Definition & Meaning: Eu- Root Word
The Greek eu, well, comes from eus, good
Examples derived directly from Greek words include eu-phony, the quality of being pleasing to the ear, the valved brass musical instrument called the euphonium derives from the same root;eulogy, a speech or piece of writing that praises someone or something highly; euphoria, a feeling or state of intense excitement and happiness.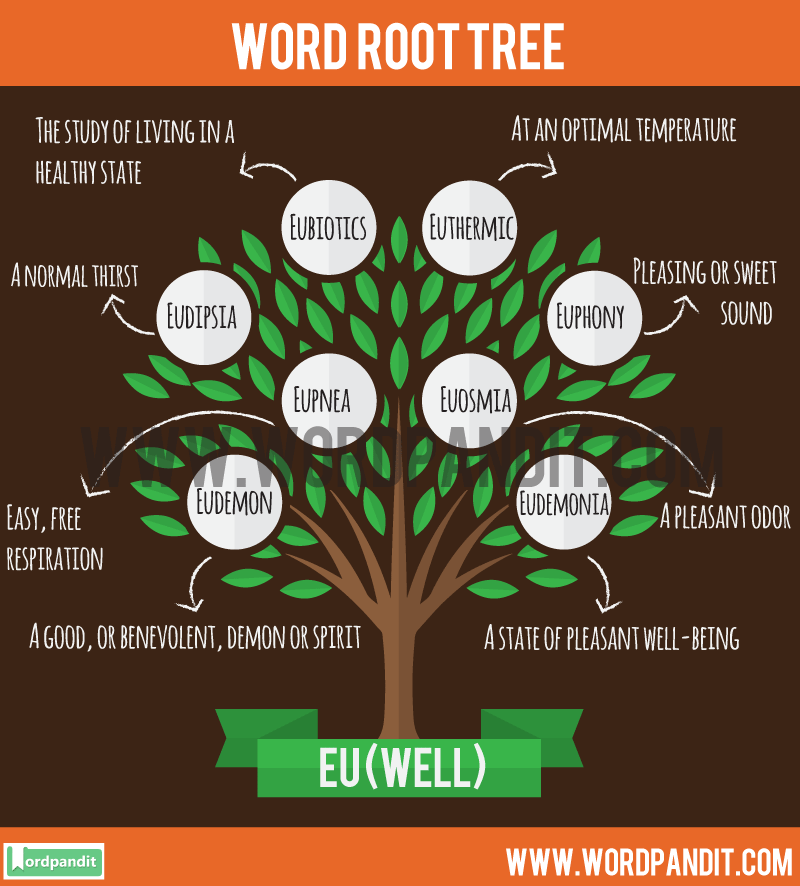
Words Based on the Eu- Root Word
Let’s go through some interesting words based on Eu root word:
1. Eubiotics: The study of living in a healthy state.
2. Eucalyptus: Any of numerous tall trees of the genus Eucalyptus
3. Eudemon: A good, or benevolent, demon or spirit.
4. Eudemonia: A state of pleasant well-being.
5. Eudipsia: A normal thirst.
6. Euesthesia: The normal or good conditions of the sensations or feelings of the body.
7. Eumorphics: A reference to the preservation of or keeping the the natural form of a cell.
8. Eumorphism: The preservation of or protecting the natural form of a cell.
9. Euosmia: A pleasant odor.
10. Euphemism: A mild or pleasant word, or phrase, which is used in place of one that might be considered too direct, too harsh, too unpleasant.
11. Euphonic: The descriptive word for a pleasant sound.
12. Euphony: Pleasing or sweet sound.
13. Euphoria: A feeling of great happiness or well-being.
14. Ecstatic: extremely happy or excited.
15. Eupnea: Easy, free respiration.
16. Euthermic: At an optimal temperature.
With this, we come to an end of this lesson on Root word Eu. Hope your learning has been immense. Keep revising, keep learning with Wordpandit. Here’s wishing you an enriching vocabulary.