its way into scientific terminology, giving rise to "ecology," the study of organisms and their environments. Today, "eco" resonates globally as a prefix emphasizing sustainability, conservation, and harmony with nature.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Eco"
Imagine a beautifully balanced terrarium labeled "ECO," where every element works together to thrive.
Mnemonic Device: “Eco is the house where Earth and life live in balance.”
4. Common Eco-Related Terms
- Ecology (ee-kol-uh-jee): The study of organisms and their relationships with the environment.
Example: "Ecology helps us understand how species coexist in ecosystems." - Ecosystem (ee-koh-sis-tuhm): A community of living organisms interacting with their physical environment.
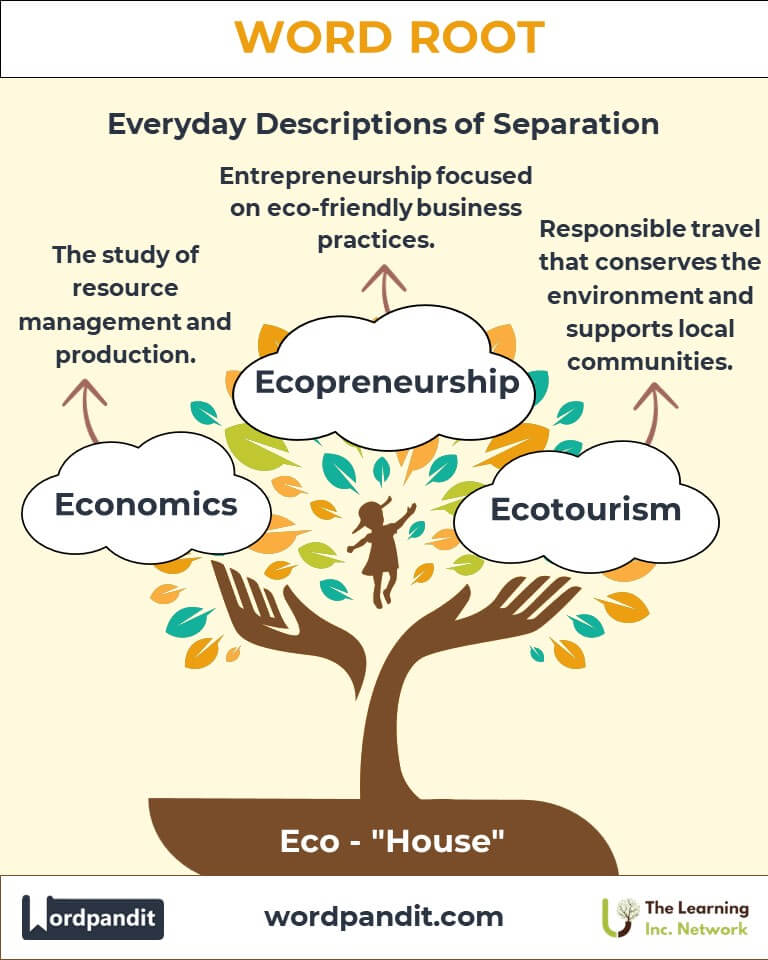
Example: "The coral reef is a vital marine ecosystem." - Economics (ee-kuh-nom-iks): The study of resource management and production.
Example: "Sustainable economics integrates environmental conservation with economic growth." - Eco-friendly (ee-koh-fren-lee): Products or practices that do not harm the environment.
Example: "Switching to reusable bags is an eco-friendly choice." - Ecotourism (ee-koh-too-riz-uhm): Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment.
Example: "Ecotourism promotes awareness of fragile ecosystems."
5. "Eco" Through Time
- Ecology (1866): Coined by Ernst Haeckel, this term laid the foundation for environmental science.
- Eco-friendly (1970s): Popularized during the environmental movement, it became a symbol of sustainability.
- Ecopreneurship (2000s): Combining "eco" with entrepreneurship, this term reflects modern green business practices.
6. "Eco" in Specialized Fields
- Environmental Science: Terms like "ecology" and "ecosystem" are central to studying biodiversity and climate change.
- Economics: "Ecological economics" addresses the balance between economic development and environmental health.
- Tourism: "Ecotourism" fosters environmental awareness while supporting local communities.
- Design and Technology: "Eco-friendly architecture" focuses on sustainable building practices and renewable energy.
7. Illustrative Story: "Eco" in Action
Ava, a passionate ecologist, led a project to restore a local wetland ecosystem. Through collaboration with the community, they planted native species and reduced pollution. Meanwhile, her friend Liam launched an eco-friendly startup selling biodegradable packaging. Together, they showcased how the "eco" spirit transforms environmental challenges into opportunities for growth and harmony.
8. Cultural Significance of the "Eco" Root
From ancient Greek philosophies about household management to modern environmental advocacy, "eco" reflects humanity's evolving relationship with nature. Its widespread use in branding, education, and activism underscores our collective responsibility to sustain the Earth for future generations.

9. The "Eco" Family Tree
- Ecol- (Greek: "environment"):
Ecology: Study of organisms and environments. - Nom- (Greek: "management"):
Economy: Management of resources. - Sust- (Latin: "uphold"):
Sustainability: Maintaining balance and health.
10. FAQs About the "Eco" Word Root
Q: What does "eco" mean?
A: The root "eco" comes from the Greek word oikos, meaning "house" or "environment." It serves as the foundation for words related to both living spaces and natural surroundings. Its dual meaning ties together ideas of community, structure, and the environment, emphasizing harmony and balance.
Q: Why is "eco" associated with sustainability?
A: Over time, "eco" has become synonymous with environmentalism and sustainability because of its connection to the natural world. Words like "eco-friendly" and "ecotourism" emerged in response to global awareness about preserving the environment and ensuring sustainable practices in all aspects of life.
Q: How is "eco" used outside environmental contexts?
A: Although "eco" is often linked to nature, its broader meaning as "house" or "system" applies to various domains. For example, in "economy," it refers to managing resources within a household, community, or country. Similarly, "ecosystem" represents an interconnected system of organisms and their surroundings.
Q: What is the difference between ecology and economics?
A: While both share the "eco" root, their focuses differ significantly:
- Ecology deals with the relationships between living organisms and their environment, emphasizing natural balance.
- Economics focuses on managing resources, production, and distribution within a human community or society.
Q: What is an ecosystem, and why is it important?
A: An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms (plants, animals, microorganisms) and their physical environment (air, soil, water) interacting as a unit. Ecosystems are essential because they provide services such as clean air, water, and food, regulate the climate, and support biodiversity.
11. Test Your Knowledge: "Eco" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "eco" mean?
2. Which field studies organisms and their environments?
3. What does "eco-friendly" refer to?
4. What is an ecosystem?
5. What does "ecotourism" promote?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Eco"
The root "eco" represents more than a connection to nature—it reflects a philosophy of harmony, sustainability, and stewardship. Whether in science, business, or daily life, its influence encourages us to preserve and cherish our environment. As global challenges grow, the "eco" legacy inspires action toward a balanced and sustainable future.














