Meta: The Root of Transformation and Insight
Discover the transformative power of the word root "meta," originating from Greek and meaning "change" or "after." From philosophical terms like "metaphor" to scientific concepts like "metamorphosis," this versatile root enriches our language with ideas of evolution, adaptation, and transcendence.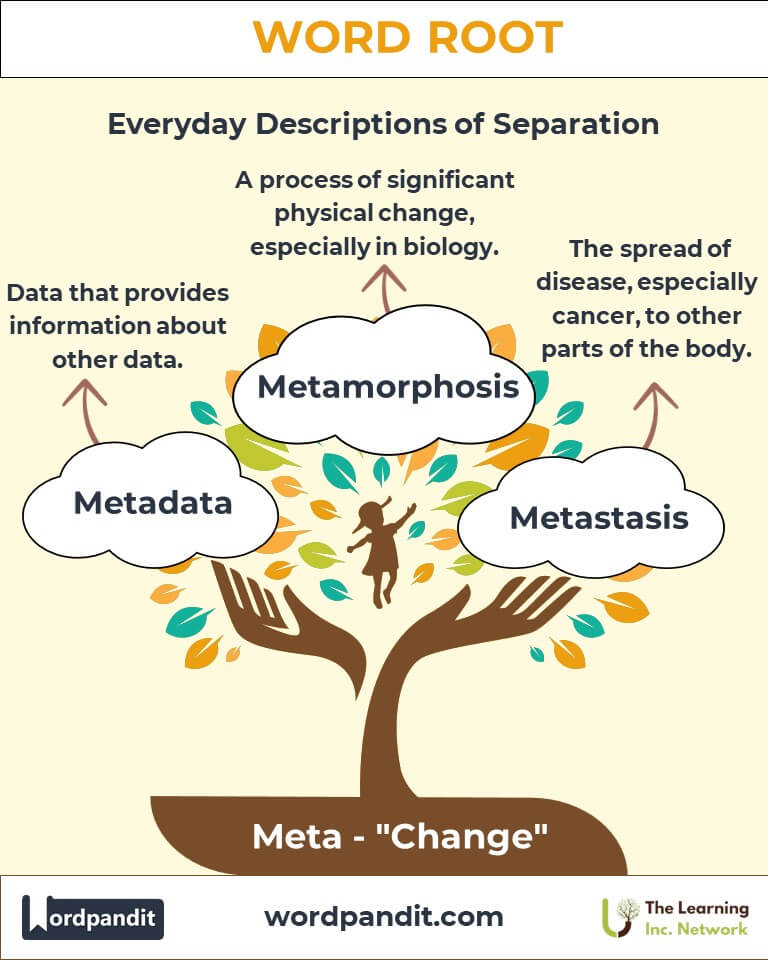
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Significance of Meta
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meta
- Common Meta-Related Terms
- Meta Through Time
- Meta in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Meta in Action
- Cultural Significance of Meta
- The Meta Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Meta
Introduction: The Significance of Meta
Have you ever considered how a caterpillar becomes a butterfly? Or how words take on symbolic meanings beyond their literal sense? These ideas connect to the root "meta" (pronounced meh-tuh), which signifies "change" or "after." Whether describing transformation in nature (metamorphosis) or abstraction in language (metaphor), "meta" is a cornerstone of understanding shifts in meaning, form, and perspective.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root meta stems from the Greek preposition "meta," meaning "after," "beyond," or "change." In ancient Greece, it appeared in works of philosophy to describe higher states or transitions. For instance, Aristotle's Metaphysics—a study that goes "beyond" physical phenomena—cemented the word's intellectual significance. Over centuries, meta found its way into Latin and English, expanding its applications across science, art, and technology.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Meta
Picture a caterpillar undergoing metamorphosis, its body transforming as it emerges as a butterfly. This vivid image encapsulates meta as the root of change and progression.
Mnemonic Device: “Meta means change—like a butterfly spreading its wings beyond the cocoon.”
Common Meta-Related Terms
- Metamorphosis (met-uh-mawr-fuh-sis): A process of significant physical change, especially in biology.
Example: “The metamorphosis of a tadpole into a frog is fascinating.”
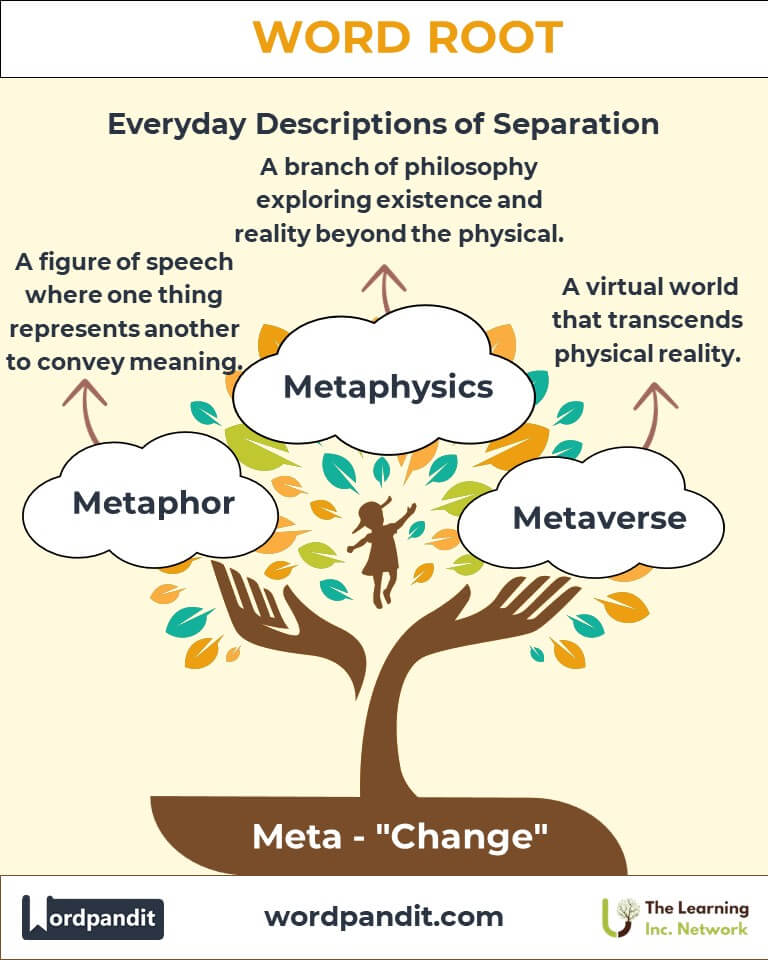
- Metaphor (met-uh-fawr): A figure of speech where one thing represents another to convey meaning.
Example: “Her smile was a metaphorical ray of sunshine.”
- Metadata (met-uh-dey-tuh): Data that provides information about other data.
Example: “The photo’s metadata included its location and timestamp.”
- Metaphysics (met-uh-fiz-iks): A branch of philosophy exploring existence and reality beyond the physical.
Example: “Metaphysics tackles profound questions about the nature of reality.”
- Metastasis (met-as-tuh-sis): The spread of disease, especially cancer, to other parts of the body.
Example: “Early detection can prevent the metastasis of cancer.”
Meta Through Time
- Metamorphosis:
Originally describing biological changes, this term broadened to metaphorical transformations, such as personal growth.
- Metaphor:
First used in ancient Greek rhetoric, metaphors now permeate art, literature, and even technology (e.g., "cloud computing").
- Metaverse:
Coined in the 1990s, this term represents digital spaces that transcend physical reality, gaining popularity with advancements in virtual reality.
Meta in Specialized Fields
- Philosophy:
Metaphysics: Examines abstract concepts like existence and causality, influencing centuries of intellectual thought.
- Technology:
- Metadata: Essential for organizing and retrieving digital information efficiently.
- Metaverse: Explores interconnected virtual spaces, revolutionizing social and economic interactions.
- Biology:
Metamorphosis: Crucial in understanding life cycles and evolutionary adaptations.
- Medicine:
Metastasis: A term central to oncology, representing the spread of cancer cells.
Illustrative Story: Meta in Action
Sophie, a high school student, struggled to see how literature could relate to her interest in biology. One day, her teacher introduced the metaphor of "metamorphosis" to describe personal growth. Inspired, Sophie realized how the same root connected her favorite books to the life cycles she loved studying. Her newfound perspective helped her write an award-winning essay on the metaphorical "metamorphosis" in Jane Eyre.
Cultural Significance of Meta
The root meta reflects humanity's fascination with transformation and abstraction. From mythical tales of shape-shifters to modern debates on the metaverse, "meta" shapes how we understand change and progression. Its usage in philosophy, science, and art symbolizes our drive to explore what lies beyond the surface.

The Meta Family Tree
- Trans- (Latin: "across, beyond"):
- Transformation: Significant change in form or nature.
- Transcend: To go beyond limits.
- Para- (Greek: "beside, beyond"):
- Parallel: Running alongside or comparable.
- Paradox: A seemingly contradictory statement that reveals truth.
- Post- (Latin: "after"):
- Posthumous: Occurring after death.
- Postscript: An additional note added after the main text.
FAQs About the "Meta" Word Root
Q: What does "meta" mean?
A: "Meta" originates from Greek and means "change," "after," or "beyond." It serves as a prefix in English to denote transformation, progression, or abstraction. For instance, in "metamorphosis," it signifies a physical transformation, and in "metaphor," it denotes a conceptual shift in meaning.
Q: Why is "meta" significant in modern language?
A: "Meta" has become prominent due to its applications in technology, science, and art. In the digital age, terms like "metadata" (data about data) and "metaverse" (a virtual universe beyond physical reality) reflect its relevance in describing abstract or secondary layers of information.
Q: What is "metamorphosis"?
A: Metamorphosis refers to a complete transformation in form, structure, or function, especially in biology. For example, a caterpillar undergoes metamorphosis to become a butterfly, showcasing the physical and functional change inherent in this process.
Q: What is "metaphor" and how is it used?
A: A metaphor is a figure of speech where one thing represents another to convey meaning beyond the literal. For example, "time is a thief" suggests that time "steals" moments from our lives. This rhetorical device helps in understanding abstract ideas through familiar imagery.
Q: How does "metadata" function in technology?
A: Metadata is information that describes other data, making it easier to organize, search, and understand. For instance, in a photograph, metadata might include the date it was taken, the camera used, and its GPS location.
Q: What does "metastasis" mean in medical terms?
A: Metastasis describes the spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to other parts of the body. It is a critical concept in oncology, as metastasis often signifies advanced stages of cancer, requiring more aggressive treatment.
Q: What is the "metaverse," and why is it important?
A: The metaverse refers to a virtual, interconnected digital space where users can interact through avatars, work, socialize, and even trade virtual goods. As technology advances, the metaverse is expected to redefine social interactions, commerce, and entertainment.
Test Your Knowledge: Meta Word Root Quiz
1. What does the root "meta" signify?
2. Which term describes a biological transformation?
3. What does "metadata" describe?
4. Which field studies existence beyond the physical?
5. What does "metastasis" refer to?
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Meta
The root meta embodies the essence of change, evolution, and exploration. From philosophical concepts to biological transformations, it enriches our understanding of the world and our place within it. As technology and culture continue to evolve, meta will remain a vital tool for expressing and navigating the complexities of existence. Let it inspire you to see beyond and embrace the transformative power of learning.















Thank u sir this type of vocabulary words send to me sir