Afore: The Precursor of Time and Sequence in Language and Thought
Explore the profound meanings and timeless applications of the word root "afore," delving into its origins, evolution, and impact across fields. Understand how this root has shaped our perception of time, order, and precedence in daily communication and specialized contexts.
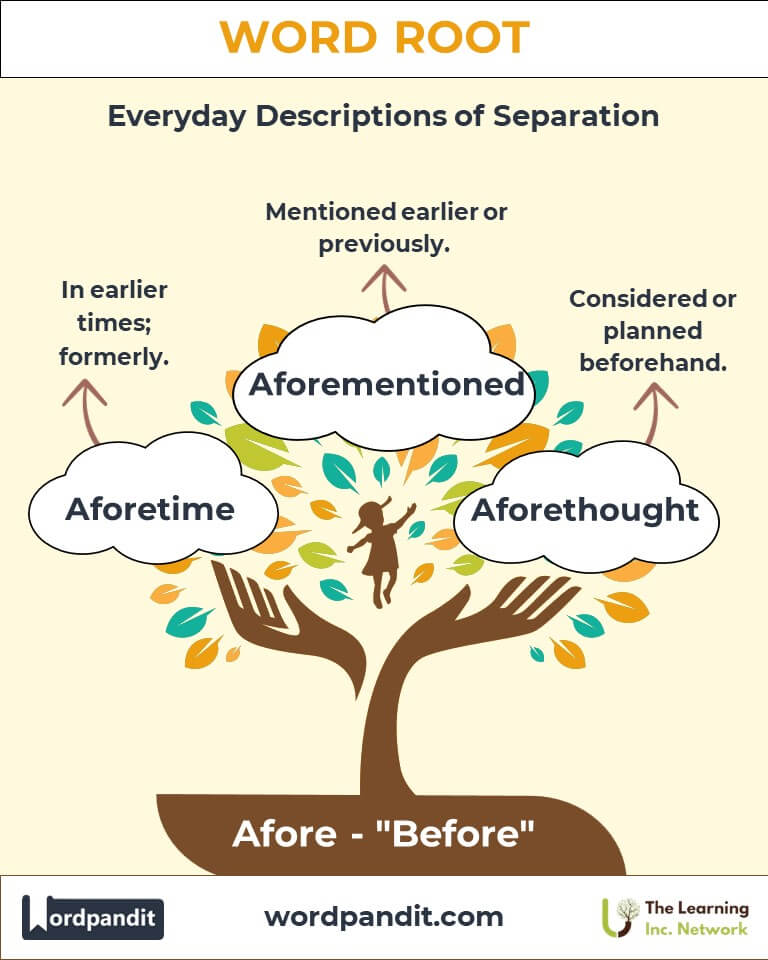
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Setting the Stage with Afore
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Afore
- Common Afore-Related Terms
- Afore Through Time
- Afore in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Afore in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Afore Root
- The Afore Family Tree
- FAQs about the Afore Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Afore Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Timeless Legacy of Afore
1. Introduction: Setting the Stage with Afore
Imagine a world without the concept of "before" or "precedence." How would we navigate relationships, historical events, or simple sequences? The word root "afore," derived from Middle English and Old English, meaning "before" or "prior," is indispensable in capturing these ideas. Pronounced "uh-for," it provides a foundation for words and phrases that denote priority in time, order, and importance. This root has resonated through literature, law, and everyday dialogue, framing our understanding of temporal and logical sequences.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "afore" finds its origin in Old English onforan, meaning "in front of" or "before." Its usage flourished in Middle English as a versatile prefix and standalone term, shaping expressions of precedence and priority. In historical texts, "afore" often denoted reverence, seniority, or anticipation. Shakespearean plays and legal documents have preserved its legacy, demonstrating its significance in framing societal and temporal hierarchies.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Afore
To remember "afore," visualize a row of dominoes. The one that falls first sets the sequence for all others. Think of "afore" as the first domino, always leading the way.
Mnemonic: "Afore" is always first, setting the stage for what comes after.
4. Common Afore-Related Terms
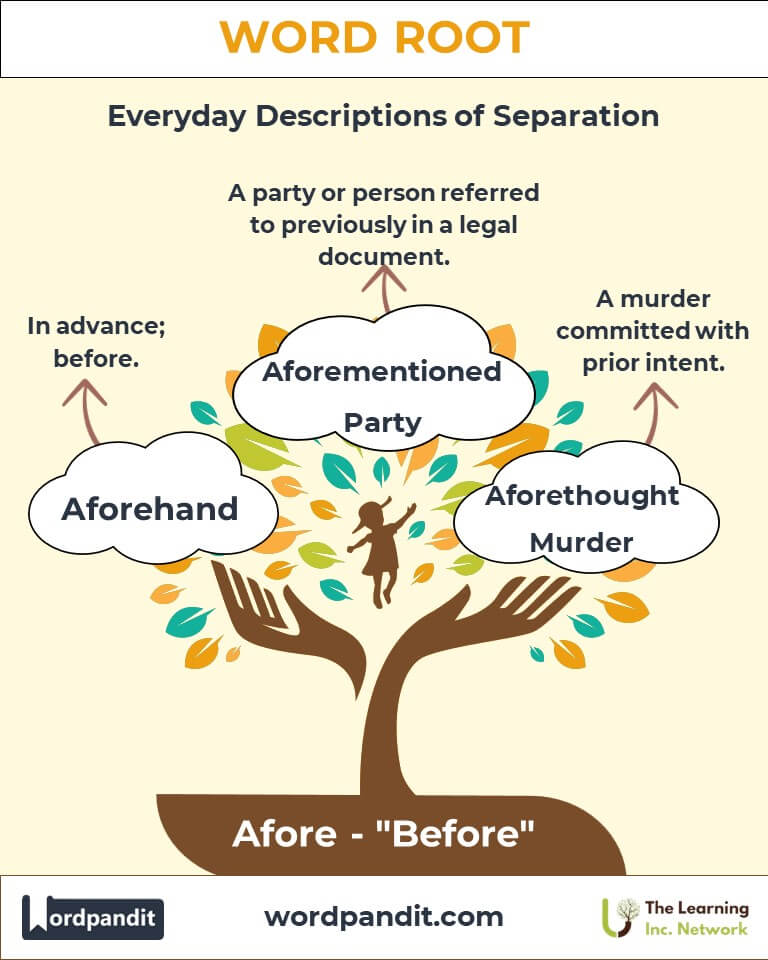
- Aforementioned (uh-for-men-shund): Previously mentioned in text or speech.
- Example: "The aforementioned points require further discussion."
- Aforethought (uh-for-thawt): Pre-planned or deliberate.
- Example: "His actions were with malice aforethought."
- Aforetime (uh-for-time): In earlier times; formerly.
- Example: "In aforetime, such traditions were held sacred."
- Aforehand (uh-for-hand): In advance; beforehand.
- Example: "Prepare your documents aforehand to avoid delays."
- Aforesee (uh-for-see): To predict or anticipate.
- Example: "He could aforesee the challenges ahead."
5. Afore Through Time
- From Temporal to Legal:
- Historical texts transformed "aforethought" from a neutral term for planning into a legal concept associated with intent and deliberation, particularly in criminal law.
- Literary Evolution:
- Once a staple in poetic and dramatic language, "afore" gradually transitioned into a more formal and occasionally archaic tone, yet remains a mark of eloquence.
6. Afore in Specialized Fields
- Law:
- Malice Aforethought: Signifies deliberate intent in criminal acts, highlighting premeditation.
- Application: Essential in distinguishing degrees of liability.
- Literature:
- Shakespeare's works used "afore" to denote past events or precedence, enhancing narrative depth.
- Example: “What’s past is prologue,” a sentiment tied to the essence of "afore."
- History:
- Historical chronology frequently relies on "aforetime" to frame events prior to the documented period.
- Business:
- Planning "aforehand" ensures preparedness and strategic foresight.
- Application: Effective project management and risk mitigation.
7. Illustrative Story: Afore in Action
Dr. Emilia Carter, a historian, was poring over ancient manuscripts describing the Battle of Hastings. As she deciphered the texts, she noted repeated references to "aforetime" events—prior battles and strategies that shaped the conflict. Her understanding of these "afore" connections enabled her to piece together a missing chapter of history, proving that strategy planned "aforehand" was pivotal to the Normans' victory. Her findings reshaped the narrative, teaching modern leaders the value of historical foresight.
8. Cultural Significance of the Afore Root
"Afore" embodies respect for history and precedence in many cultures. Traditional rituals often honor "those who came afore," reinforcing lineage and heritage. The term also echoes in legal and literary traditions, reminding us of the importance of forethought and preparation.

9. The Afore Family Tree
- Fore: Root meaning "before" or "in front of."
- Foremost: First in rank or importance.
- Foretell: Predict or prophesy.
- Foreword: An introductory section in a book.
- Pre (Latin prae): A prefix denoting "before."
- Predict: Say something will happen in the future.
- Prepare: Make ready beforehand.
- Precede: Come before in time or order.
- Ante (Latin): Denoting "before" or "prior."
- Antecedent: A preceding event or condition.
- Anterior: Situated before or at the front.
- Antedate: Precede in time.
FAQs About the Afore Word Root
Q: What does "afore" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Afore" means "before" or "prior." It is often used in formal or literary contexts to describe something that precedes another in time, order, or importance. For example, in legal language, "aforementioned" refers to something previously mentioned in a document.
Q: Why is "afore" considered archaic in modern language?
A: The word "afore" has been largely replaced by simpler and more modern terms like "before" or "previously." However, it retains its presence in formal, historical, and legal contexts, where tradition and specificity are valued.
Q: What is the meaning of "malice aforethought"?
A: "Malice aforethought" is a legal term indicating deliberate intent to commit a harmful act, particularly in cases of serious crimes like murder. It is critical in determining the degree of premeditation and intent in criminal law.
Q: How does "aforetime" differ from "aforementioned"?
A: "Aforetime" refers to a point in the distant past, emphasizing temporal precedence. In contrast, "aforementioned" simply points to something already mentioned in the text or conversation.
Q: What is the origin of the word "afore"?
A: The word "afore" originates from Old English onforan, meaning "in front of" or "before." Its usage expanded in Middle English to denote precedence and priority in various contexts.
Q: Is "afore" interchangeable with "before"?
A: While they share the same meaning, "afore" is more archaic and formal. "Before" is universally accepted in modern English for both casual and formal contexts.
Test Your Knowledge: Afore Word Root Quiz
1. What is the primary meaning of "afore"?
2. Which term means "planned beforehand"?
3. In what context is "malice aforethought" used?
4. What does "aforetime" signify?
5. Which root is synonymous with "afore"?

12. Conclusion: The Timeless Legacy of Afore
The "afore" root offers a linguistic bridge to our understanding of time, order, and precedence. Its resonance in legal, literary, and historical contexts demonstrates its enduring relevance. As we continue to value foresight and preparation, the essence of "afore" reminds us to honor the past while shaping the future.













