Aceto: The Root That Defines Acidity and Fermentation
Discover the versatility of the root Aceto, derived from the Latin word acetum (meaning "vinegar" or "sour"). This root forms the basis of terms that encapsulate the essence of acidity, fermentation, and chemical reactions. From the culinary tang of vinegar to the scientific precision of acetone, Aceto plays a pivotal role in language, science, and culture.
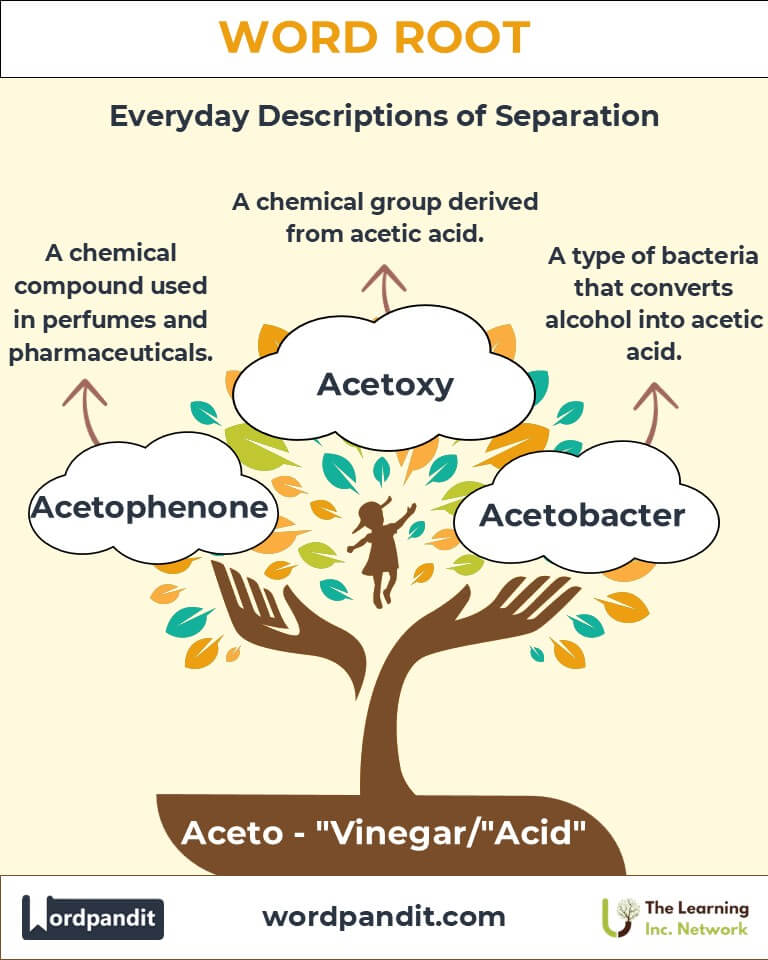
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Chemistry of Aceto
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aceto
- Common Aceto-Related Words
- Aceto Through Time
- Aceto in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Aceto in Action
- Cultural Significance of Aceto
- The Aceto Family Tree
- FAQs about the Aceto Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Aceto Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Sour Significance of Aceto
1. Introduction: The Chemistry of Aceto
Have you ever smelled the sharp tang of vinegar or wondered about the solvent used in nail polish removers? These experiences share a common linguistic root: Aceto, pronounced ah-see-toh. Originating from the Latin term for vinegar (acetum), this root defines substances and processes tied to sourness, acidity, and fermentation. Aceto underscores a fascinating intersection of chemistry, biology, and culinary traditions.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The journey of the Aceto root begins with Latin, where acetum meant vinegar. The term was derived from acidus, meaning "sour" or "sharp." Over centuries, Aceto found its way into scientific nomenclature, particularly in chemistry and biology, to describe compounds associated with acetic acid, fermentation, and solvent properties. From ancient vinegar-making techniques to modern industrial applications, the root evolved, symbolizing transformation and utility.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aceto
Visualize a bubbling laboratory flask filled with vinegar, representing Aceto as the essence of sourness and chemical reaction.
Mnemonic Device:
“Aceto adds sourness to science, from vinegar to solvents!”
4. Common Aceto-Related Words
- Acetone (as-uh-tone): A colorless, flammable liquid used as a solvent.
- Example: “Acetone is commonly used in nail polish remover.”
- Acetous (as-uh-tuhs): Vinegary or sour in taste.
- Example: “The acetous smell of the pickling jars was unmistakable.”
- Acetobacter (as-uh-toh-bak-ter): A genus of bacteria used in vinegar fermentation.
- Example: “Acetobacter converts alcohol into acetic acid.”
- Acetophenone (as-uh-toh-fuh-nohn): An aromatic compound used in perfumes and solvents.
- Example: “Acetophenone adds a subtle floral note to some fragrances.”
- Acetometer (as-uh-tom-uh-ter): An instrument for measuring the concentration of acetic acid.
- Example: “Vinegar producers rely on an acetometer to ensure product consistency.”
5. Aceto Through Time
- Acetone: Initially used as a household solvent, acetone now has applications in scientific research and industrial manufacturing.
- Acetobacter: Once central to artisanal vinegar production, it now drives large-scale fermentation processes.
- Acetometer: From basic vinegar-making tools to advanced chemical measuring devices, this instrument highlights the evolution of precision in acidity measurements.
6. Aceto in Specialized Fields
- Chemistry:
- Acetolysis: A decomposition reaction involving acetic acid.
- Example: “Acetolysis is used in the synthesis of complex organic compounds.”
- Microbiology:
- Acetobacter: These bacteria are vital in food and beverage industries, particularly for producing vinegar and kombucha.
- Example: “Acetobacter ensures the perfect tang in fermented drinks.”
- Medicine:
- Acetaminophen: A common pain reliever and fever reducer.
- Example: “Acetaminophen provides effective relief for mild to moderate pain.”
- Industrial Applications:
- Acetophenone: Used in the production of plastics, resins, and fragrances.
- Example: “Acetophenone exemplifies Aceto’s industrial relevance.”
7. Illustrative Story: Aceto in Action
In a small vinegar factory, the Acetobacter bacteria worked tirelessly to convert alcohol into acetic acid. Meanwhile, a chemist nearby used acetone as a solvent in a critical experiment. Across town, a perfumer relied on acetophenone to craft a unique fragrance. These interconnected stories reveal how Aceto’s versatility weaves through industries, linking science, art, and tradition.
8. Cultural Significance of Aceto
The root Aceto symbolizes humanity’s ingenuity in harnessing natural processes. From ancient vinegar-making traditions to modern chemistry, Aceto reflects the transformation of simple substances into valuable products. Its cultural resonance extends from culinary traditions to scientific innovations, emphasizing sourness as both a sensory and functional cornerstone.

9. The Aceto Family Tree
- Acid- (Latin: "sour, sharp"):
- Acidity: The quality of being acidic.
- Example: “The acidity of lemon juice makes it a great cleaning agent.”
- Acidify: To make something acidic.
- Example: “Chefs often acidify sauces to enhance flavor.”
- Acidity: The quality of being acidic.
- Vineg- (Latin: "vinegar"):
- Vinegar: A sour liquid containing acetic acid.
- Example: “Vinegar is a staple in many global cuisines.”
- Vinegary: Having the qualities or smell of vinegar.
- Example: “The pickles had a vinegary tang.”
- Vinegar: A sour liquid containing acetic acid.
- Ferment- (Latin: "fermentation"):
- Fermentation: A metabolic process producing acids, gases, or alcohol.
- Example: “Fermentation is essential for making bread and beer.”
- Fermentable: Capable of undergoing fermentation.
- Example: “The fermentable sugars in fruit make it ideal for winemaking.”
- Fermentation: A metabolic process producing acids, gases, or alcohol.
FAQs About the Aceto Word Root
Q: What does “Aceto” mean?
A: The root “Aceto” originates from the Latin word acetum, meaning “vinegar” or “sour.” It commonly refers to substances or processes related to acetic acid, sourness, and fermentation. This root is foundational in chemistry, biology, and everyday terms describing acidity and transformation.
Q: What is Acetone used for?
A: Acetone is a versatile solvent widely used in industries and households. It dissolves substances like resins, plastics, and varnishes and is commonly found in nail polish removers. Its ability to evaporate quickly makes it valuable for cleaning surfaces and in laboratories for drying equipment.
Q: What is Acetobacter?
A: Acetobacter is a genus of bacteria essential in the production of vinegar. These bacteria convert alcohol into acetic acid through a process called acetification. Beyond vinegar, Acetobacter plays a role in producing kombucha and other fermented beverages.
Q: What does “Acetous” mean?
A: Acetous refers to something that has a sour, vinegary quality. The term is often used to describe smells, tastes, or chemical reactions where acetic acid or similar compounds are present. For example, the characteristic odor of a pickling jar is acetous.
Q: What is an Acetometer, and how is it used?
A: An acetometer measures the concentration of acetic acid in a solution, like vinegar. It ensures that the acidity levels meet specific standards, particularly in food production. This tool is essential for manufacturers to maintain consistency and quality.
Q: What is Acetolysis?
A: Acetolysis is a chemical reaction where acetic acid acts as a catalyst to break down other substances. It is significant in organic chemistry, particularly for modifying compounds or synthesizing new ones. Acetolysis often involves ester bonds and is used in biochemical research.
Test Your Knowledge: Aceto Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root “Aceto” signify?
2. Which bacterium is essential for vinegar production?
3. What is Acetone commonly used for?
4. Which term describes a tool for measuring acetic acid?
5. What is Acetophenone used in?

12. Conclusion: The Sour Significance of Aceto
The root Aceto embodies transformation, from the tangy essence of vinegar to the scientific precision of acetone. Its influence spans fields as diverse as microbiology, chemistry, and culinary arts. By understanding Aceto, we unlock a world where sourness drives innovation and discovery. Let the legacy of Aceto inspire you to explore the powerful intersections of nature, science, and language.













