Bio: The Root of Life in Language and Science
Discover the profound impact of the root "Bio," derived from the Greek word "bios," meaning "life." From the fascinating field of biology to compelling biographies, "Bio" has become a cornerstone of terms that connect us to the essence of life and its myriad stories.
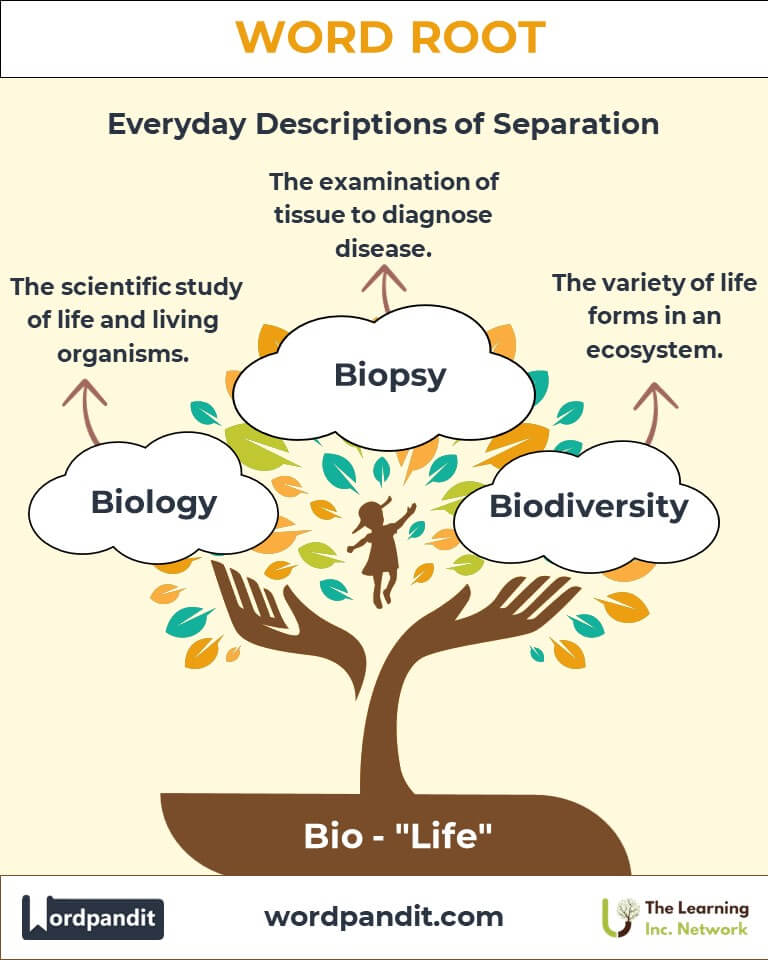
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Bio"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Bio"
- Common "Bio"-Related Terms
- "Bio" Through Time
- "Bio" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Bio" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Bio" Root
- The "Bio" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Bio" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Bio" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Bio"
Introduction: The Essence of "Bio"
The root "Bio," pronounced "bye-oh," means "life" and serves as the foundation for numerous terms across disciplines. Whether we delve into biology, the study of life, or read a biography, the life story of an individual, "Bio" connects us to the vitality and narratives that define existence.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Bio" originates from the Greek word bios, which means "life" or "way of living." Early Greek philosophers used it to differentiate between physical existence and the essence of being. Over time, "Bio" found its way into Latin and later English, forming the basis for scientific and literary terms that explore life's diversity and depth.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Bio"
Picture a vibrant tree with roots labeled "Bio," symbolizing life and growth. The branches represent biology, biography, and biodiversity, illustrating how this root branches into various fields of knowledge.
Mnemonic Device: “Bio brings life to words, from biology to biographies.”
Common "Bio"-Related Terms
- Biology (bye-AW-luh-jee): The scientific study of life and living organisms.
- Example: "Biology helps us understand ecosystems and how life evolves."
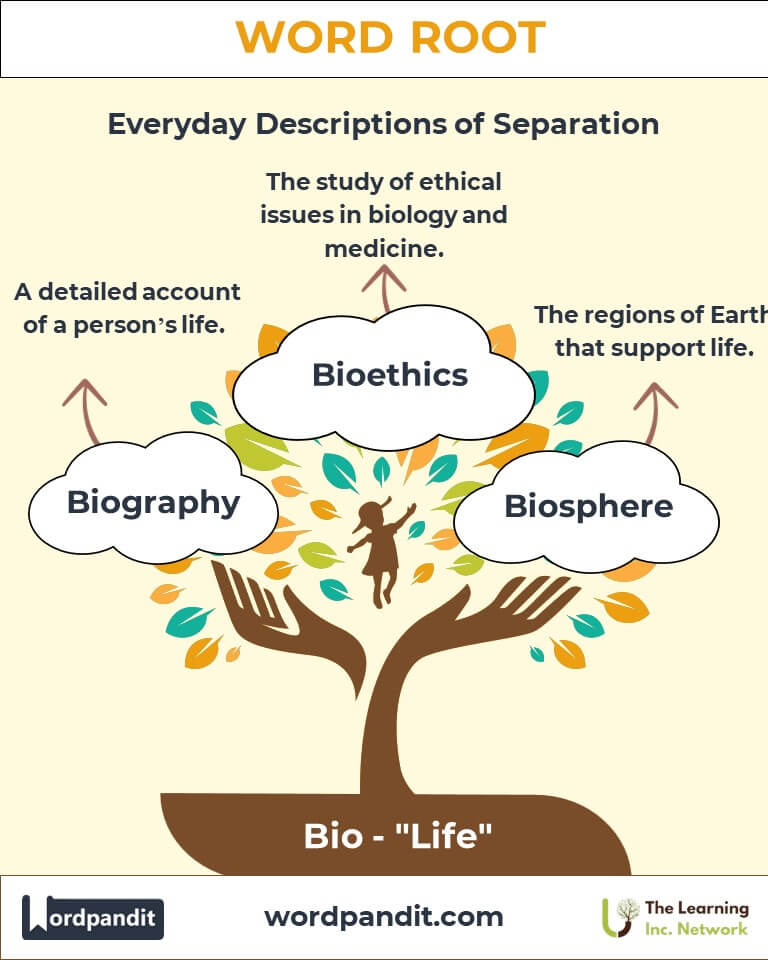
- Biography (bye-AW-gruh-fee): A detailed account of a person's life.
- Example: "The biography of Marie Curie inspired countless scientists."
- Biosphere (BYE-oh-sfeer): The regions of Earth that support life.
- Example: "The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on our planet."
- Biometrics (BYE-oh-meh-triks): The measurement and analysis of unique physical or behavioral traits.
- Example: "Biometric security systems use fingerprints or facial recognition."
- Bioethics (BYE-oh-eh-thiks): The study of ethical issues in biology and medicine.
- Example: "Bioethics addresses dilemmas like organ transplantation."
"Bio" Through Time
- Biology (18th Century): Initially coined as a broad term for the study of living beings, it has since evolved into a sophisticated field covering genetics, evolution, and ecology.
- Biography (16th Century): Originally referring to written life stories, biographies now extend to films and multimedia narratives.
"Bio" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
- Biopsy: The examination of tissue to diagnose disease.
- Importance: A critical tool in detecting cancer and other conditions.
- Technology:
- Biometrics: Enhances security by using unique biological traits.
- Application: Found in smartphones, airports, and banking.
- Ecology:
- Biodiversity: Describes the variety of life forms in ecosystems.
- Relevance: A measure of environmental health.
Illustrative Story: "Bio" in Action
Dr. Clara devoted her career to studying biodiversity in rainforests. She marveled at the complex web of life, from microscopic fungi to towering trees. One day, her research uncovered a plant with properties that could fight a deadly disease. This discovery was not just a triumph of biology but a story worthy of a biography, showcasing how the root "Bio" intertwines knowledge and life.
Cultural Significance of the "Bio" Root
"Bio" has shaped human understanding through fields like philosophy, literature, and science. Biographies inspire us by chronicling lives of achievement, while biology bridges the gap between humanity and the natural world. This root's significance lies in its ability to connect diverse facets of life.

The "Bio" Family Tree
- Vita (Latin): Life
- Vitality: Energy and liveliness.
- Vitamin: A substance necessary for life.
- Anim (Latin): Soul, spirit
- Animal: A living organism.
- Animate: To bring to life.
- Zoo (Greek): Animal, living being
- Zoology: The study of animals.
- Zooid: A single animal in a colony.
FAQs About the "Bio" Word Root
Q: What does "Bio" mean?
A: "Bio" is a root word derived from the Greek bios, meaning "life." It forms the basis for numerous terms across science, literature, and technology, connecting to anything related to living organisms or life processes.
Q: What is the origin of the word "Biology"?
A: The term "Biology" comes from the Greek words bios (life) and logos (study). It was first used in the 19th century to describe the scientific study of living organisms, encompassing everything from cellular processes to ecosystems.
Q: How does "Bio" relate to modern technology?
A: In modern technology, "Bio" appears in terms like biometrics, which use biological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition for identification and security. This reflects the integration of life sciences into digital advancements.
Q: What is the biosphere?
A: The biosphere refers to the global sum of all ecosystems—the regions of Earth that support life. It includes everything from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountain peaks where living organisms thrive.
Q: How is "Bio" used in literature?
A: In literature, "Bio" is present in terms like biography and autobiography. A biography is a detailed account of a person's life written by someone else, while an autobiography is a life story written by the subject themselves.
Q: What does "Biometrics" measure?
A: Biometrics involves measuring unique physical or behavioral traits of living organisms, especially humans, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or voice recognition. It’s widely used in security, healthcare, and digital interfaces.
Q: What is bioethics?
A: Bioethics is a field that examines ethical issues arising from advancements in biology and medicine. For example, debates on cloning, organ transplantation, and genetic editing fall under the scope of bioethics.
Q: What is biodiversity, and why is it important?
A: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within a particular habitat or ecosystem. It’s essential because it ensures ecological balance, provides resources for survival, and supports resilience to environmental changes.
Q: What is the significance of a biopsy?
A: A biopsy is a medical procedure in which tissue is extracted from a living organism for diagnostic purposes, often to detect diseases like cancer. It exemplifies how the root "Bio" relates to studying life at a microscopic level.
Q: How is "Bio" used in sustainability efforts?
A: "Bio" plays a central role in sustainability, seen in terms like biofuel and biodegradable. Biofuels are derived from organic matter, while biodegradable materials break down naturally, reducing environmental impact.
Test Your Knowledge: "Bio" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "Bio" signify?
2. What is the study of living organisms called?
3. What does "Biopsy" involve?
4. What does the term "Biodiversity" refer to?
5. Which word describes ethical issues in medicine?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Bio"
The root "Bio" serves as a reminder of life's interconnectedness and complexity. From scientific breakthroughs to personal stories, it enriches our understanding of existence. As we explore new frontiers in biology, technology, and storytelling, the legacy of "Bio" continues to inspire curiosity and innovation.
\













