Aero: Exploring the Boundless Reach of Air in Language and Innovation
Discover the linguistic charm of "Aero," a root derived from the Greek word "aēr," meaning air. From words like "aerobic" to "aerosol," this versatile root has inspired terms spanning fitness, technology, and even environmental science. Let’s dive into the fascinating world shaped by this root and its impact on modern language and industries.
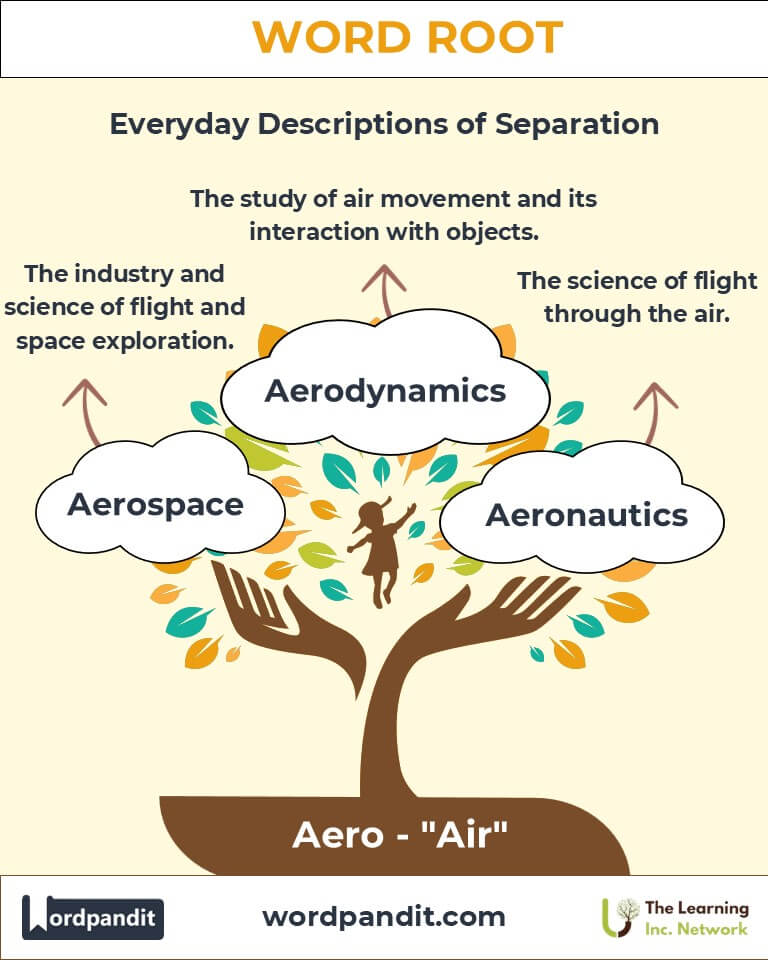
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Aero
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aero
- Common Aero-Related Terms
- Aero Through Time
- Aero in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Aero in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Aero Root
- The Aero Family Tree
- FAQs About the Aero Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Aero Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Aero
Introduction: The Essence of Aero
Imagine the feeling of wind against your face or watching an airplane cut through the sky. These experiences evoke the root "aero," meaning air, which derives from the Greek aēr. Pronounced air-oh, this root forms the foundation of countless words, connecting our understanding of air to concepts in science, health, and technology. Its influence stretches across disciplines, shaping how we explore and harness the invisible yet vital substance around us.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "aero" finds its origins in ancient Greek, where aēr referred to air or the atmosphere. As civilizations grew more curious about the skies, the term evolved to encompass not just the air itself but also the science and mechanics of utilizing it. With advancements during the Industrial Revolution and the development of aviation, "aero" became a cornerstone of modern terminology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Aero
Picture a majestic eagle soaring effortlessly through the open skies, embodying the freedom and omnipresence of air.
Mnemonic Device: "Aero lifts life like air lifts wings."
Common Aero-Related Terms
- Aerobic (air-oh-bik):
Involving oxygen or air for energy production.
Example: "Aerobic exercises, like running, improve cardiovascular health."
- Aerosol (air-oh-sawl):
A suspension of fine particles in the air.
Example: "Aerosols from factories can affect air quality and climate."
- Aerodynamics (air-oh-die-nam-iks):
The study of air in motion and its interaction with objects.
Example: "The car's aerodynamics reduce drag, increasing fuel efficiency."
- Aerospace (air-oh-space):
The industry and science of flight and space exploration.
Example: "Aerospace engineers design rockets for interstellar travel."
- Aeronautics (air-oh-naw-tiks):
The science of flight through the air.
Example: "The Wright brothers revolutionized aeronautics with their flying machine."
Aero Through Time
- Aerostat (18th Century): Early balloons and airships that used lighter-than-air gases for lift.
Evolution: Led to the development of modern aviation technology.
- Aerosol (20th Century): Initially used in scientific contexts, it now spans industries from personal care to climate science.
Aero in Specialized Fields
- Fitness and Health:
Aerobic Exercise: Builds stamina and strengthens the heart by utilizing oxygen.
Impact: A cornerstone of modern fitness regimens.
- Environmental Science:
Aerosols: Their study is crucial for understanding pollution and climate change.
Relevance: Influences policies on air quality.
- Engineering and Technology:
Aerodynamics: Designs vehicles and structures to minimize resistance.
Application: Critical in industries like automotive, aviation, and sports.
- Space Exploration:
Aerospace: Combines aeronautics and astronautics to explore Earth's atmosphere and beyond.
Significance: Pushes the boundaries of human innovation.
Illustrative Story: Aero in Action
On a windy afternoon, Maya observed her friend flying a kite. Inspired, she researched how aerodynamics made it possible for the kite to soar. Years later, Maya became an aerospace engineer, designing drones that delivered medical supplies to remote areas. Her journey—from playing with air to harnessing its power—highlighted the transformative role of "aero" in human lives.
Cultural Significance of the Aero Root
"Aero" has always been symbolic of freedom and innovation. From ancient myths of Icarus soaring through the skies to modern-day marvels like the Mars Rover, air has represented the human aspiration to rise above limitations. This root encapsulates humanity’s enduring fascination with the skies and the boundless potential they hold.

The Aero Family Tree
Explore related roots and terms:
- Atmo- (Greek: air):
Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding Earth.
Example: "The atmosphere protects us from harmful solar radiation."
- Anemo- (Greek: wind):
Anemometer: An instrument measuring wind speed.
Example: "Anemometers are vital for weather forecasting."
- Avi- (Latin: bird, flight):
Aviation: The art and science of flying aircraft.
Example: "Aviation has revolutionized global travel."
FAQs About the "Aero" Word Root
Q: What does "aero" mean?
A: "Aero" is a root derived from the Greek word "aēr," meaning "air." It signifies anything related to air or the atmosphere. For example, words like "aerobic" describe processes that require oxygen, a key component of air.
Q: What is the origin of the root "aero"?
A: The root originates from ancient Greek and has been used in various languages to describe air and its related phenomena. Its influence expanded with advancements in aviation and environmental sciences.
Q: Is "aero" used only in scientific contexts?
A: No, while "aero" is commonly found in technical fields like aerodynamics and aerospace, it is also used in everyday language. For instance, "aerosol" refers to a spray or mist of particles, and "aerobic" is a term frequently used in fitness.
Q: What is the difference between aerodynamics and aerospace?
A: Aerodynamics focuses on the movement of air and how it interacts with objects, often for improving vehicle design. Aerospace encompasses the broader field of flight within Earth's atmosphere and beyond, including space exploration.
Q: What are aerosols, and why are they important?
A: Aerosols are tiny particles or droplets suspended in the air. They play a critical role in climate science, affecting weather patterns and air quality. Additionally, they are widely used in products like spray cans and medicines.
Q: Why is "aero" significant in environmental science?
A: The study of aerosols and air quality is essential for understanding pollution and mitigating its effects. Terms like "aerobic respiration" also relate to processes that are crucial for sustaining life.
Q: What is aeronautics? How is it different from aerospace?
A: Aeronautics specifically refers to the science of flight within Earth's atmosphere, like airplanes and helicopters. Aerospace is broader, including aeronautics as well as space travel, like rockets and satellites.
Test Your Knowledge: Aero Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "aero" signify?
2. Which word describes oxygen-dependent exercise?
3. What industry combines aviation and space exploration?
4. What do aerosols significantly affect?
5. Which term relates to the study of air movement around objects?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Aero
The root "aero" serves as a linguistic bridge to the boundless wonders of air and its applications. From science to fitness, this root embodies innovation and connectivity, driving progress across fields. As we continue to explore and harness the power of air, "aero" remains a testament to humanity’s ingenuity and aspirations. Embrace this root to deepen your understanding of the unseen yet essential element that surrounds us.












