Exo: Exploring the "Outside" in Language and Science
Discover the fascinating world of the root "exo," derived from Greek, meaning "outside" or "external." From biological marvels like exoskeletons to specialized terms like exocrine, this root unveils a diverse spectrum of applications across science, language, and culture.
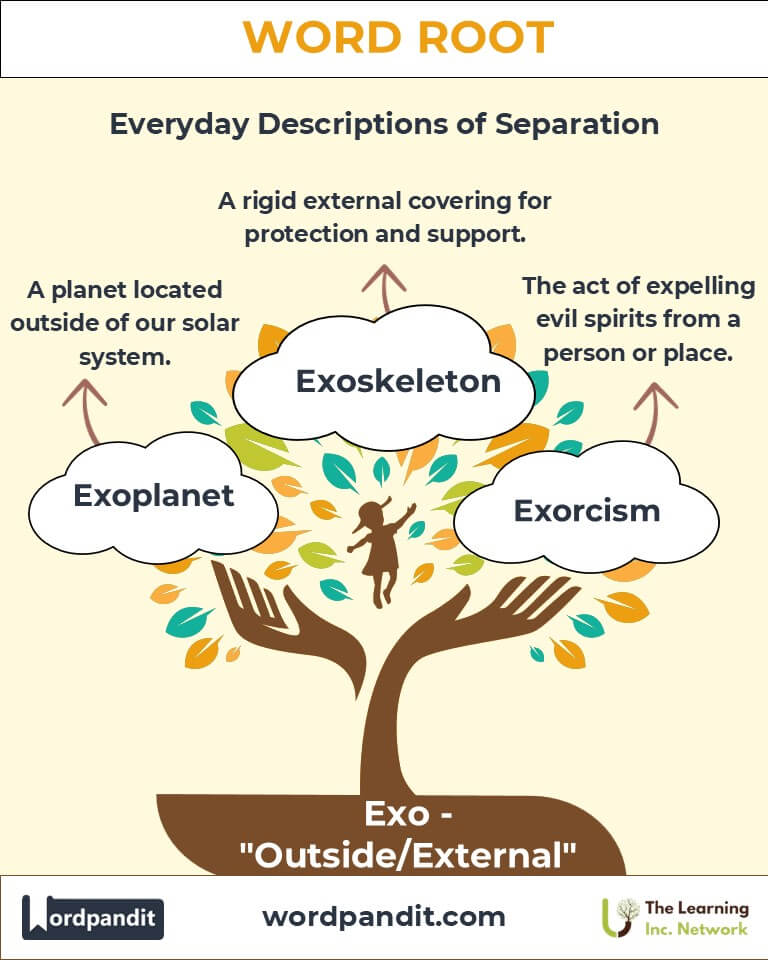
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Exo"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Exo"
- Common "Exo"-Related Terms
- "Exo" Through Time
- "Exo" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Exo" in Action
- Cultural Significance of the "Exo" Root
- The "Exo" Family Tree
- FAQs about the "Exo" Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: "Exo" Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Exo"
Introduction: The Essence of "Exo"
Have you ever wondered how certain creatures like crabs and insects have hard shells to protect their bodies? These structures, known as exoskeletons, embody the root "exo," meaning "outside" or "external." Pronounced ek-soh, this Greek root has become a cornerstone of scientific and everyday vocabulary, describing phenomena that occur on the exterior or extend beyond.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "exo" originates from the Greek prefix exo- (ἔξω), which translates to "outside" or "outer." It has been used since ancient times to describe external phenomena, from geography (exogenous landscapes) to biology (exocrine systems). Over centuries, this root found its way into English, enriching scientific terminology and enhancing our understanding of the external world.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Exo"
Picture a crab wearing a sturdy armor labeled "EXO." This armor, its exoskeleton, symbolizes "exo" as the root of all things external.
Mnemonic Device: "Exo means armor on the outside, protecting life from harm worldwide."
Common "Exo"-Related Terms
- Exoskeleton (ek-soh-skel-uh-ton):
A rigid outer structure supporting and protecting the bodies of certain animals.
Example: "The exoskeleton of a beetle is both lightweight and durable."
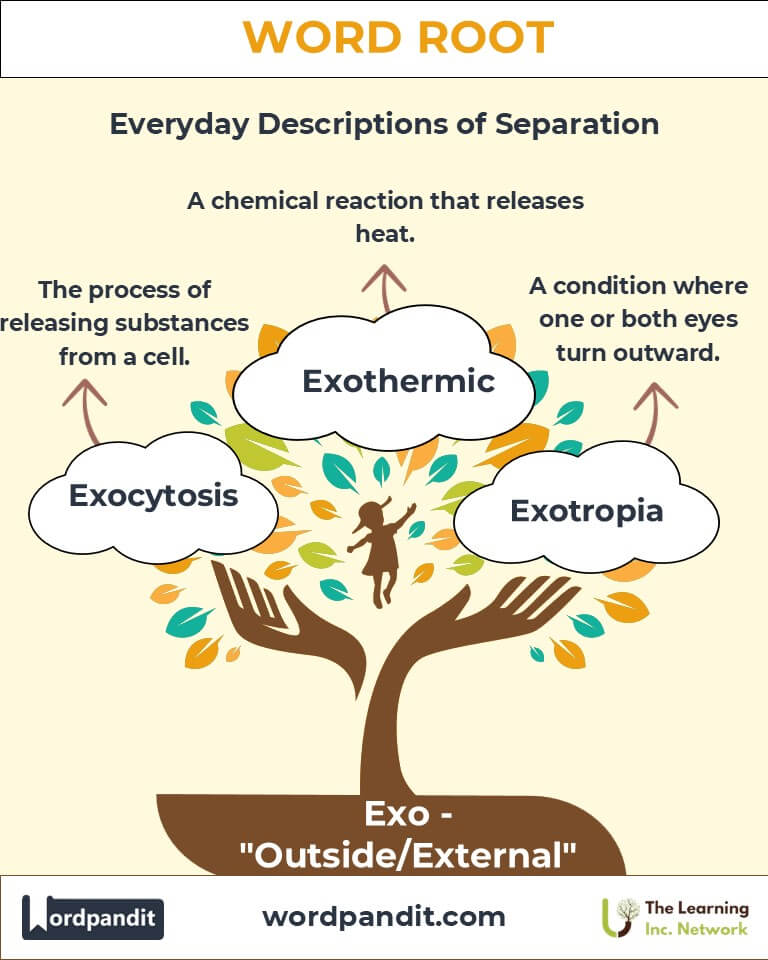
- Exocrine (ek-soh-krin):
Glands that release substances outside the body or into a duct.
Example: "Sweat glands are an example of exocrine glands."
- Exoplanet (ek-soh-plan-it):
A planet outside our solar system.
Example: "Scientists recently discovered an exoplanet with conditions similar to Earth."
- Exothermic (ek-soh-thur-mik):
Referring to chemical reactions that release heat.
Example: "Combustion is an exothermic reaction."
- Exodus (ek-soh-duhs):
A mass departure of people.
Example: "The exodus from the city occurred after the earthquake warning."
"Exo" Through Time
- Exoteric (Ancient): Originally describing teachings accessible to the general public, contrasting with esoteric (secretive knowledge).
- Exoskeleton (Biological Evolution): Fossil records reveal that arthropods evolved exoskeletons over 500 million years ago, enabling their survival in diverse environments.
"Exo" in Specialized Fields
- Biology: Exoskeletons protect insects, crustaceans, and other arthropods, playing a vital role in their mobility and survival.
- Astronomy: Exoplanets expand our understanding of the universe, revealing planets orbiting stars outside our solar system.
- Chemistry: Exothermic reactions are critical in energy production, from burning fuel to industrial synthesis.
- Medicine: Exocrine glands regulate essential bodily functions, such as digestion and thermoregulation.
Illustrative Story: "Exo" in Action
Dr. Kieran was an exobiologist studying the possibility of life on exoplanets. One day, while observing crabs with tough exoskeletons on a remote island, she drew parallels between these terrestrial creatures and hypothetical alien species with protective outer shells. Her research combined the mysteries of biology and astronomy, showcasing the universal relevance of "exo."
Cultural Significance of the "Exo" Root
The concept of "outside" resonates in many cultural contexts. In ancient Greece, "exoteric" philosophies were deemed public, in contrast to secretive teachings. Today, "exo" captures our quest to explore the unknown, from exoplanets to external body armor.

The "Exo" Family Tree
Explore related roots and terms:
- Ecto- (outside):
Ectoderm: The outermost layer of cells in an embryo.
- Extra- (beyond):
Extraterrestrial: Existing beyond Earth.
- Endo- (inside):
Endocrine: Glands secreting directly into the bloodstream.
FAQs About the "Exo" Word Root
Q: What does "exo" mean?
A: "Exo" is a root derived from Greek, meaning "outside" or "external." It serves as a prefix in various scientific and everyday terms, highlighting elements or phenomena that occur outside or beyond something. For example, an exoskeleton is an external skeleton that protects certain animals.
Q: What is an exoskeleton, and why is it important?
A: An exoskeleton is a rigid, external covering found in animals like insects and crustaceans, providing protection and structural support. It functions like armor, shielding the body from physical harm and desiccation while also aiding movement through attachment points for muscles.
Q: How do exocrine glands differ from endocrine glands?
A: Exocrine glands release substances through ducts to the exterior of the body or onto surfaces (e.g., sweat or digestive enzymes). Endocrine glands, on the other hand, secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate internal processes like growth or metabolism.
Q: What are exoplanets, and how do they differ from planets in our solar system?
A: Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars outside our solar system. Unlike familiar planets like Earth or Jupiter, exoplanets are detected using specialized techniques such as the transit method, where their passage in front of a star causes a slight dimming of the star’s light.
Q: What is an exothermic reaction, and why is it significant?
A: An exothermic reaction is a chemical process that releases heat into the surrounding environment. These reactions, such as combustion or condensation, are essential in everyday life and industrial processes. For example, the burning of fuels to generate energy is an exothermic reaction critical to powering homes and vehicles.
Q: What does "exodus" mean, and where does the term come from?
A: "Exodus" refers to a large-scale departure or migration, often under challenging circumstances. The term originates from the Greek word exodos (meaning "way out") and is famously associated with the biblical story of the Israelites' escape from Egypt.
Q: Can the root "exo" appear in both scientific and non-scientific contexts?
A: Yes, the root "exo" is versatile. In science, it appears in terms like exoskeleton and exocrine, while in broader contexts, it appears in words like exodus, referring to mass departures, or exoteric, meaning knowledge accessible to all.
Test Your Knowledge: "Exo" Mastery Quiz
1. What does "exo" mean?
2. Which term refers to a planet beyond our solar system?
3. What is the function of an exoskeleton?
4. What type of gland releases substances outside the body?
5. What is the root of "exothermic"?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Exo"
The root "exo" opens doors to understanding the external world, from natural phenomena like exoskeletons to astronomical discoveries like exoplanets. Its applications in science and culture highlight humanity’s drive to explore and understand what lies beyond. The legacy of "exo" inspires us to keep looking outward, where infinite possibilities await.














