Embryo: The Root of Growth and Beginnings in Science and Nature
Discover the transformative power of the root "embryo," derived from the Greek "embryon," meaning "growing within." This root has nurtured words like "embryonic" and "embryology," symbolizing development, potential, and life at its earliest stages. Explore how this root shapes scientific language and our understanding of life's origins.
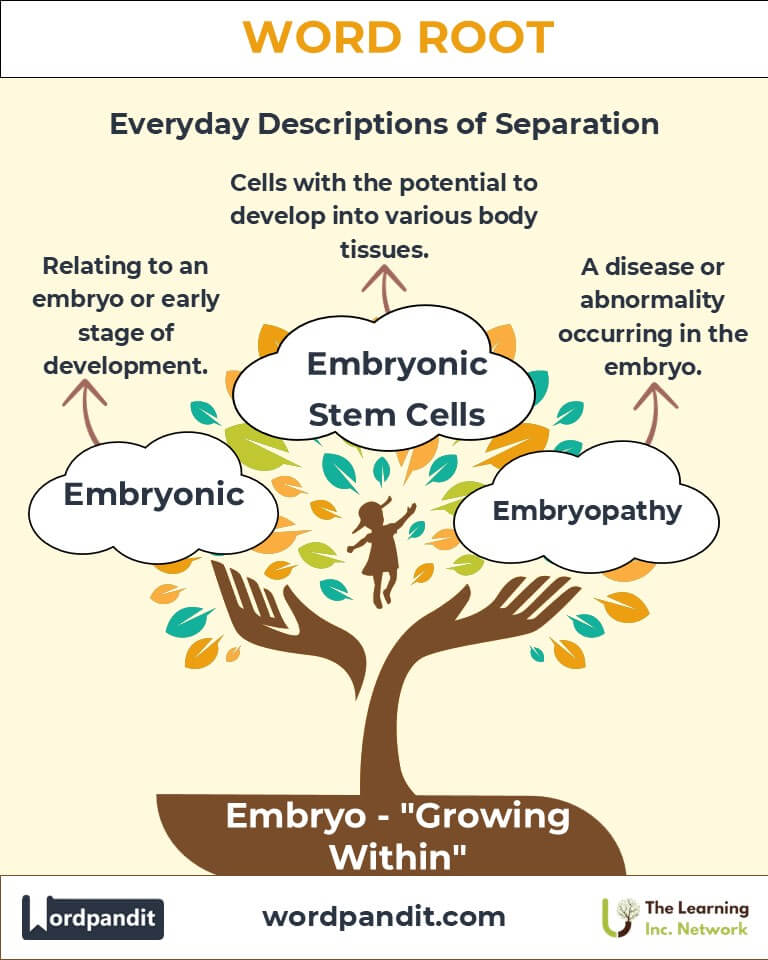
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Promise of "Embryo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Embryo"
- Common "Embryo"-Related Terms
- "Embryo" Through Time
- "Embryo" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Embryo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Embryo" Root
- The "Embryo" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Embryo" Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Embryo" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Embryo"
Introduction: The Promise of "Embryo"
What sparks the beginning of life? The root "embryo," pronounced em-bree-oh, captures the essence of growth and potential. Derived from the Greek word embryon (meaning "growing within"), this root forms the basis of words like "embryology" and "embryonic," both pivotal in describing life's early stages. Its significance spans biology, medicine, and beyond, representing the promise and intricacies of development.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The word "embryo" traces its roots to the Greek en (in) and bryein (to swell), symbolizing something growing or developing within. Early Greek philosophers and physicians used the term to describe unborn organisms, emphasizing the mystery and potential of life's beginnings. Over centuries, it became central to the study of reproduction and development, influencing languages and scientific discourse worldwide.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Embryo"
To remember "embryo," visualize a sprouting seed hidden within the soil, symbolizing the start of growth and life.
Mnemonic Device: "Embryo begins within, like a seed that swells to grow into life."
Common "Embryo"-Related Terms
- Embryonic (em-bree-on-ik):
Meaning: Relating to an embryo or early stage of development.
Example: "The idea is still embryonic, but it has great potential."
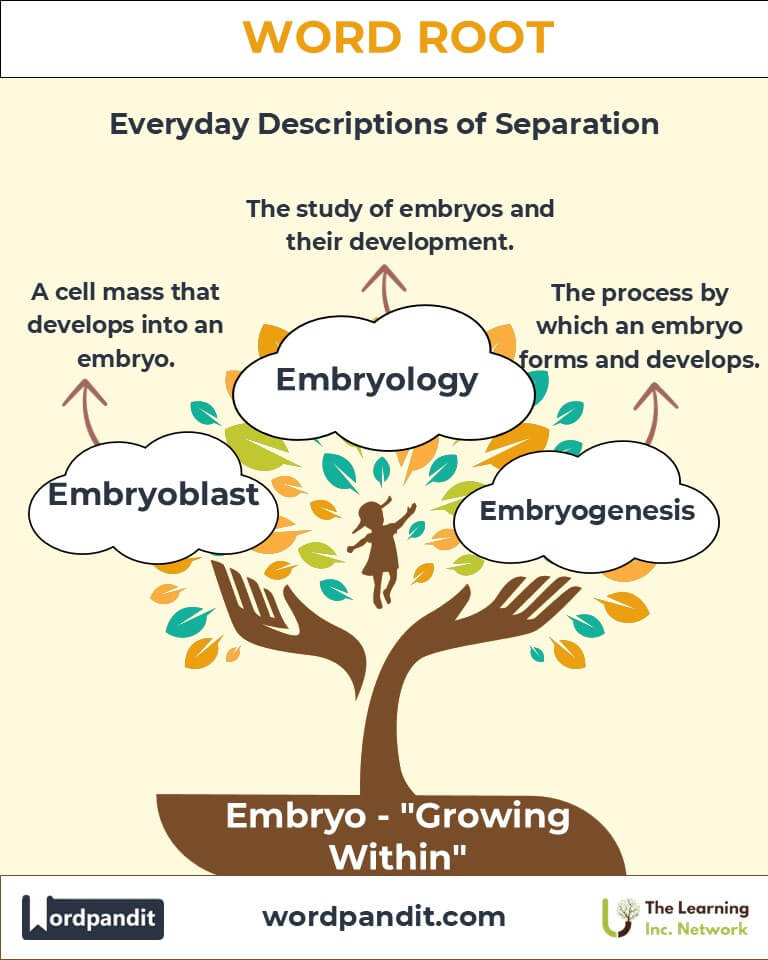
- Embryology (em-bree-ol-oh-jee):
Meaning: The branch of biology that studies the formation and development of embryos.
Example: "Embryology reveals the complexities of life's origins."
- Embryogenesis (em-bree-oh-jen-uh-sis):
Meaning: The process by which an embryo forms and develops.
Example: "Embryogenesis is a critical focus in developmental biology."
- Embryoblast (em-bree-oh-blast):
Meaning: The mass of cells within a blastocyst that will develop into an embryo.
Example: "The embryoblast differentiates into various tissues and organs."
- Embryopathy (em-bree-oh-path-ee):
Meaning: Any disease or abnormality occurring in the embryo.
Example: "Research into embryopathies helps prevent congenital conditions."
"Embryo" Through Time
Historical Context:
- In ancient Greece, "embryo" symbolized the early mysteries of life. Aristotle’s writings reflected an early attempt to understand embryonic development.
- During the Renaissance, advancements in microscopy transformed embryology, revealing intricate processes of growth.
- Modern genetic research now integrates "embryo" into the exploration of DNA and cellular mechanisms.
Modern Usage: Today, the term is frequently used metaphorically to describe ideas or projects in their formative stages, as in "an embryonic industry."
"Embryo" in Specialized Fields
- Medicine:
Embryology: Critical for understanding congenital conditions and reproductive health.
Embryopathies: Conditions treated or prevented through advanced medical interventions.
- Biotechnology:
Embryonic stem cells are pivotal in regenerative medicine, offering potential cures for various diseases.
- Agriculture:
Understanding plant embryos aids in crop improvement and genetic engineering.
Illustrative Story: "Embryo" in Action
Dr. Li was a renowned embryologist passionate about uncovering the secrets of human development. When a rare embryopathy threatened a newborn, her expertise in embryonic research enabled an early diagnosis and life-saving intervention. Inspired by this success, she developed new tools for studying embryogenesis, helping countless families worldwide. Her story exemplifies how the "embryo" root fosters hope and innovation.
Cultural Significance of the "Embryo" Root
The concept of "embryo" resonates deeply in cultural and philosophical traditions. From ancient myths about creation to modern ethical debates about stem cell research, the root encapsulates humanity's fascination with life's beginnings and potential.

The "Embryo" Family Tree
Explore related roots and their meanings:
- Gen- (birth, creation): Genesis (origin or beginning).
- Blast- (bud, sprout): Blastocyst (a structure formed in the early development of mammals).
- Morph- (form, structure): Morphogenesis (the development of structure in an organism).
FAQs About the "Embryo" Root
Q: What does the word "embryo" mean?
A: The word "embryo" originates from the Greek "embryon," meaning "growing within." It refers to the earliest stage of development for a living organism, whether human, animal, or plant, symbolizing growth, potential, and beginnings.
Q: What is embryology, and why is it important?
A: Embryology is the branch of biology that studies embryos and their development from fertilization to the fetal stage. It is crucial for understanding congenital conditions, improving fertility treatments, and advancing knowledge of developmental biology.
Q: What does "embryonic" mean when describing a project or idea?
A: When used metaphorically, "embryonic" describes something in its earliest, undeveloped stages. For example, an "embryonic project" is an idea that is still forming and has great potential for growth and refinement.
Q: What are embryonic stem cells, and why are they significant?
A: Embryonic stem cells are cells derived from embryos that can develop into nearly any type of cell in the body. They are significant in medical research because they offer the potential to treat diseases such as Parkinson’s, diabetes, and spinal cord injuries through regenerative therapies.
Q: How does the "embryo" root appear in plant sciences?
A: In plants, the "embryo" refers to the part of a seed that develops into a new plant. Understanding plant embryos helps scientists improve crop yields, develop resilient species, and enhance food security.
Q: What is embryogenesis?
A: Embryogenesis is the process by which an embryo forms and develops. This involves cell division, differentiation, and the establishment of body structures. It is a critical phase studied extensively in developmental biology and medicine.
Q: What is the relationship between embryopathies and medical advancements?
A: Embryopathies are diseases or abnormalities occurring in the embryo during development. Medical advancements, such as prenatal diagnostics and gene editing, are helping prevent or treat these conditions, ensuring healthier outcomes.
Test Your Knowledge: "Embryo" Mastery Quiz
1. What does the root "embryo" signify?
2. What does embryology study?
3. What is an embryonic idea?
4. What is an embryoblast?
5. What does embryogenesis involve?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Embryo"
The root "embryo" captures life's earliest promise, from biological studies to metaphorical applications. Its journey from ancient Greece to modern laboratories exemplifies humanity's enduring curiosity about growth and potential. As science and technology advance, the "embryo" root will remain a cornerstone of innovation, symbolizing the beginning of possibilities.














