🌍 Environmental Science: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Environmental Science is a multidisciplinary subject that addresses some of the most critical challenges facing humanity today. For GMAT and CAT Reading Comprehension passages, it often serves as a backdrop to explore arguments, analyze solutions, and understand the interplay of science, policy, and ethics. By mastering key concepts in this field, you can enhance your ability to identify arguments, evaluate evidence, and draw logical conclusions—essential skills for tackling complex RC questions.
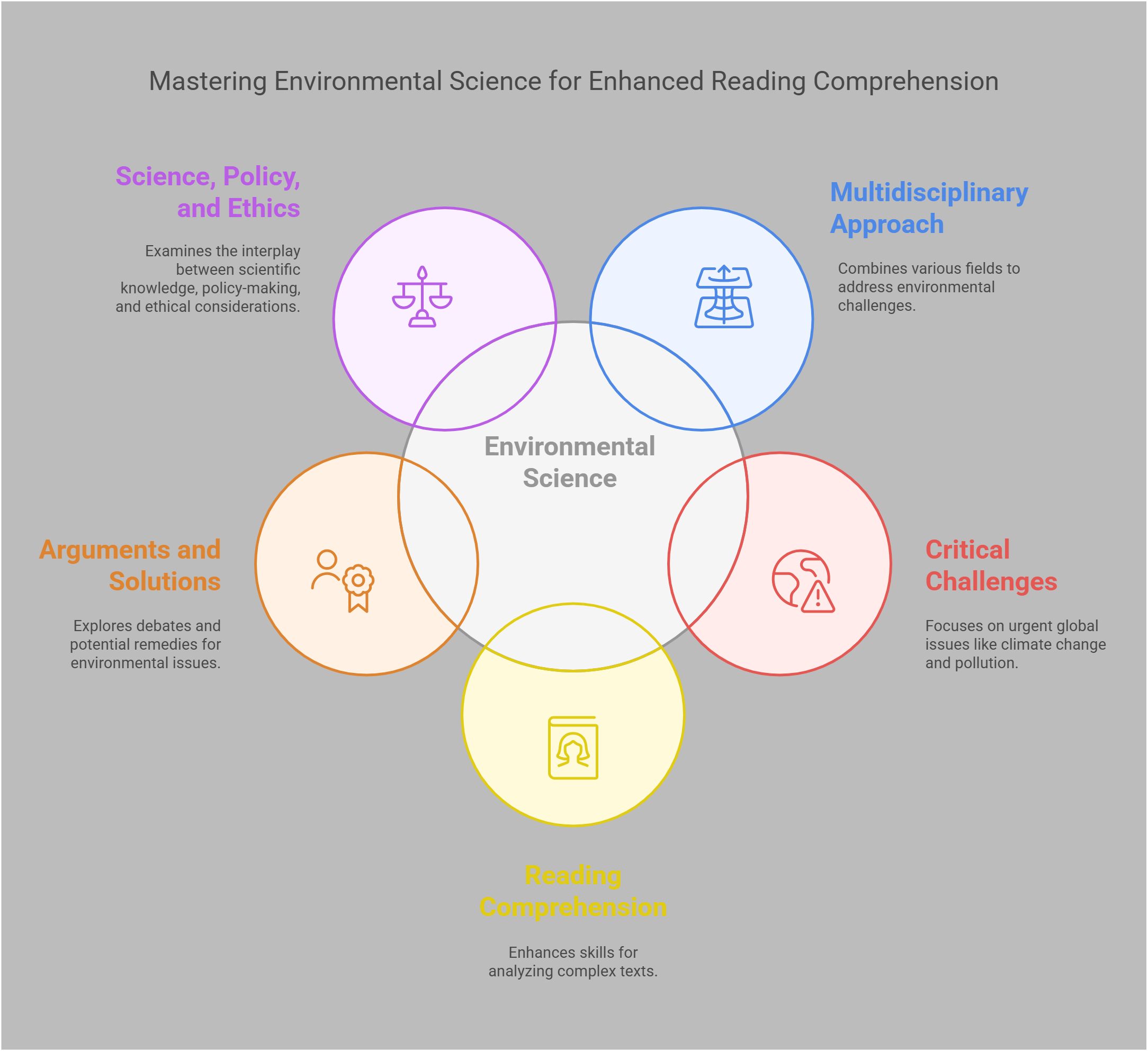
📋 Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these key Environmental Science-related concepts:
- Conservation Biology
- Environmental Policy
- Climate Science
- Renewable Resources
- Pollution Control
- Ecology
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Sustainable Development
- Biodiversity
- Environmental Management
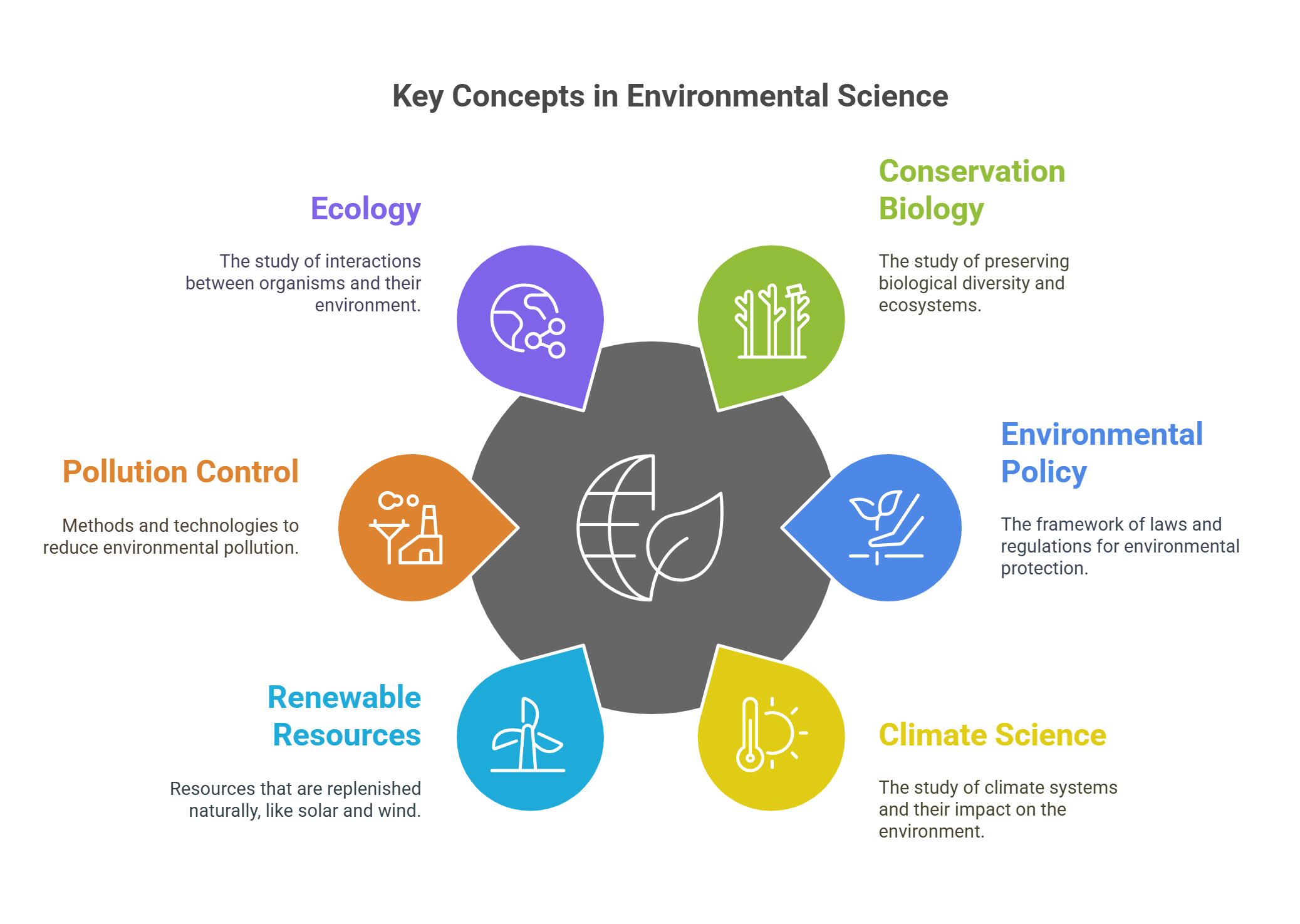
🔍 Detailed Explanations
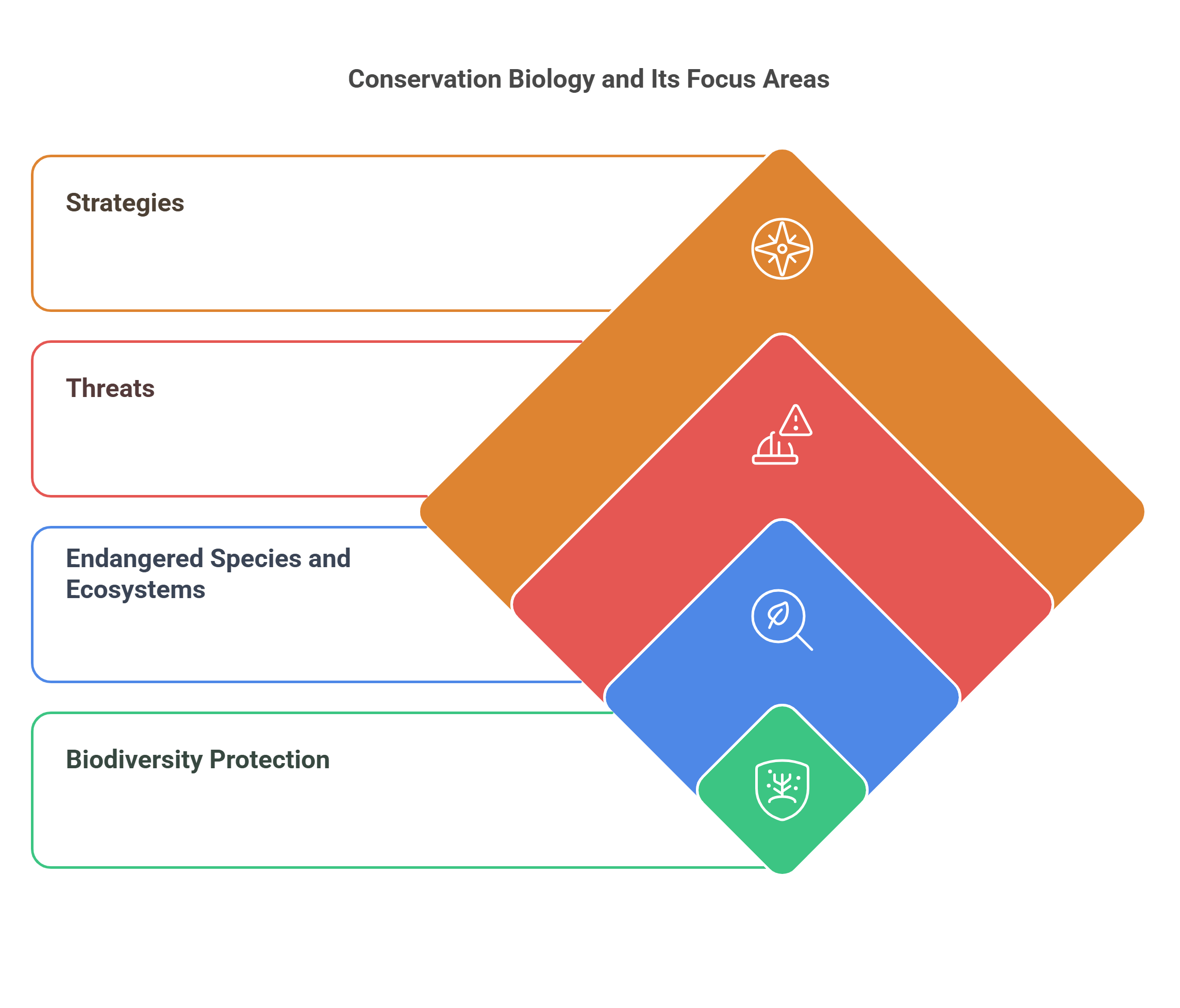
1. Conservation Biology
Conservation Biology focuses on protecting Earth’s biodiversity, including endangered species, ecosystems, and genetic diversity. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining natural habitats and ecological balance to ensure the survival of life on Earth.
- Studies endangered species and ecosystems.
- Addresses threats like deforestation, habitat loss, and poaching.
- Advocates for wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
- Balances ecological preservation with human development.
- Involves cross-disciplinary research combining biology, sociology, and ethics.
Explained Simply: Imagine your favorite zoo animals have a home in the wild. Conservation Biology is like a superhero team that makes sure these animals’ homes are safe and that they have enough food and space to live happily without worrying about humans cutting down their forests.
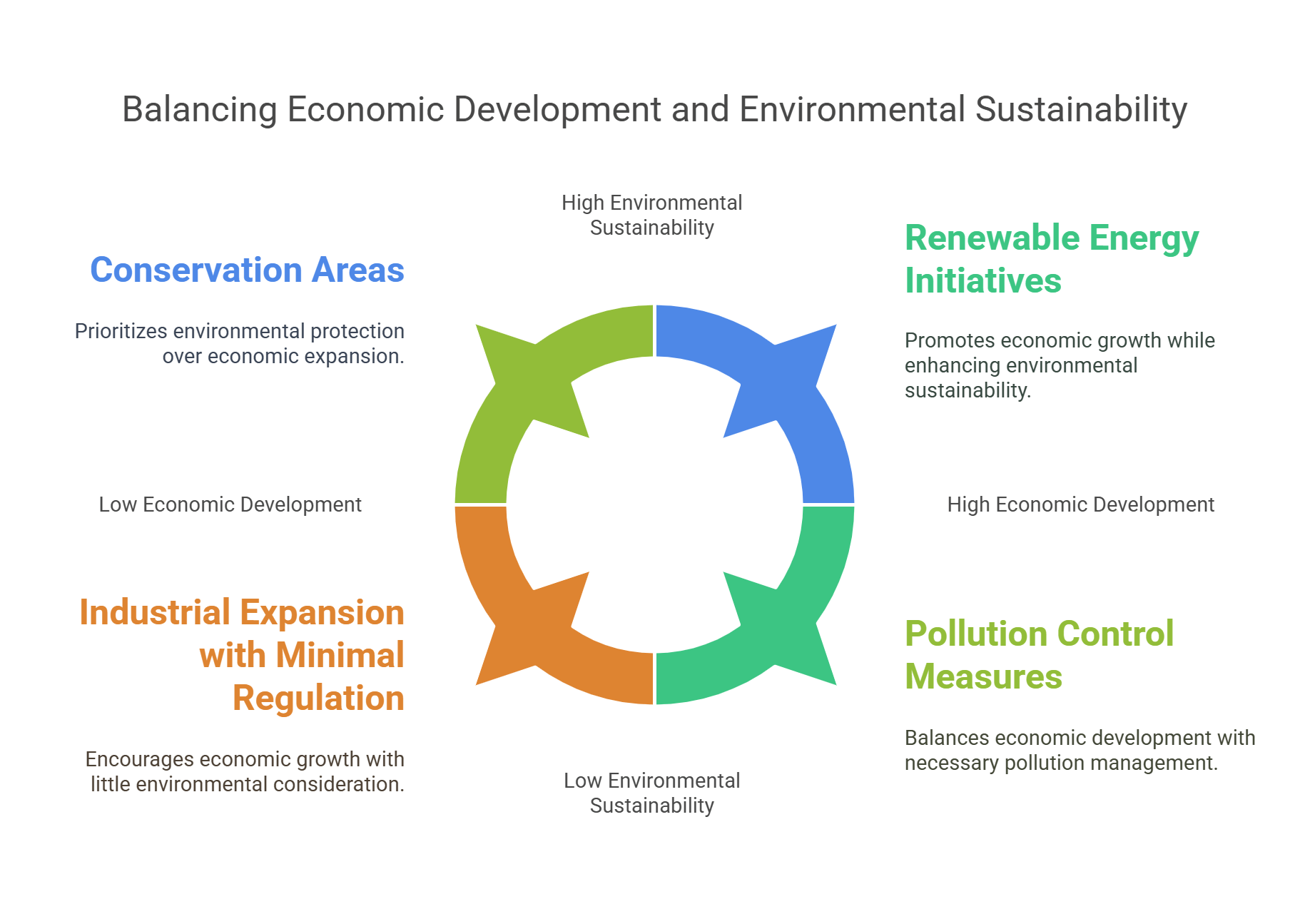
2. Environmental Policy
Environmental Policy involves rules and laws that governments create to protect the environment. These policies regulate industrial activities, manage natural resources, and address pollution. They often reflect the balancing act between economic development and environmental sustainability.
- Deals with laws and regulations like carbon emission caps.
- Encourages renewable energy use.
- Mitigates pollution and deforestation.
- Influences international agreements like the Paris Climate Accord.
- Balances environmental conservation with industrial growth.
Explained Simply: Think of it like house rules to keep your home clean and safe. If your house is Earth, these rules make sure no one throws garbage on the floor, wastes water, or breaks furniture.
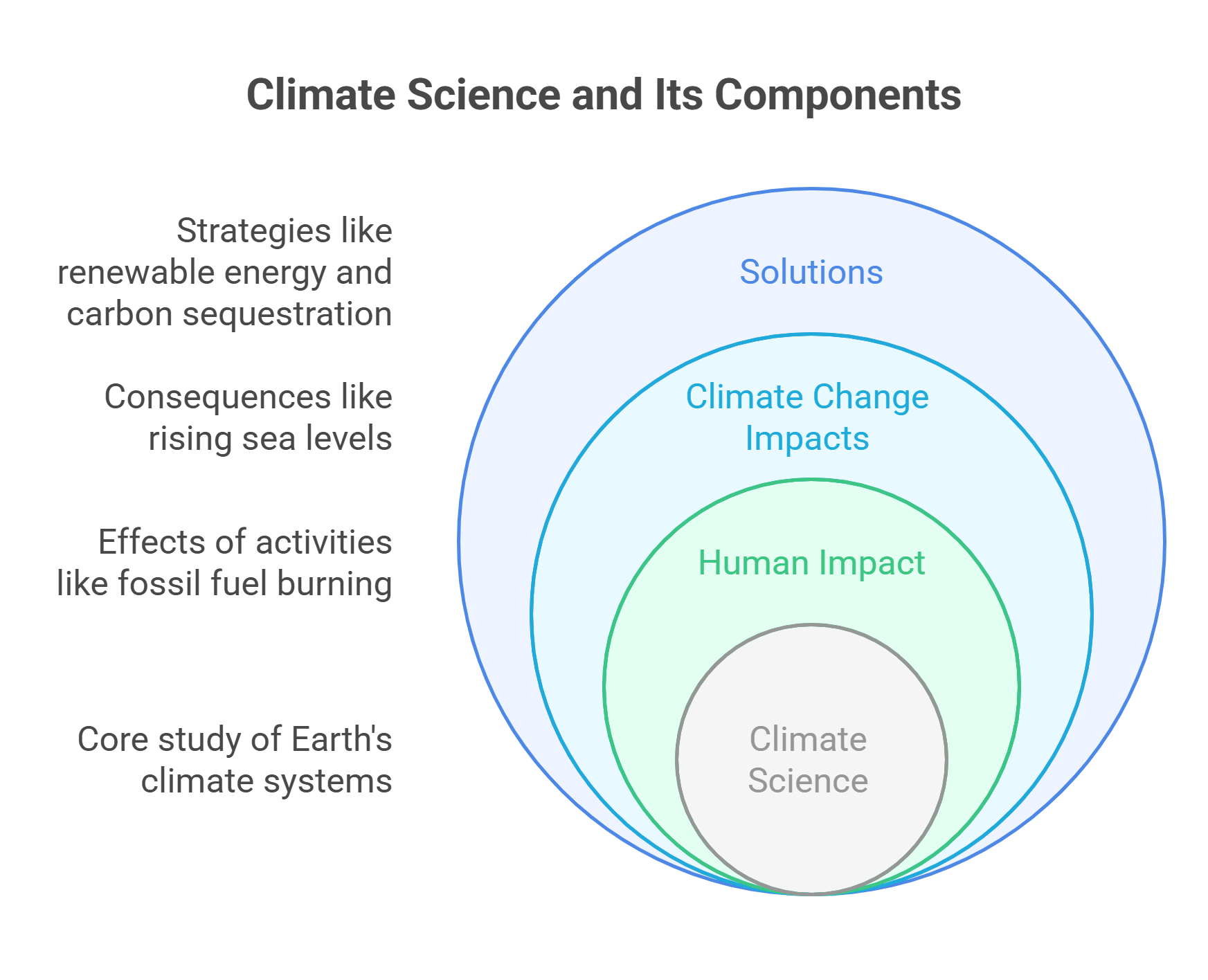
3. Climate Science
Climate Science studies Earth’s climate systems, including weather patterns, atmospheric conditions, and the long-term impacts of greenhouse gases. It examines how human activities, like burning fossil fuels, contribute to global warming and explores strategies to mitigate these effects.
- Studies weather patterns and climate trends.
- Examines greenhouse gas emissions and their effects.
- Analyzes climate change impacts like rising sea levels and extreme weather.
- Investigates solutions like carbon sequestration and renewable energy.
- Highlights the interconnectedness of global ecosystems.
Explained Simply: Think of Earth as wearing a blanket. If the blanket gets too thick because of pollution, the planet gets too hot. Climate Science helps us figure out how to remove that extra blanket so Earth stays cozy, not sweaty.
4. Renewable Resources
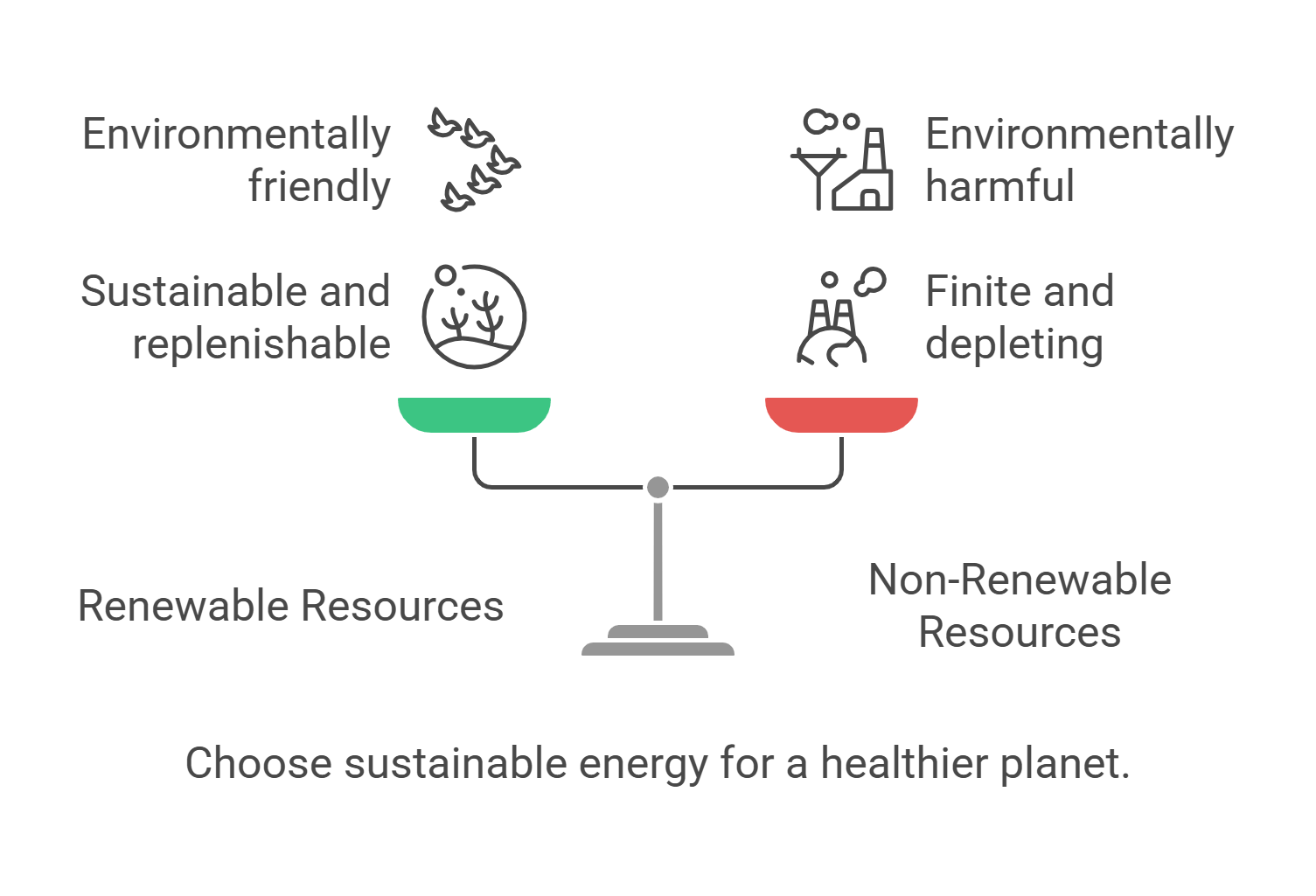
Renewable resources are natural materials or energy sources that replenish naturally, like sunlight, wind, and water. These resources are essential for sustainable development as they provide alternatives to non-renewable sources like coal and oil, which deplete over time and harm the environment.
- Includes solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- Minimizes environmental degradation.
- Supports sustainable practices.
- Encourages innovation in green technology.
Explained Simply: Imagine you have a toy that runs on sunlight instead of batteries. The sun never runs out, so you can play forever! Renewable resources are like that—they give us energy without running out or hurting the planet.
5. Pollution Control
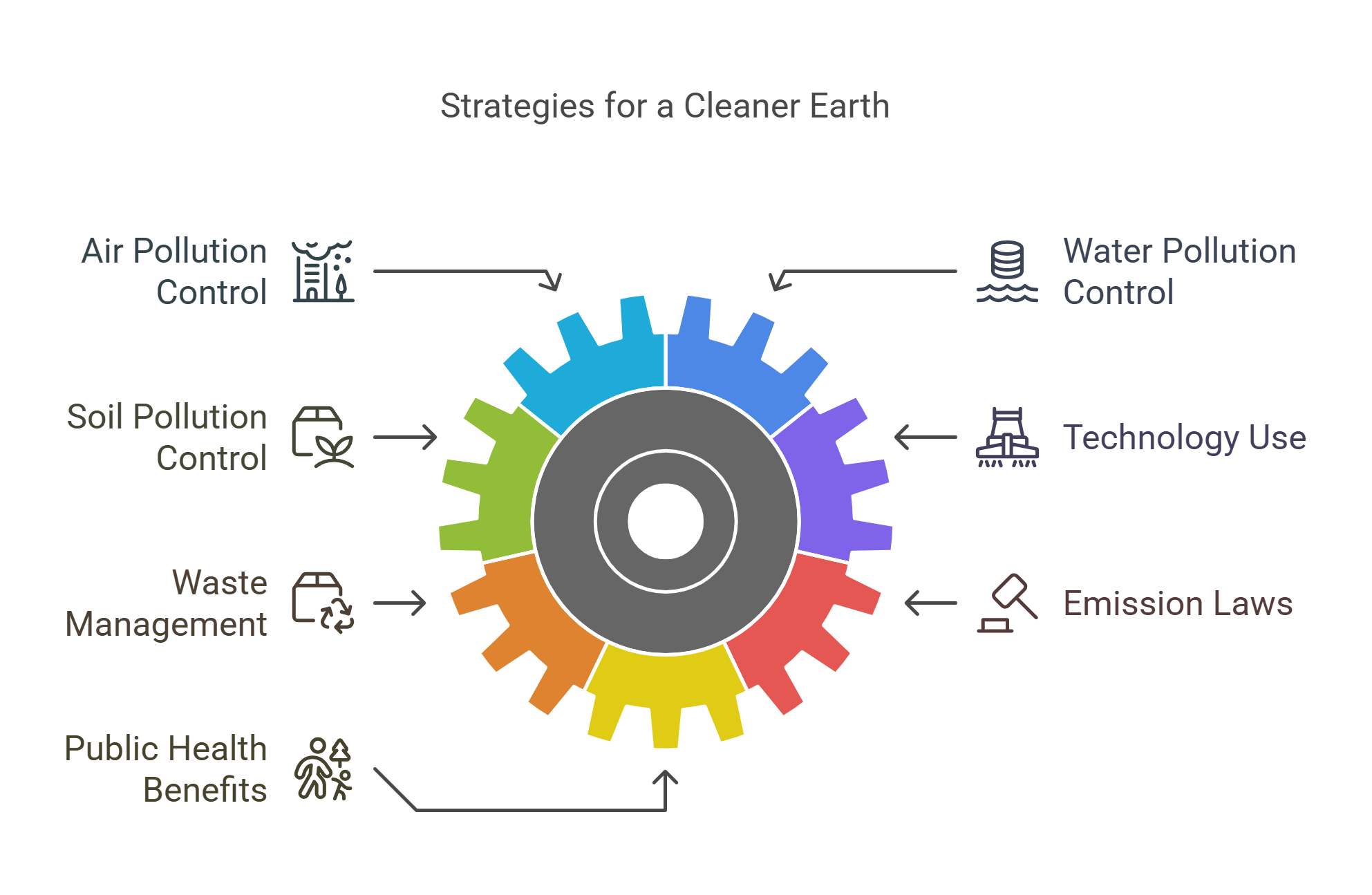
Pollution control involves strategies to reduce or eliminate harmful substances from air, water, and land. It encompasses waste management, emission controls, and cleaner production techniques to protect human health and ecosystems.
- Addresses air, water, and soil pollution.
- Uses technology like scrubbers and filters in industries.
- Promotes recycling and waste management.
- Enforces laws to limit emissions.
- Improves public health and ecosystem balance.
Explained Simply: Think of pollution as litter that gets everywhere—in the air you breathe, the water you drink, and the ground where plants grow. Pollution control is like a big cleanup crew that keeps our Earth tidy and healthy.
6. Ecology
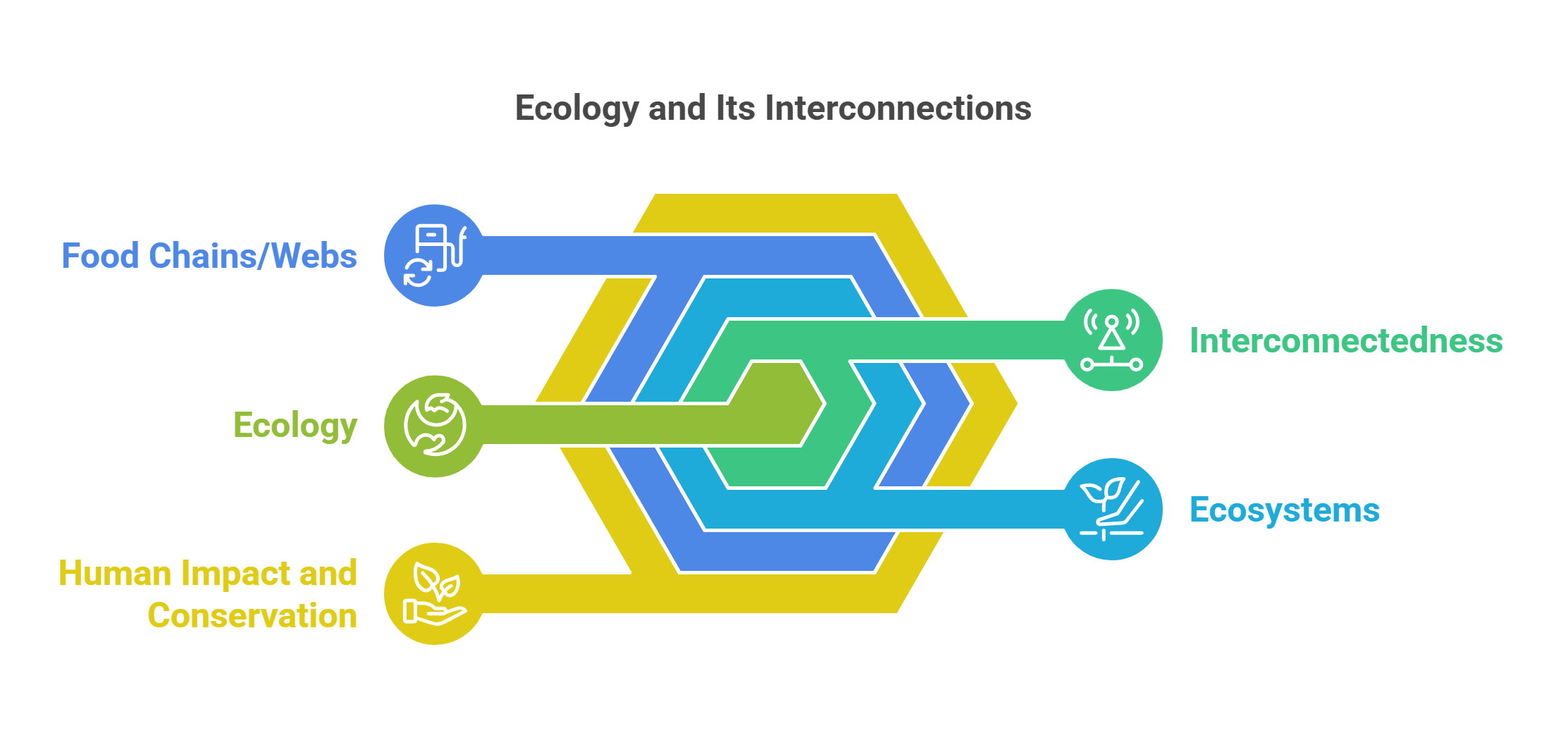
Ecology is the study of how living organisms interact with each other and their environments. It examines ecosystems, food chains, and the balance of natural systems, helping us understand the interconnectedness of all life forms.
- Explores relationships between organisms and their habitats.
- Analyzes food webs and energy flow in ecosystems.
- Examines impacts of human activities on ecosystems.
- Highlights biodiversity’s role in ecosystem health.
- Supports conservation efforts and sustainable practices.
Explained Simply: Think of a spider web where every strand connects to another. If one strand breaks, the web weakens. Ecology helps us understand how everything in nature is connected and how to keep it strong.
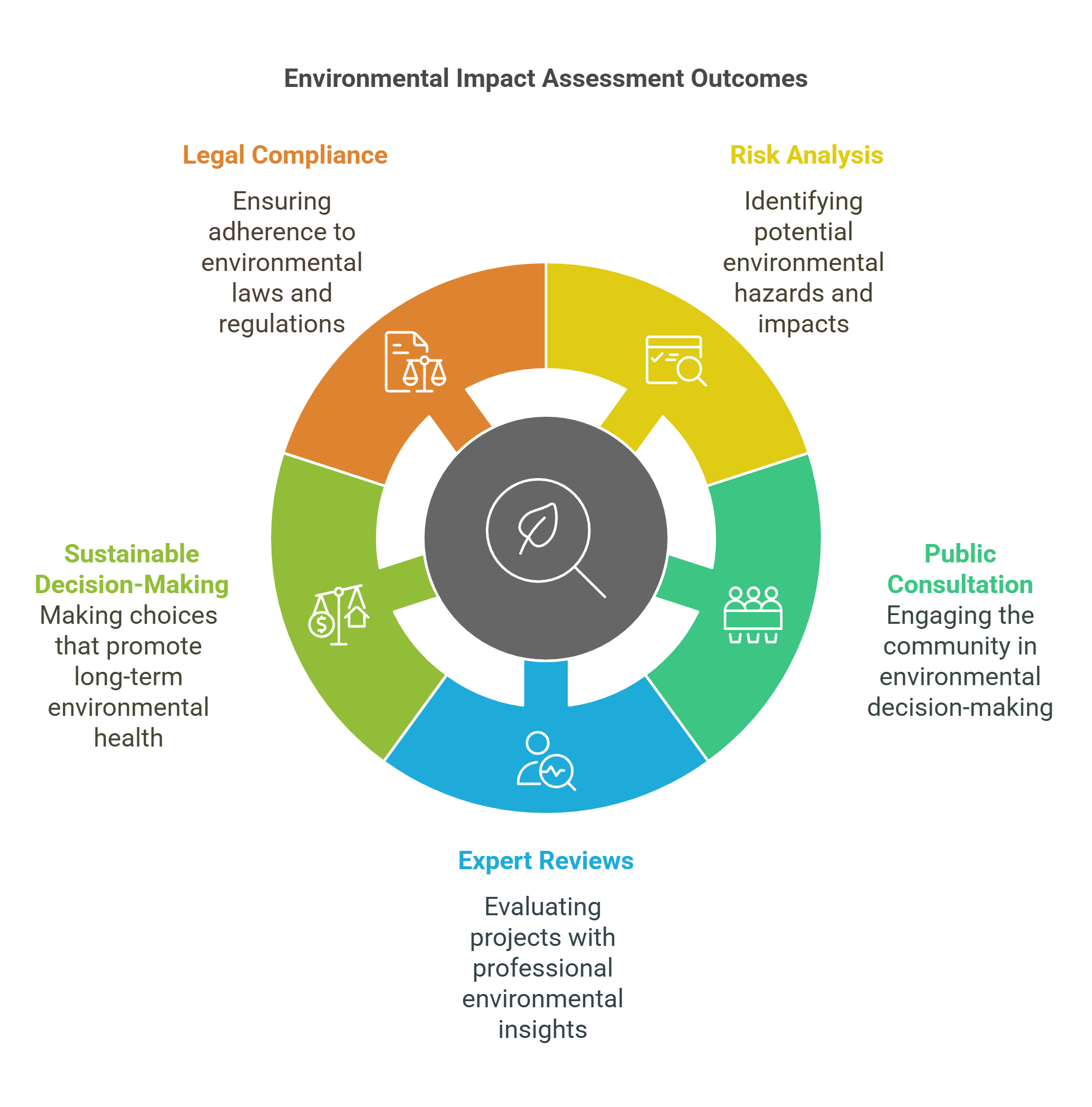
7. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) evaluates the potential effects of a proposed project or development on the environment. It aims to prevent or mitigate negative consequences by assessing risks and recommending solutions.
- Analyzes potential environmental risks of projects.
- Includes assessments of air, water, and soil impacts.
- Involves public consultation and expert reviews.
- Guides sustainable decision-making in development projects.
- Enforces legal compliance with environmental regulations.
Explained Simply: Imagine building a treehouse and checking if it would harm the animals living nearby. An EIA is like that—it checks if projects hurt the environment and finds ways to fix problems before starting.
8. Sustainable Development
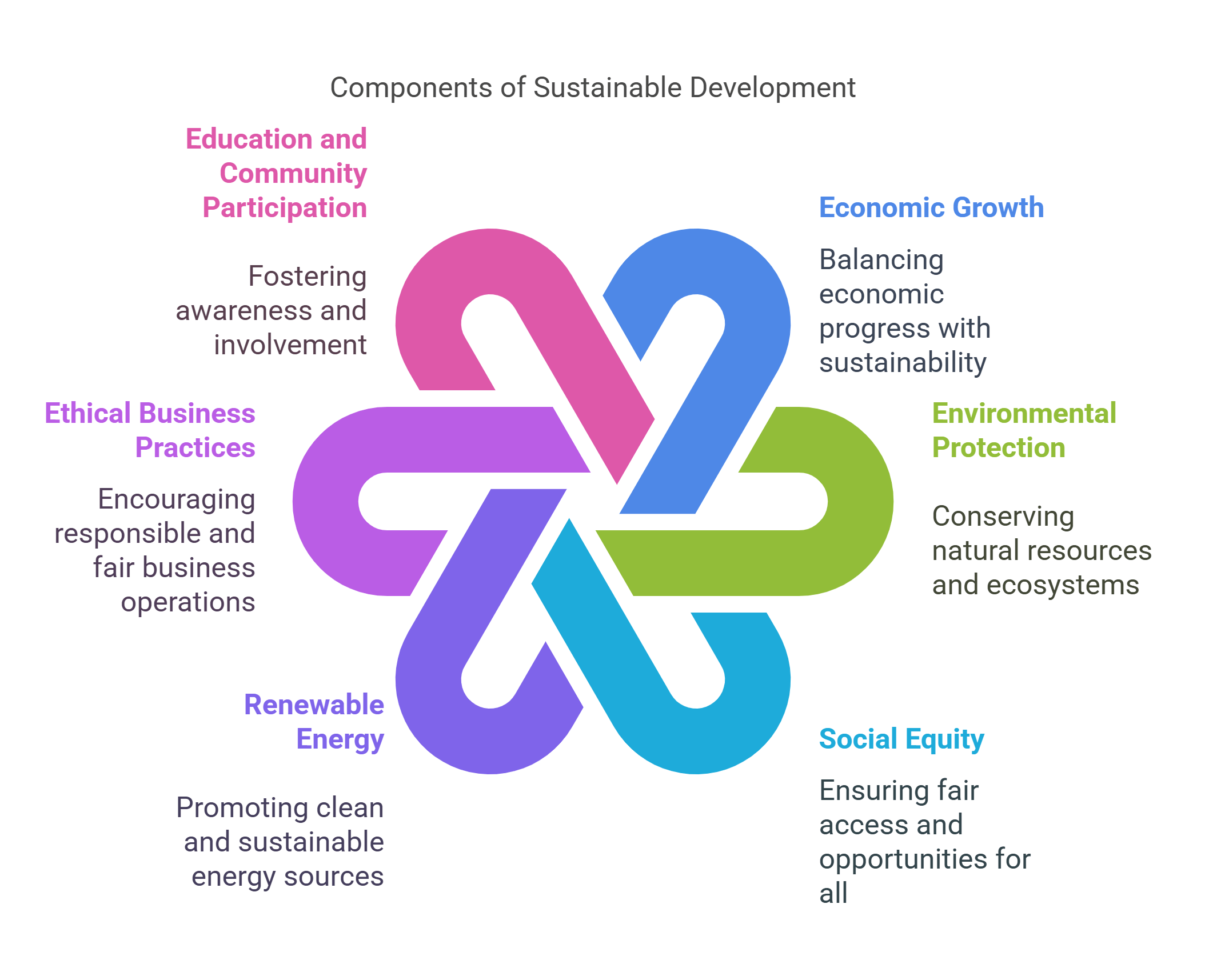
Sustainable Development seeks to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. It integrates economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity.
- Focuses on balancing development with conservation.
- Promotes renewable energy and green infrastructure.
- Encourages ethical business practices.
- Highlights education and community participation.
- Addresses global challenges like poverty and climate change.
Explained Simply: Imagine sharing a pie with friends but leaving enough so everyone tomorrow can enjoy it too. Sustainable Development is about using resources wisely so the planet stays healthy for future generations.
9. Biodiversity
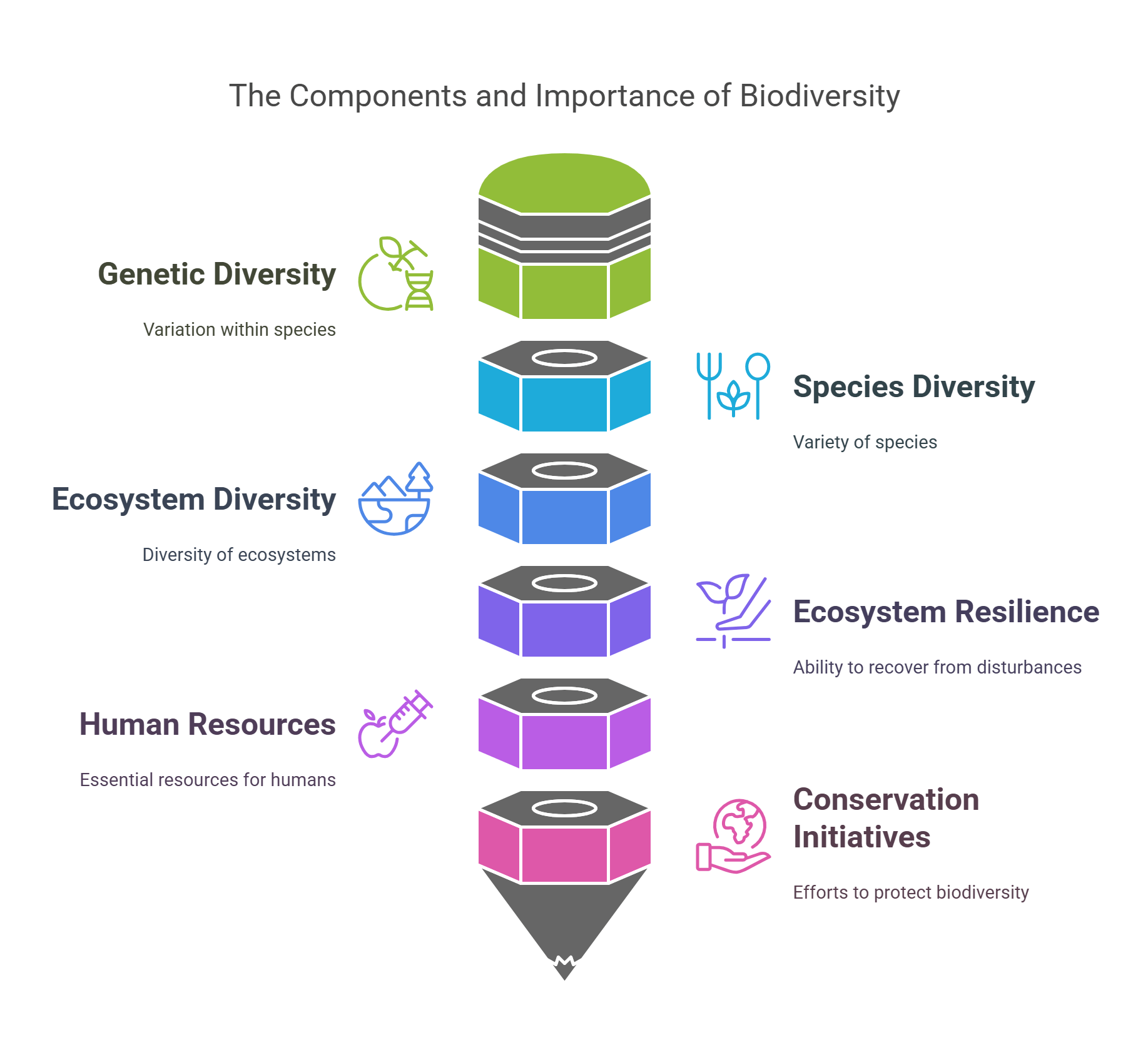
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, from tiny microbes to massive whales. It ensures ecosystem resilience and provides humans with essential resources like food, medicine, and clean air.
- Includes genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Supports ecosystem health and stability.
- Threatened by habitat destruction and climate change.
- Essential for agriculture, medicine, and industry.
- Promotes global conservation initiatives.
Explained Simply: Biodiversity is like a garden with many kinds of flowers, each adding beauty and helping the garden thrive. If too many flowers disappear, the garden won’t grow as well.
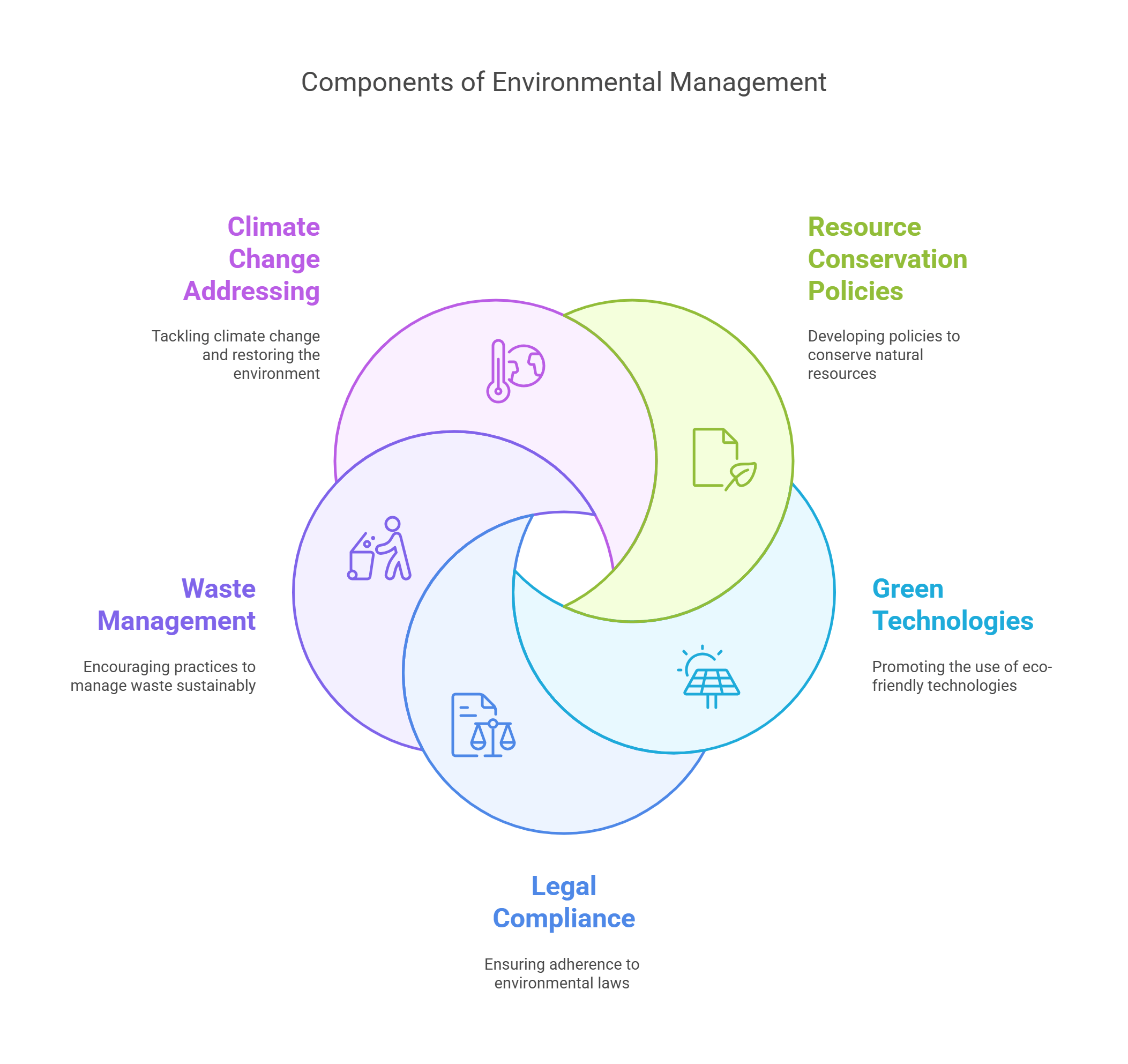
10. Environmental Management
Environmental Management involves planning and implementing strategies to reduce human impact on nature. It focuses on sustainable resource use, pollution prevention, and conservation.
- Develops policies for resource conservation.
- Promotes green technologies and renewable energy.
- Ensures compliance with environmental laws.
- Encourages sustainable waste management practices.
- Addresses climate change and environmental restoration.
Explained Simply: Environmental Management is like having a team of caretakers for the planet. They make sure we use resources wisely and fix problems like pollution and deforestation.
✨ Conclusion
Environmental Science concepts are not only foundational for understanding RC passages but also crucial for engaging with pressing global issues. By mastering topics like Climate Science, Pollution Control, and Sustainable Development, you build the analytical and interpretive skills required for complex RC questions. This knowledge not only helps in exams but also enriches your understanding of the world, enabling you to approach texts with greater insight and confidence.













