⚔️ Military History: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Military history examines the evolution of warfare, strategy, and military institutions over time. It explores the social, political, and technological contexts that shape conflicts and their outcomes. RC passages on military history often delve into themes such as the causes of wars, the impact of technological advancements, and the role of military leaders. Understanding these concepts equips readers to analyze the complexities of historical conflicts and their broader implications.
🔑 Key Concepts
This guide will explore the following essential military history concepts:
- The Causes of War
- Evolution of Military Technology
- Key Military Strategies and Tactics
- Role of Leadership in Warfare
- Significant Wars and Conflicts
- Impact of Geography on Military History
- Civil-Military Relations
- Military Alliances and Treaties
- Total War vs. Limited War
- The Changing Nature of Modern Warfare
🔍 Detailed Explanations
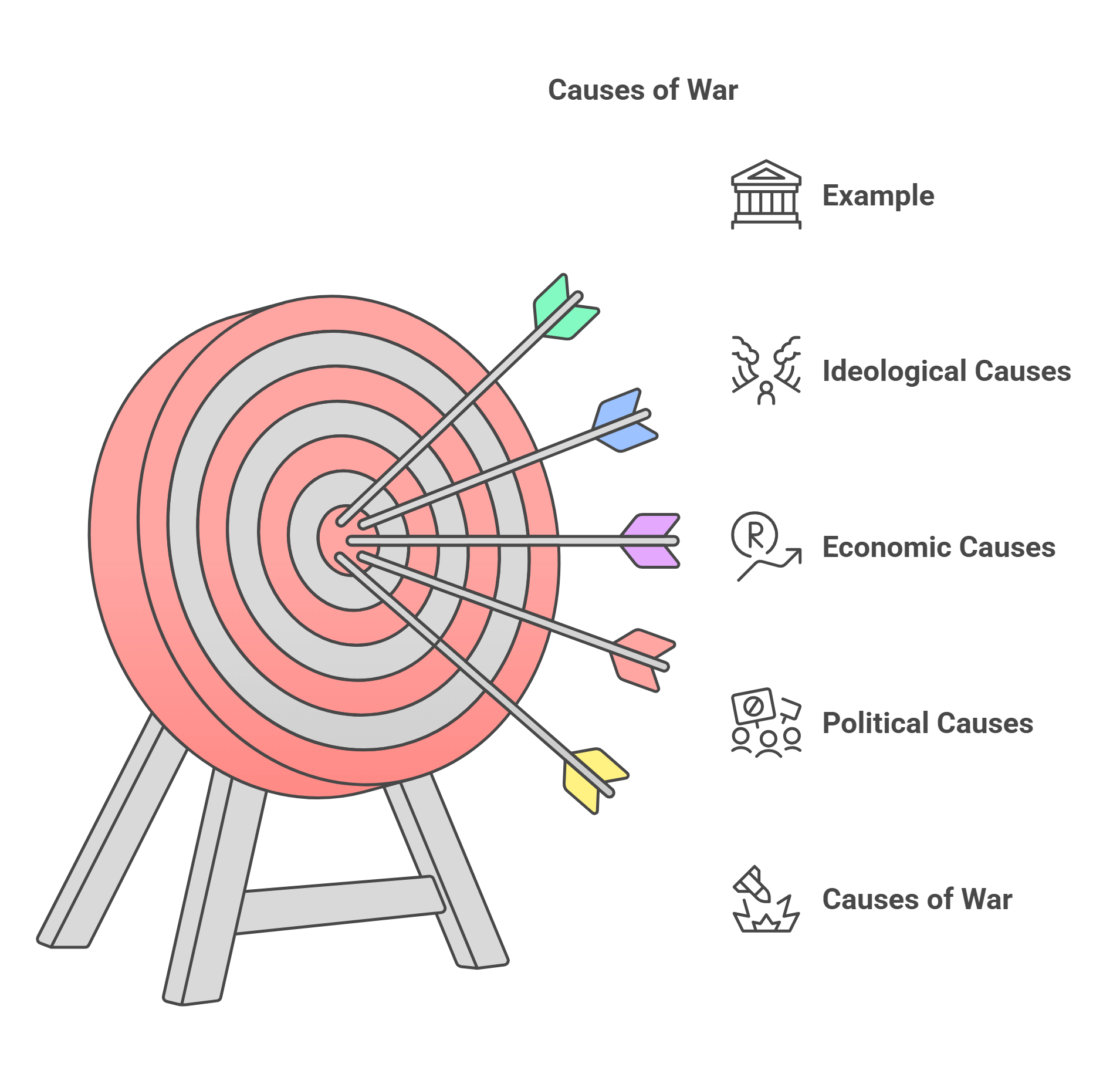
1. The Causes of War
Wars arise from a variety of factors, including political disputes, economic competition, and ideological differences. Understanding the root causes provides insight into how conflicts escalate and are resolved.
- Political Causes: Territorial disputes, power struggles.
- Economic Causes: Competition for resources, trade disputes.
- Ideological Causes: Religious conflicts, revolutionary movements.
- Example: World War I was triggered by political alliances and the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, but deeper causes included nationalism and militarism.
Explained Simply: The causes of war are like the sparks that ignite a fire, often fueled by deeper tensions beneath the surface.
2. Evolution of Military Technology
Advances in technology have profoundly shaped warfare, influencing strategies, tactics, and outcomes.
- Ancient Innovations: The phalanx formation in Greek warfare.
- Industrial Era: Invention of tanks, airplanes, and machine guns.
- Modern Era: Use of drones and cyberwarfare.
- Example: The development of nuclear weapons during World War II changed global military strategy.
Explained Simply: Military technology is like the tools of war, evolving from swords to satellites, each changing the way battles are fought.

3. Key Military Strategies and Tactics
Strategies and tactics determine how wars are planned and executed, influencing the probability of success.
- Strategies: Long-term plans, such as Napoleon’s continental blockade.
- Tactics: Battlefield maneuvers, like guerrilla warfare.
- Example: Blitzkrieg (lightning war) was a key German strategy during World War II, focusing on rapid, concentrated attacks.
Explained Simply: Strategies are like the big-picture game plan, while tactics are the moves made on the field.

4. Role of Leadership in Warfare
Military leaders shape the course of conflicts through their decisions, charisma, and ability to inspire troops.
- Examples of Leaders: Alexander the Great, who expanded his empire through strategic brilliance; Winston Churchill, who led Britain during World War II.
- Characteristics: Strategic thinking, decisiveness, and adaptability.
- Impact: Effective leadership often turns the tide of battles and wars.
Explained Simply: Leadership in warfare is like the captain steering a ship—their vision and decisions guide the course of events.

5. Significant Wars and Conflicts
Understanding key wars and conflicts offers insights into the development of societies and international relations.
- Examples:
- Ancient: The Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta.
- Modern: World War I and II, which reshaped the global order.
- Contemporary: The Cold War, characterized by ideological competition rather than direct conflict.
- Lessons Learned: Highlight the consequences of war and the importance of diplomacy.
Explained Simply: Significant wars are like milestones in history, showing how societies clash, change, and grow.
6. Impact of Geography on Military History
Geography plays a crucial role in determining the strategies and outcomes of conflicts.
- Examples:
- Mountains in Afghanistan have historically hindered invasions.
- Rivers like the Rhine have served as natural defense lines.
- Significance: Terrain, climate, and access to resources shape military decisions.
Explained Simply: Geography in warfare is like the playing field in a game—it defines the rules and strategies.
7. Civil-Military Relations
Civil-military relations refer to the interactions between military forces and civilian governments or societies.
- Key Themes: Civilian control of the military, the role of the military in politics.
- Examples: The U.S. tradition of civilian oversight ensures military accountability.
- Challenges: Military coups or political interference in military operations.
Explained Simply: Civil-military relations are like a partnership, where balance is key to maintaining democracy and security.
8. Military Alliances and Treaties
Alliances and treaties strengthen collective security and define the rules of engagement in international relations.
- Examples: NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and the Treaty of Versailles.
- Benefits: Share resources, deter aggression, and promote stability.
- Challenges: Balancing national interests with alliance commitments.
Explained Simply: Military alliances are like friendships—they provide support but require trust and cooperation.

9. Total War vs. Limited War
Wars can be classified based on their scope and objectives.
- Total War: Involves entire societies and economies, like World War II.
- Limited War: Focuses on specific goals, such as the Falklands War.
- Impact: Total wars demand extensive resources, while limited wars often have localized effects.
Explained Simply: Total war is like an all-out battle, while limited war is more focused and restrained.

10. The Changing Nature of Modern Warfare
Modern warfare has shifted from traditional battlefields to include cyberwarfare, terrorism, and asymmetric conflicts.
- Technologies: Drones, artificial intelligence, and cyberattacks.
- Asymmetric Warfare: Small groups using unconventional tactics against larger forces.
- Examples: Cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure, such as power grids.
Explained Simply: Modern warfare is like a new game with evolving rules, where technology and strategy redefine conflict.

✨ Conclusion
Military history offers valuable lessons about human conflict, leadership, and resilience. By mastering concepts like the causes of war, technological advancements, and civil-military relations, readers can better analyze RC passages on this topic. Understanding military history provides insights into the complexities of warfare and its impact on societies and global politics. ⚔️












