Archeo: Unlocking the Roots of History and Antiquity
Delve into the fascinating world of "Archeo," a root derived from the Greek word "arkhaios," meaning "ancient" or "original." From archaeology to archetype, this root unveils the secrets of the past and the foundational principles of humanity’s journey through time.
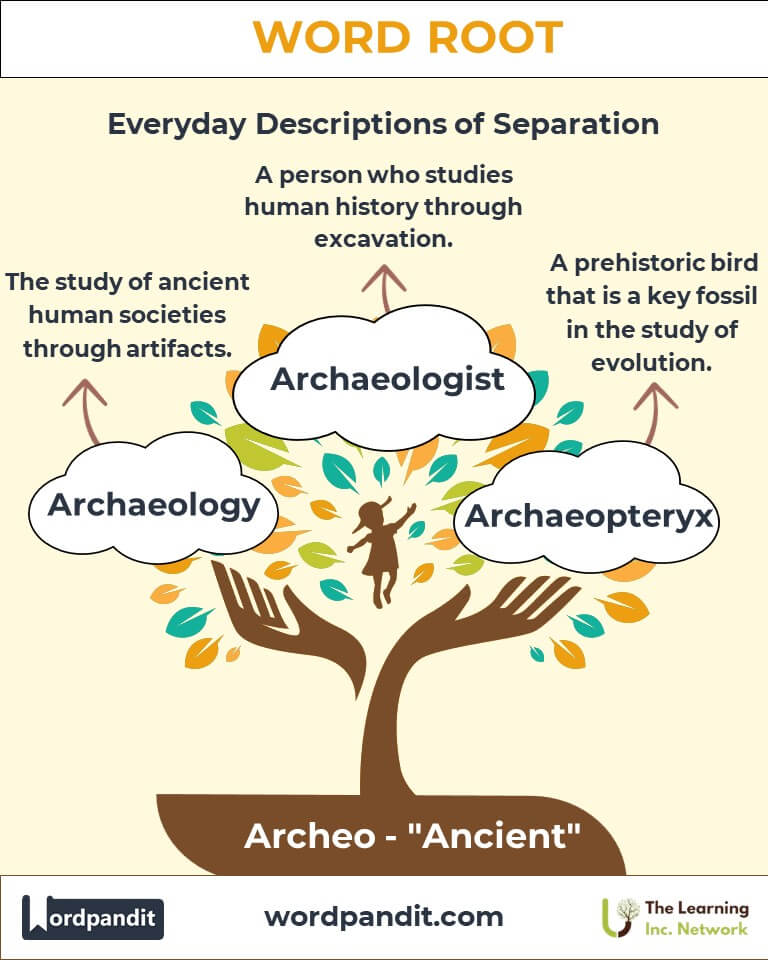
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of Archeo
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Archeo
- Common Archeo-Related Terms
- Archeo Through Time
- Archeo in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Archeo in Action
- Cultural Significance of Archeo
- The Archeo Family Tree
- FAQs About the Archeo Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Archeo Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Timeless Legacy of Archeo
1. Introduction: The Essence of Archeo
What connects ancient ruins, philosophical ideas, and the study of humanity’s origins? The answer lies in the root "Archeo," pronounced ar-kee-oh, which signifies "ancient" or "original." This root forms the foundation of words that explore beginnings, uncover historical truths, and define archetypes in art and culture. Archeo invites us to journey back in time to unravel the mysteries of our past and their influence on the present.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Archeo" stems from the Greek arkhaios (ancient), which itself is derived from arkhē (beginning, origin). It entered the English language through Latin and French during the Renaissance, a period of renewed interest in classical antiquity. Over time, Archeo became associated with various disciplines focused on the study of ancient artifacts, texts, and ideas, enriching fields like archaeology, anthropology, and philosophy.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Archeo
Imagine an ancient treasure chest labeled "ARCHEO," filled with artifacts like scrolls, pottery, and ancient tools. Each item represents a fragment of history waiting to be rediscovered.
Mnemonic Device: “Archeo opens the chest of the past, revealing ancient origins and timeless stories.”
4. Common Archeo-Related Terms
- Archaeology (ar-kee-ol-uh-jee): The scientific study of ancient human history and prehistory through artifacts and structures.
Example: "The archaeology team unearthed a 5,000-year-old settlement in Mesopotamia." - Archetype (ar-kee-type): A perfect or typical example of something; often a universal symbol in art or literature.
Example: "The hero’s journey is a common archetype in storytelling." - Archeogenetics (ar-kee-oh-jeh-net-iks): The study of ancient DNA to understand human evolution and migration.
Example: "Archeogenetics revealed connections between prehistoric populations across continents." - Archeography (ar-kee-og-ruh-fee): The study and description of ancient manuscripts or inscriptions.
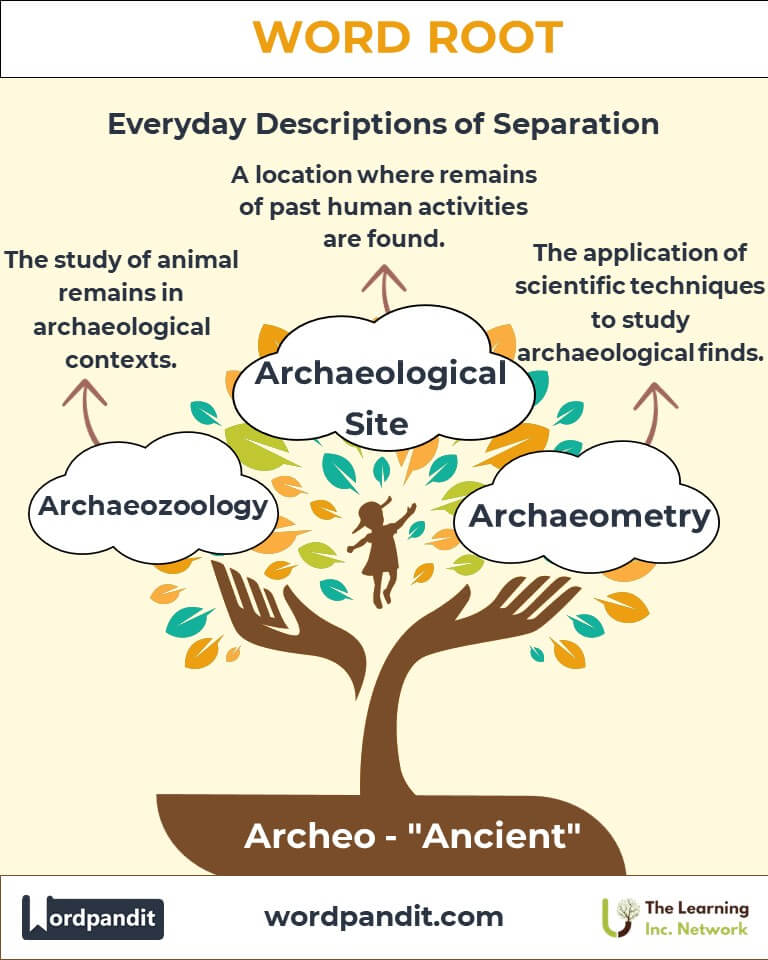
Example: "Experts in archeography decoded the inscriptions on the ancient tablet." - Archaeometry (ar-kee-om-uh-tree): The application of scientific techniques to date and analyze archaeological finds.
Example: "Using archaeometry, scientists dated the pottery shard to 2000 BCE."
5. Archeo Through Time
- Archaeon (Ancient): In classical Greek, it referred to anything ancient or original.
- Archaeology (19th Century): Formalized as a discipline during the Enlightenment when Europe’s fascination with antiquity spurred systematic exploration.
- Archeogenetics (Modern Era): A 21st-century field revolutionizing our understanding of human ancestry through genetic analysis.
6. Archeo in Specialized Fields
- Anthropology: Archaeology helps uncover ancient societies and their cultural practices.
Example: "Excavations of burial sites reveal insights into rituals and belief systems." - Genetics: Archeogenetics explores human migration and interbreeding with extinct species like Neanderthals.
Example: "Modern humans carry traces of ancient DNA from prehistoric interbreeding." - Art and Literature: Archetypes form the backbone of storytelling and creative expression.
Example: "The 'wise old mentor' archetype appears across cultures and ages."
7. Illustrative Story: Archeo in Action
Dr. Elena Martinez, an archaeologist, embarked on an expedition to uncover the remnants of an ancient civilization in the Amazon rainforest. Her team unearthed intricately carved stone tablets bearing symbols never seen before. Collaborating with experts in archeography and archeogenetics, they decoded the inscriptions, which revealed a sophisticated society that thrived 3,000 years ago. Their findings reshaped our understanding of early human ingenuity.
8. Cultural Significance of Archeo
Archeo-rooted concepts resonate in culture, from the preservation of ancient artifacts in museums to the enduring appeal of mythological archetypes. By connecting us to our origins, Archeo fosters a sense of continuity and shared heritage, emphasizing the importance of understanding where we come from to navigate where we are headed.

9. The Archeo Family Tree
- Paleo- (Ancient): Related to prehistoric times or fossils.
Example: Paleontology, Paleolithic. - Proto- (First): Denotes the earliest or primary form.
Example: Prototype, Proto-Indo-European. - Neo- (New): Often paired with Archeo to describe revivals of ancient ideas.
Example: Neoclassicism.
FAQs About the "Archeo" Word Root
Q: What does "Archeo" mean?
A: "Archeo" means "ancient" or "original." Derived from the Greek word arkhaios, it refers to anything related to the distant past or foundational origins, making it an essential root in words dealing with history, ancient cultures, and foundational concepts.
Q: What is Archeology?
A: Archeology is the scientific study of human history and prehistory through the excavation and analysis of artifacts, structures, and other physical remains. This field helps us piece together the lives, cultures, and environments of ancient civilizations, bridging the gap between past and present.
Q: What is Archeogenetics?
A: Archeogenetics is a modern field that examines ancient DNA to understand human evolution, migration, and interactions with extinct species. It reveals how ancient populations were connected, their genetic traits, and how they adapted to environmental changes.
Q: How is Archeo different from Paleo?
A: Both roots relate to the past but serve different purposes. "Archeo" focuses on ancient civilizations and foundational aspects of history, while "Paleo" emphasizes prehistoric times, fossils, and early life forms before recorded history, such as dinosaurs and early hominids.
Q: What role does Archeometry play in archeology?
A: Archeometry is the application of scientific methods, such as radiocarbon dating, to determine the age, composition, and origins of archeological artifacts. It combines technology and archeology to provide precise data, making it crucial for validating historical timelines.
Test Your Knowledge: Archeo Mastery Quiz
1. What does Archeo mean?
2. Which field studies ancient DNA?
3. What is an Archetype?
4. What does Archeometry involve?
5. What does an archeologist study?
12. Conclusion: The Timeless Legacy of Archeo
The root "Archeo" serves as a gateway to understanding humanity’s origins and evolution. Its applications span diverse fields, from uncovering ancient civilizations to decoding genetic mysteries. As we continue to explore the past, Archeo reminds us of the enduring significance of history in shaping the future. Embrace the Archeo legacy and unlock the stories that connect us all.














