Luc: Illuminating the Language of Light and Clarity
Explore the luminous world of the root "Luc," derived from Latin, signifying light and brightness. This root has permeated languages to illuminate concepts of clarity, enlightenment, and transparency in science, literature, and philosophy.
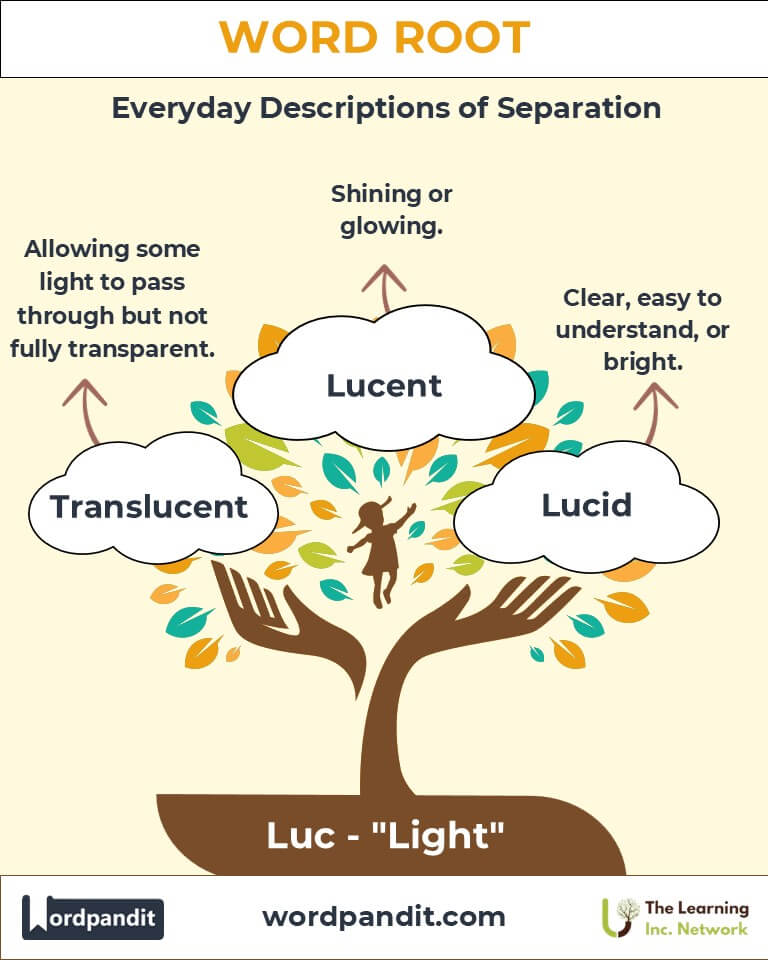
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Shining Light on "Luc"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Luc
- Common Luc-Related Terms
- Luc Through Time
- Luc in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Luc in Action
- Cultural Significance of Luc
- The Luc Family Tree
- FAQs About the Luc Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Luc Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Luc
1. Introduction: Shining Light on "Luc"
"How do we bring clarity to the unseen?" The root Luc, from Latin lux meaning "light," represents the essence of illumination—both physical and metaphorical. Pronounced "luhk," it plays a pivotal role in terms related to brightness, understanding, and transparency. From scientific principles to poetic imagery, Luc brightens our vocabulary, symbolizing both literal and figurative enlightenment.

2. Etymology and Historical Journey
The Latin lux, meaning "light," evolved into lucere, "to shine," and expanded into modern languages as words symbolizing brightness and clarity. In ancient Rome, lux was associated with divinity and purity. The concept of light extended into philosophy during the Enlightenment, where clarity of thought paralleled physical light. This root journeyed into French and English, giving us words like lucid and translucent.
3. Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Luc
Picture a glowing lantern piercing through a dense fog, revealing a clear path ahead. Just as light brings clarity to darkness, Luc signifies illumination.
Mnemonic Device: "Luc lights up the path to understanding."
4. Common Luc-Related Terms
- Lucid (loo-sid): Clear and easy to understand.
Example: "Her lucid explanation made the complex topic accessible to everyone." - Translucent (trans-loo-sent): Allowing light to pass through diffusely.
Example: "The translucent curtains bathed the room in a soft, golden glow." - Elucidate (ee-loo-si-date): To clarify or make something clear.
Example: "The professor elucidated the formula with a detailed diagram." - Lucifer (loo-si-fer): Historically, "light-bringer," but also the name for a fallen angel in Christian theology.
Example: "In mythology, Lucifer symbolized the quest for knowledge and its consequences." - Lucent (loo-sent): Glowing or shining.
Example: "The lucent moonlight danced on the water’s surface."
5. Luc Through Time
- Lucid: Once used in classical Latin to describe physical brightness, it now commonly refers to mental clarity.
Evolution: From "light" to "clear thinking." - Lucifer: Originally meaning "light-bringer" in Roman mythology, it transitioned into Christian contexts, symbolizing the duality of enlightenment and hubris.
6. Luc in Specialized Fields
- Physics: Lucent materials refer to those that emit or allow light to pass through.
Example: "Optical fibers rely on lucent materials for data transmission." - Psychology: The term lucid dreaming describes being aware within a dream.
Real-world use: Studied for therapeutic applications in trauma and creativity. - Art and Design: Translucence is crucial in architectural and lighting design.
Example: "Frosted glass combines aesthetics with functionality." - Literature: Lucid is often used to describe clarity in writing or thought.
Significance: Writers strive for lucidity to connect effectively with their audience.
7. Illustrative Story: Luc in Action
In a bustling city newsroom, investigative journalist Lucy finds herself on a challenging assignment: uncovering a financial scandal shrouded in legal jargon. Armed with her sharp mind and commitment to transparency, she begins her research. As she "elucidates" the convoluted documents, the truth begins to shine through like sunlight piercing a storm. Her lucid reporting not only brings clarity to the case but also illuminates a path to justice for countless affected individuals.
8. Cultural Significance of Luc
Light has always been a powerful symbol in cultures worldwide:
- Ancient Rome: Lux symbolized divinity and wisdom.
- Enlightenment Era: Light represented reason and scientific discovery.
- Modern Usage: Transparency and clarity are often described metaphorically as "shedding light."

9. The Luc Family Tree
- Lumin (Latin lumen, "light"):
Gives us illuminate, luminary, and luminescence. - Phot (Greek phos, "light"):
Appears in photograph and photosynthesis. - Flam (Latin flamma, "flame"):
Found in flame and inflammable, linking light with heat.
FAQs About the Luc Word Root
Q: What does "Luc" mean and where does it originate?
A: "Luc" originates from the Latin word lux, meaning "light." It symbolizes illumination, clarity, and understanding in both physical and metaphorical contexts. This root has been integral to words that describe brightness or insight, linking it to scientific, literary, and philosophical fields.
Q: Is there a difference between "Lucid" and "Lucent"?
A: Yes, there is a difference. Lucid refers to mental clarity or something easily understood, such as "a lucid argument." Lucent, on the other hand, describes physical brightness or something glowing softly, like "lucent crystals in the moonlight."
Q: What is the role of "Luc" in the term "Lucifer"?
A: "Lucifer" originally meant "light-bringer" in Latin, referring to the planet Venus as the morning star. In Christian theology, it became associated with a fallen angel symbolizing the pursuit of knowledge and its potential consequences.
Q: How do "Transparent" and "Translucent" differ in their use of "Luc"?
A: Both involve light, but they differ in how light passes through an object. Transparent means light passes clearly, allowing you to see through (e.g., clear glass). Translucent allows light to pass but scatters it, blurring visibility (e.g., frosted glass).
Q: What is "Elucidation," and why is it important?
A: Elucidation means making something clear or explaining it. It is crucial in education, science, and communication, as it transforms complex ideas into understandable concepts, much like light dispelling darkness.
Q: How does Luc relate to lucid dreaming?
A: Lucid dreaming refers to being aware that you are dreaming while still in the dream. The term ties to "Luc" because it represents clarity of consciousness, illuminating the dreamer’s awareness within a typically unconscious state.
Q: How has the word "Luc" influenced technology?
A: Lucent technologies, such as fiber optics, leverage the root’s association with light, as these materials transmit data using light waves. This innovation underscores the lasting relevance of "Luc" in modern science and engineering.
Q: What’s the historical significance of the root "Luc"?
A: Historically, Luc has been a symbol of enlightenment, from ancient Rome’s reverence for light as divine to its central role in the Enlightenment era, where "shedding light" on knowledge was a key cultural metaphor.
Test Your Knowledge: Luc Word Root Quiz
1. What does "Luc" primarily signify?
2. Which term means "to clarify"?
3. What describes light passing diffusely through an object?
4. Which word relates to glowing material?
5. What is a common application of lucent materials?
12. Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Luc
The word root Luc continues to brighten our linguistic and conceptual horizons, connecting us to themes of light, clarity, and understanding. From ancient philosophies to modern technologies, Luc is an enduring beacon of enlightenment. Its potential to evolve alongside human innovation ensures its relevance in both language and life. As Luc sheds light on our journey, it reminds us to seek clarity in all we pursue.













Hello Prashant
I tried making the following sentences using the different forms of the word ‘elucidate’.
Can you please check.
This is an elucidating technique that helps students to do the practical without any outside help.
Would you like to elucidate the matter any further?
This elucidative appendix helps the modern readers to understand the book thoroughly.
This day of elucidation changed the lives of millions.
Thanks 🙂
Hey Seerat
Better construction for the sentences is as follows:
This technique elucidates to the students how to do the practical without any outside help.
This appendix, with its elucidation, helps the modern readers to understand the book thoroughly.
Regards
Wordpandit