Political Science: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Introduction
Political science explores the systems, ideas, and power dynamics that shape societies and governance. Its importance in reading comprehension lies in its ability to unpack complex issues like governance, international relations, and policy impacts. Passages often analyze ideological conflicts, historical shifts, and the role of political institutions in contemporary debates. Understanding these concepts sharpens analytical skills essential for interpreting arguments and evaluating evidence in RC passages.
Overview
In this guide, we’ll explore these key political science concepts:
- Geopolitical Shifts
- Liberalism vs. Realism
- Role of the United Nations
- Democracy in the Digital Age
- Nationalism
- Political Ideologies
- Electoral Systems
- Public Policy
- Governance
- International Relations
Detailed Explanations
1. Geopolitical Shifts
Geopolitical shifts refer to changes in the global balance of power among nations and regions. These shifts are influenced by economic growth, military capability, technological advancements, and alliances.
- Redistribution of global power.
- Influence of economic and military factors.
- Rise of emerging powers like China and India.
- Impacts on alliances and international relations.
- Reorganization of global trade and security.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine a classroom where one student used to be the strongest, but now more students are becoming just as strong. They all have to figure out how to share the playground and work together without fighting.
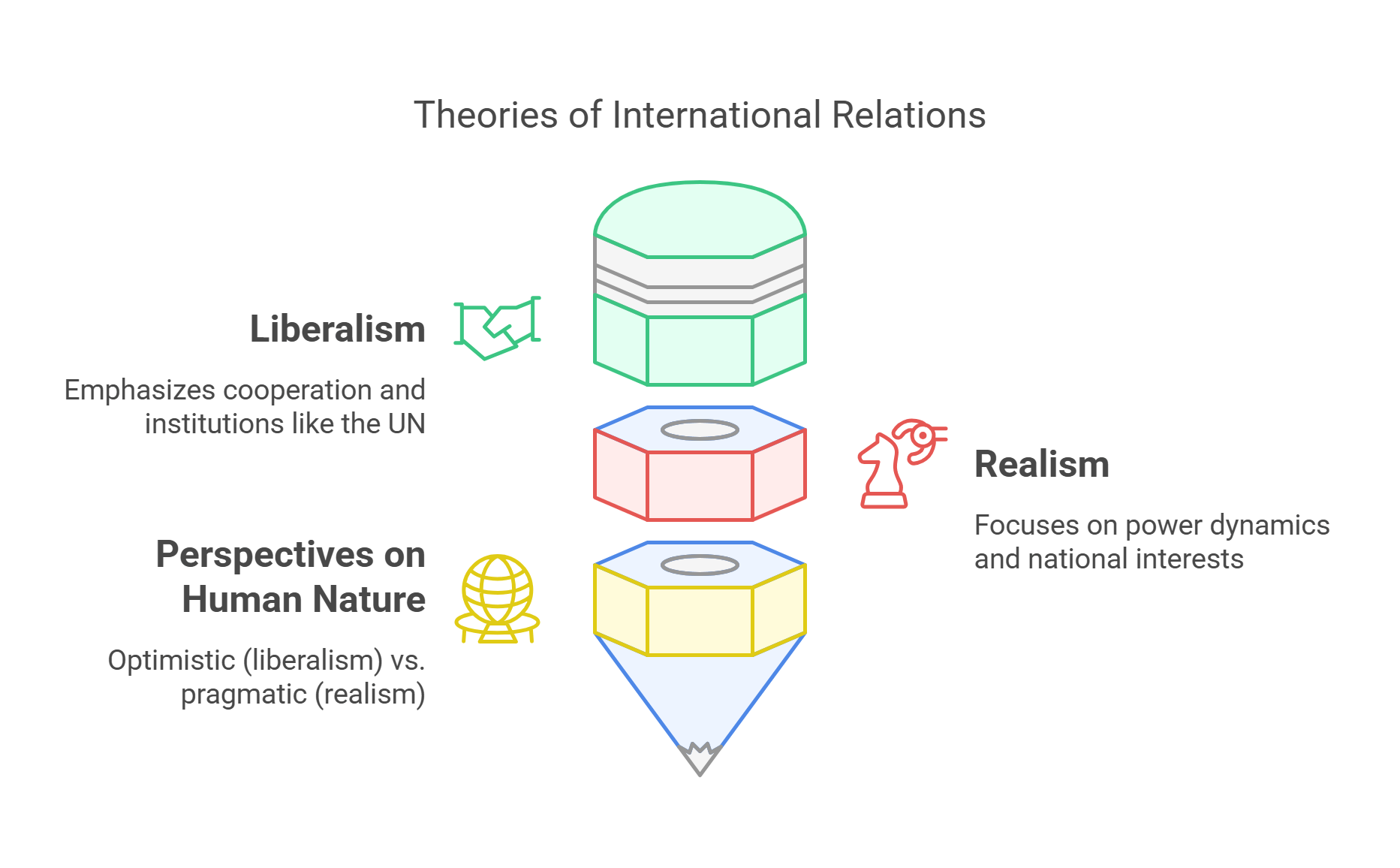
2. Liberalism vs. Realism
Liberalism and realism are two foundational theories in international relations. Liberalism emphasizes cooperation, institutions, and mutual benefits, advocating that nations can work together for collective progress through diplomacy and trade. Realism, on the other hand, focuses on power dynamics, national interests, and competition, arguing that conflict is inevitable in a world driven by self-interest.
- Liberalism: Promotes cooperation and institutions like the UN.
- Realism: Focuses on national power and security.
- Perspectives on human nature: optimistic (liberalism) vs. pragmatic (realism).
- Explains foreign policy decisions and conflicts.
- Interplay in global governance and diplomatic strategies.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Think of countries as kids on a playground. Some kids believe sharing toys and playing together makes everyone happier (liberalism). Others think they need to keep their toys safe because someone might try to take them (realism).
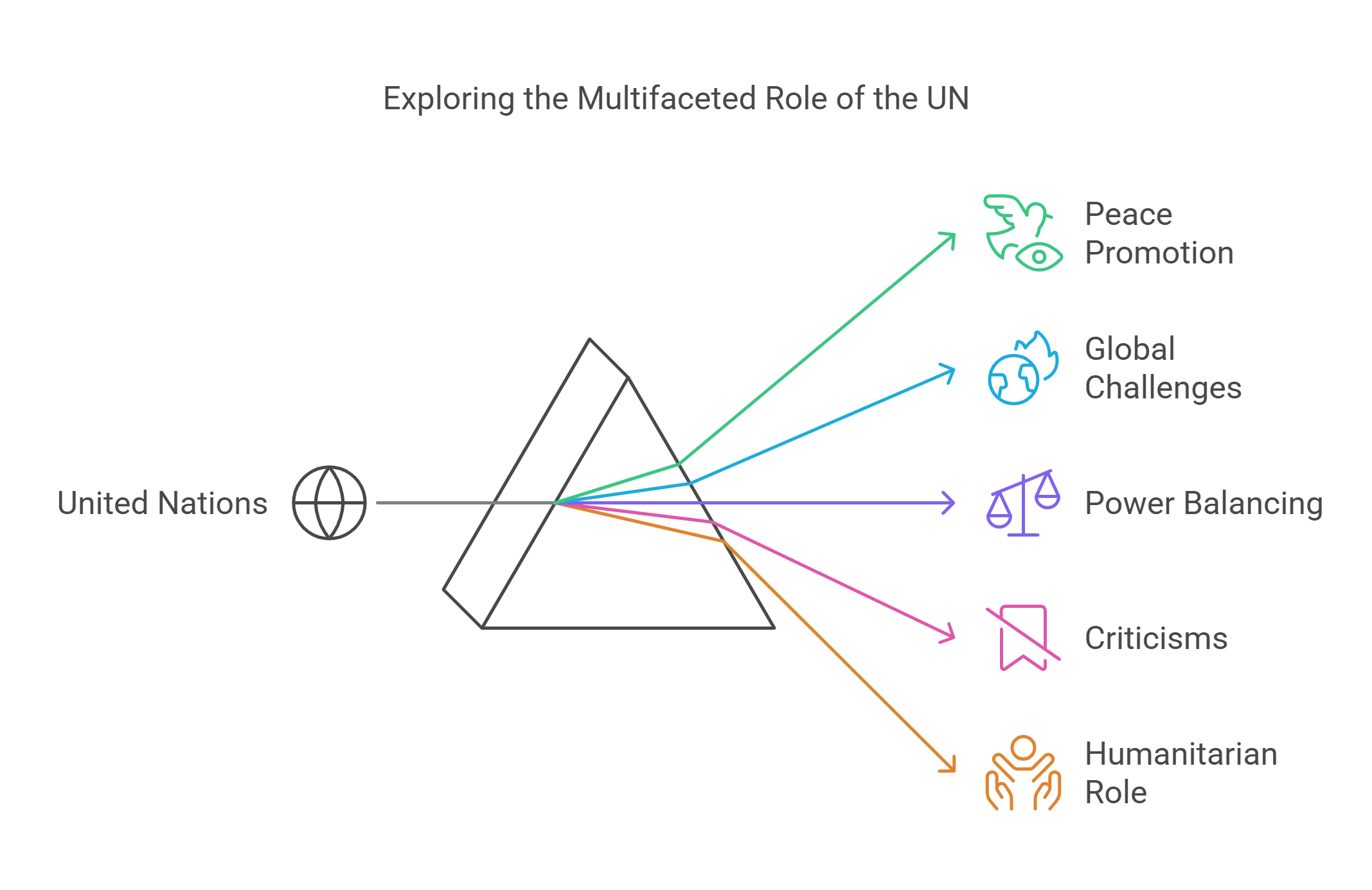
3. Role of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization established to promote peace, security, and cooperation among nations. It serves as a forum where countries address global challenges like climate change, poverty, and conflict resolution.
- Established to promote peace and cooperation post-World War II.
- Addresses global challenges like poverty and climate change.
- Balances collective action with power structures (e.g., veto power).
- Criticized for bureaucracy and limited enforcement mechanisms.
- Plays a key role in humanitarian and development programs.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
The United Nations is like a big team where kids from all over the world come together to solve problems, like cleaning up the playground or stopping fights. But sometimes, some kids with the most toys have more say in what the team does.
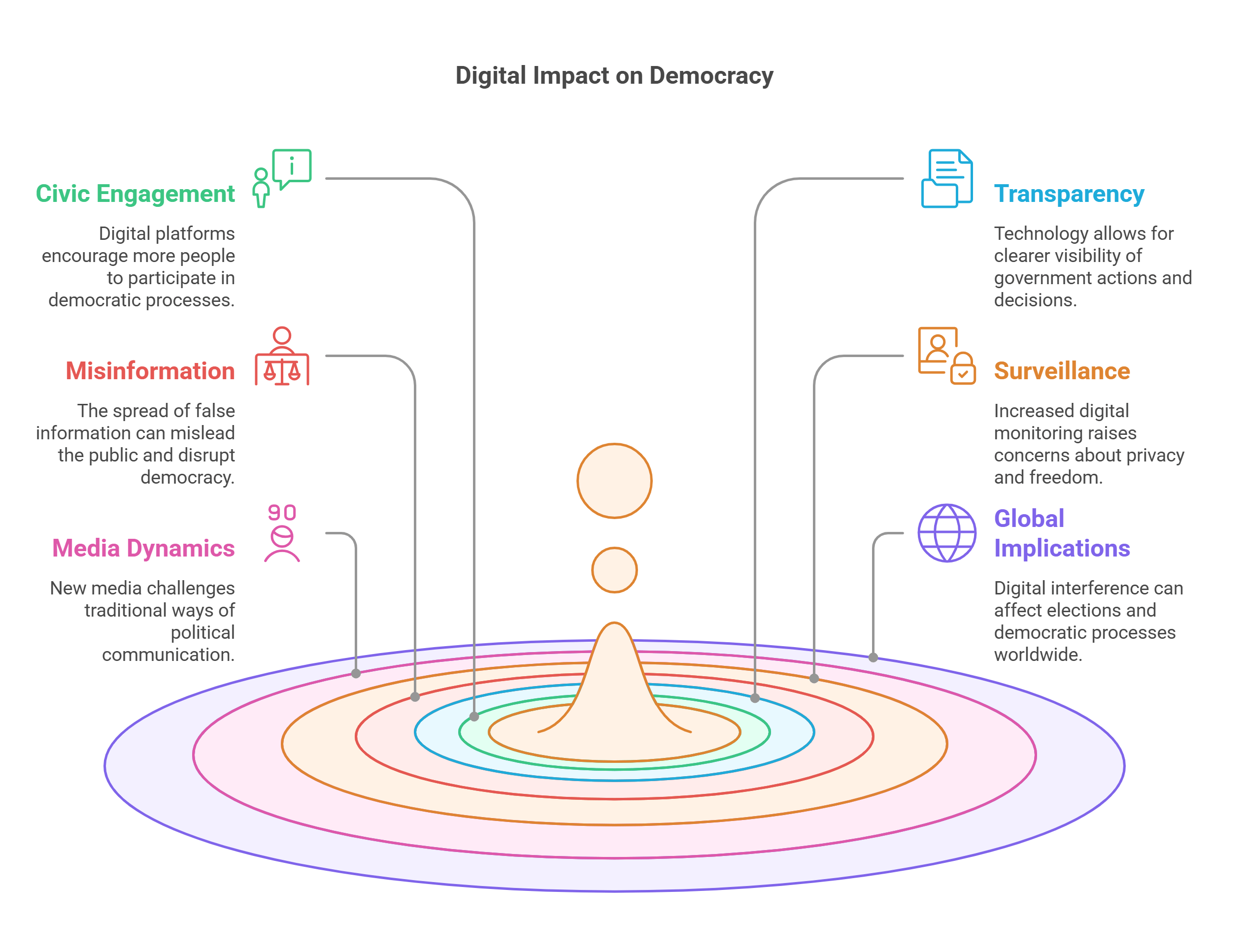
4. Democracy in the Digital Age
The digital age has transformed democracy by enabling faster communication, greater transparency, and wider citizen participation. Social media platforms allow individuals to share opinions, organize protests, and hold governments accountable.
- Enhances civic engagement through digital platforms.
- Facilitates transparency and accountability.
- Risks include misinformation and digital surveillance.
- Challenges traditional democratic norms with new media dynamics.
- Global implications, as seen in online election interference.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine using a phone to tell everyone about a class vote and sharing ideas about what should happen in school. But if some kids spread fake news or shout the loudest, it can confuse everyone and make it hard to decide fairly.
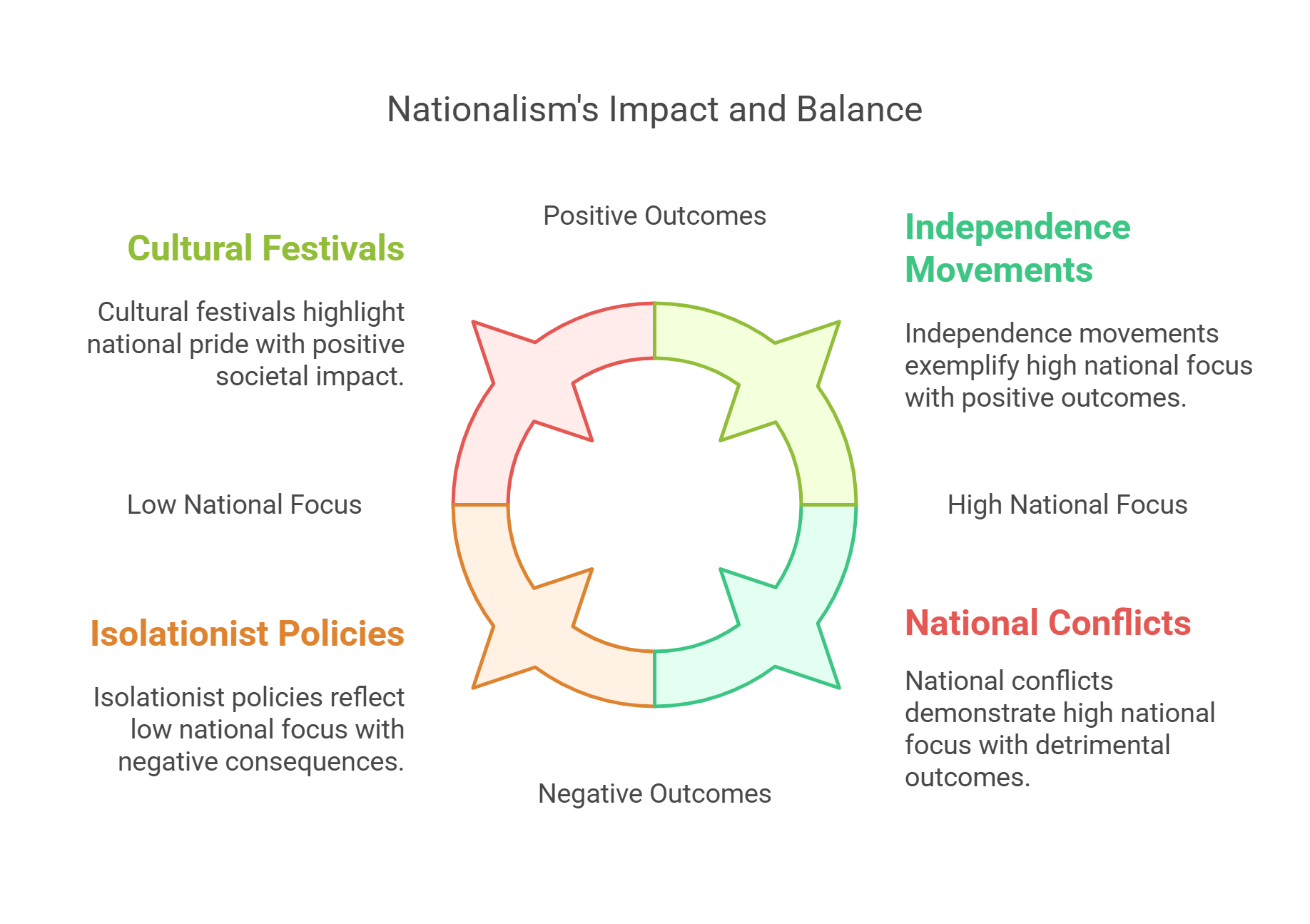
5. Nationalism
Nationalism is the belief in prioritizing a nation’s interests, culture, and identity over global or external influences. It fosters pride and unity but can also lead to exclusion or conflict when pushed to extremes.
- Focus on national identity and pride.
- Drives policies prioritizing domestic interests.
- Can unite or divide societies depending on context.
- Shapes immigration, trade, and foreign relations.
- Key factor in independence movements and conflicts.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like cheering for your school’s team during a game. You want your team to win and do its best, but if you think your team is the only one that matters, it can upset other schools and make the game less fun for everyone.
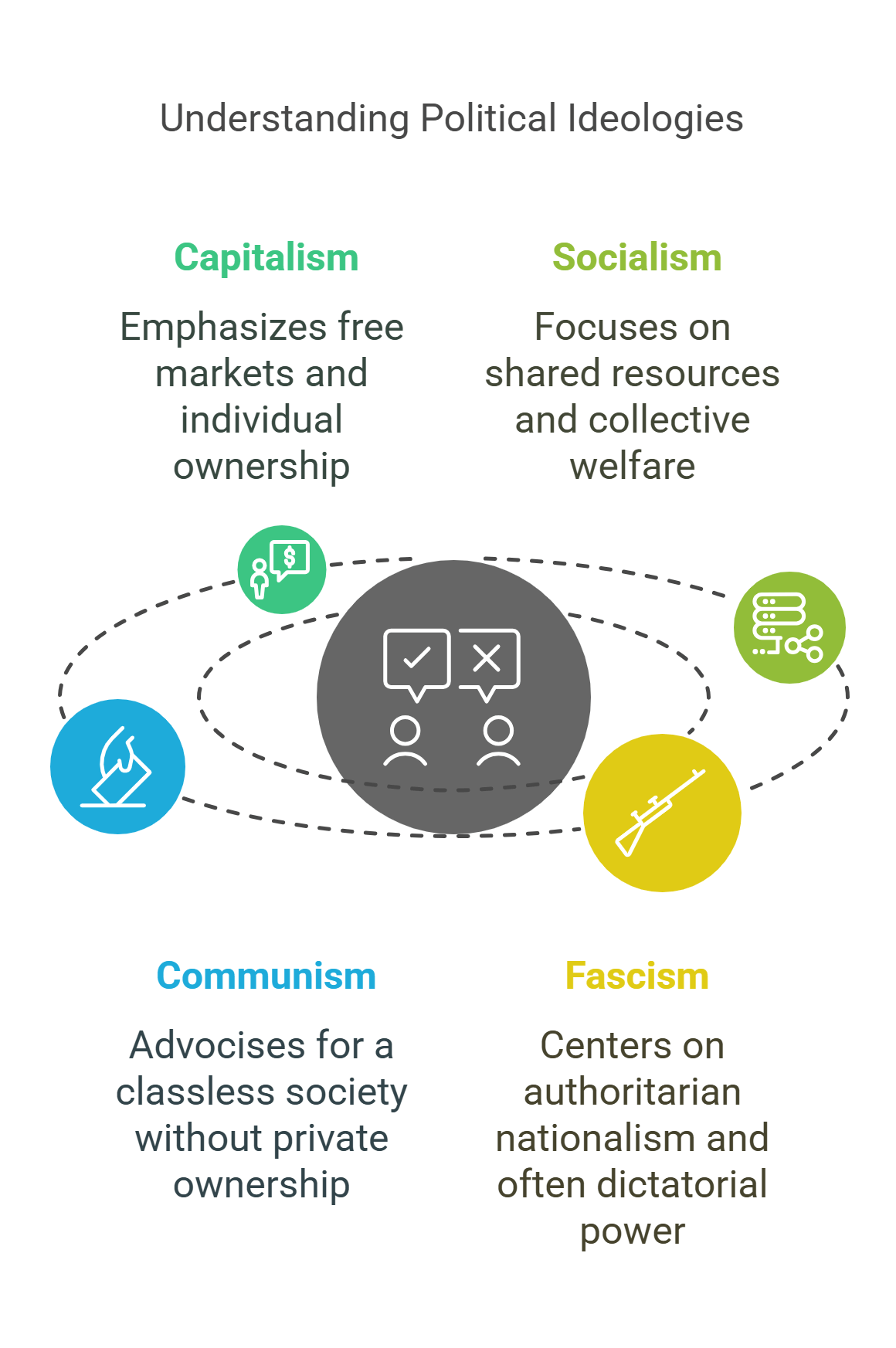
6. Political Ideologies
Political ideologies are systems of beliefs and values that shape how societies are governed. Examples include capitalism, socialism, communism, and fascism. These ideologies guide policies on economics, individual freedoms, and social equality.
- Frameworks of beliefs guiding governance.
- Examples: capitalism (free markets), socialism (shared resources), communism (classless society).
- Impacts policies on economy, freedom, and equality.
- Often central to political debates and conflicts.
- Helps explain historical and contemporary governance models.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Imagine four kids deciding how to share candies: one says everyone should get an equal number (socialism), another says only those who work get any (capitalism), and a third says all candies belong to everyone equally, with no one owning them (communism).
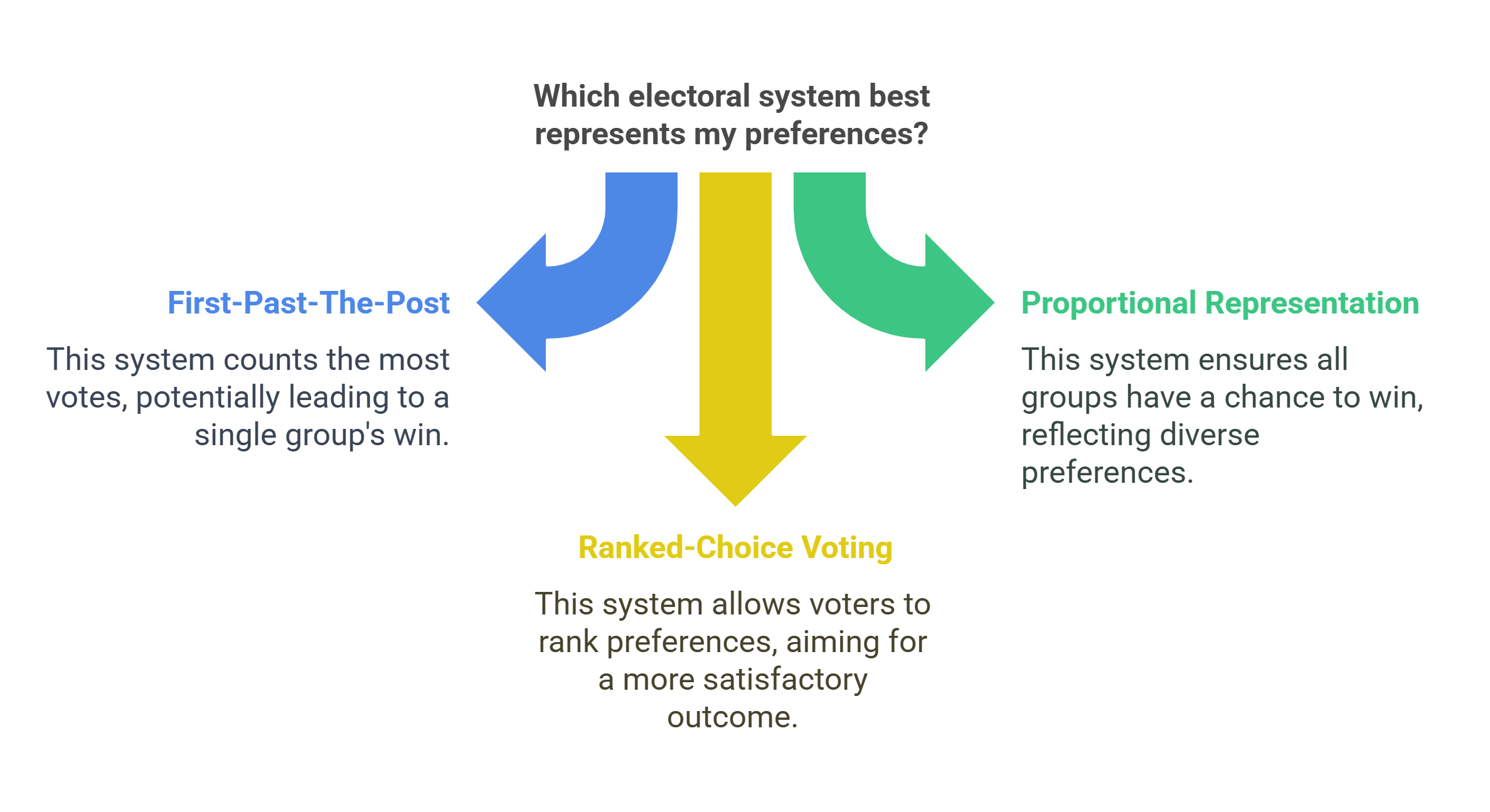
7. Electoral Systems
Electoral systems are the rules and processes through which governments are elected. Examples include proportional representation, first-past-the-post, and ranked-choice voting. These systems influence election outcomes, representation, and governance.
- Rules guiding how votes translate into power.
- Examples: proportional representation, ranked-choice voting.
- Shapes governance and representation.
- Influences voter engagement and political strategy.
- Affects outcomes in democratic systems globally.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
Think of a class election where one method counts the most votes (first-past-the-post), and another tries to make sure everyone’s voice is heard by giving each group a chance to have their favorite win (proportional representation).
8. Public Policy
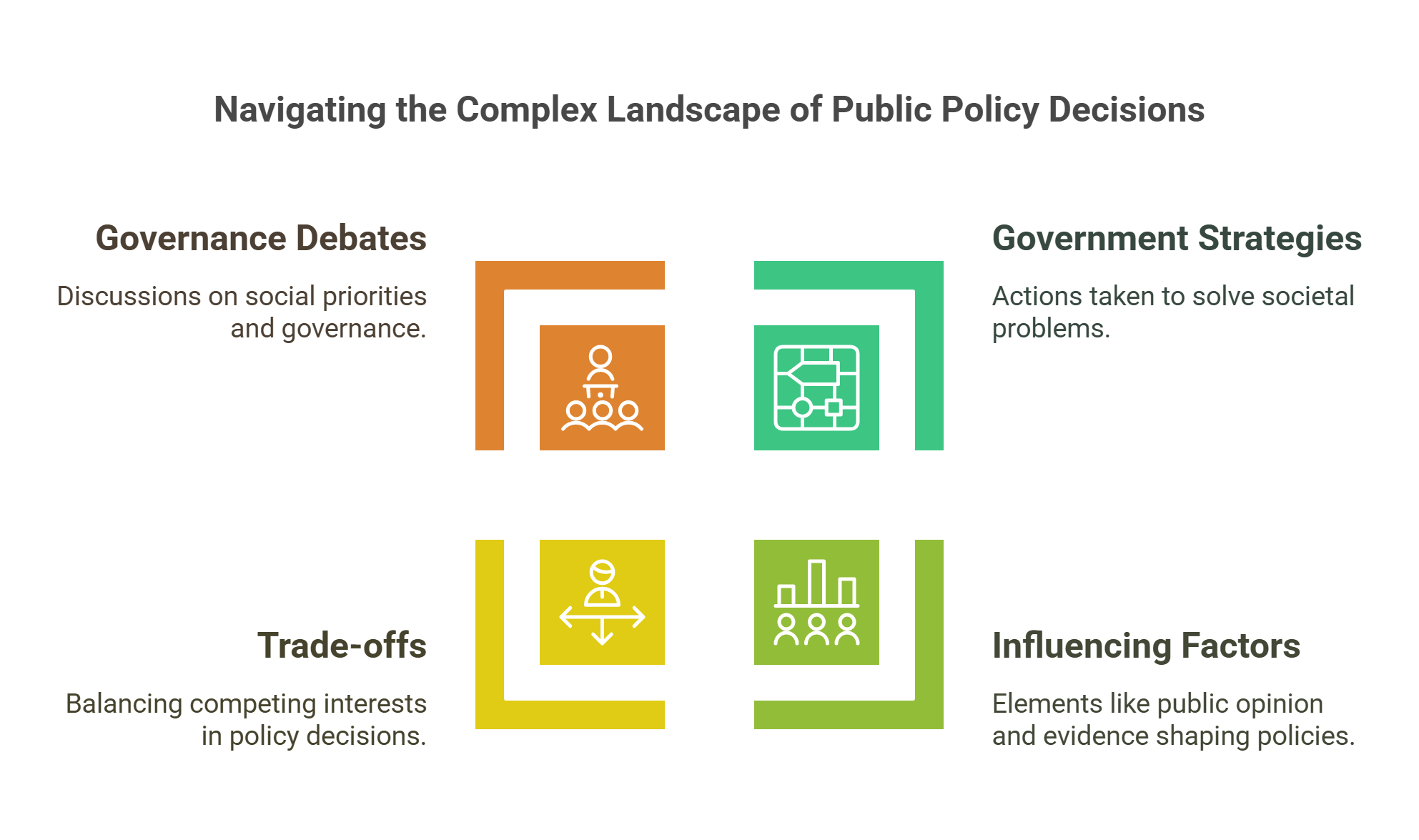
Public policy refers to government actions designed to address societal issues like healthcare, education, and security. Policies are shaped by public needs, expert advice, and political ideologies.
- Government strategies to address societal problems.
- Covers areas like health, education, and environment.
- Influenced by public opinion, evidence, and ideology.
- Involves trade-offs between competing interests.
- Central to debates on governance and social priorities.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like when your teacher makes a rule to solve a problem in class—like limiting how many toys you can bring to make playtime fair for everyone.
9. Governance
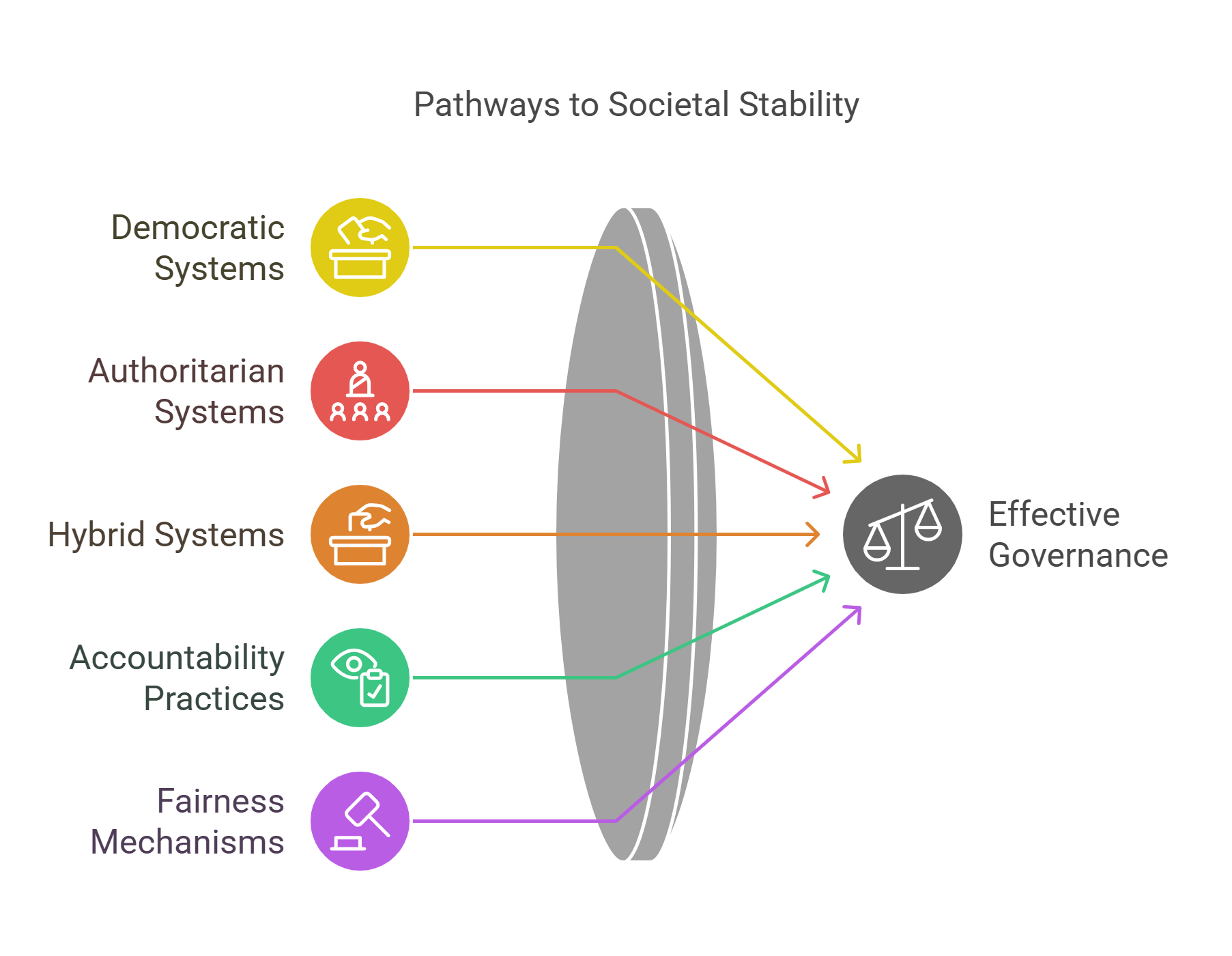
Governance refers to the way societies are organized and managed. It includes systems of rules, institutions, and practices that ensure accountability and fairness.
- Systems and practices for managing societies.
- Types: democratic, authoritarian, hybrid.
- Balances rights, responsibilities, and power.
- Effective governance promotes stability and fairness.
- Often a theme in debates about societal progress and reform.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like how your school is run. If everyone gets to vote on rules, it’s fairer but slower (democracy). If one person makes all the rules, it’s faster but may not be fair (authoritarian).
10. International Relations
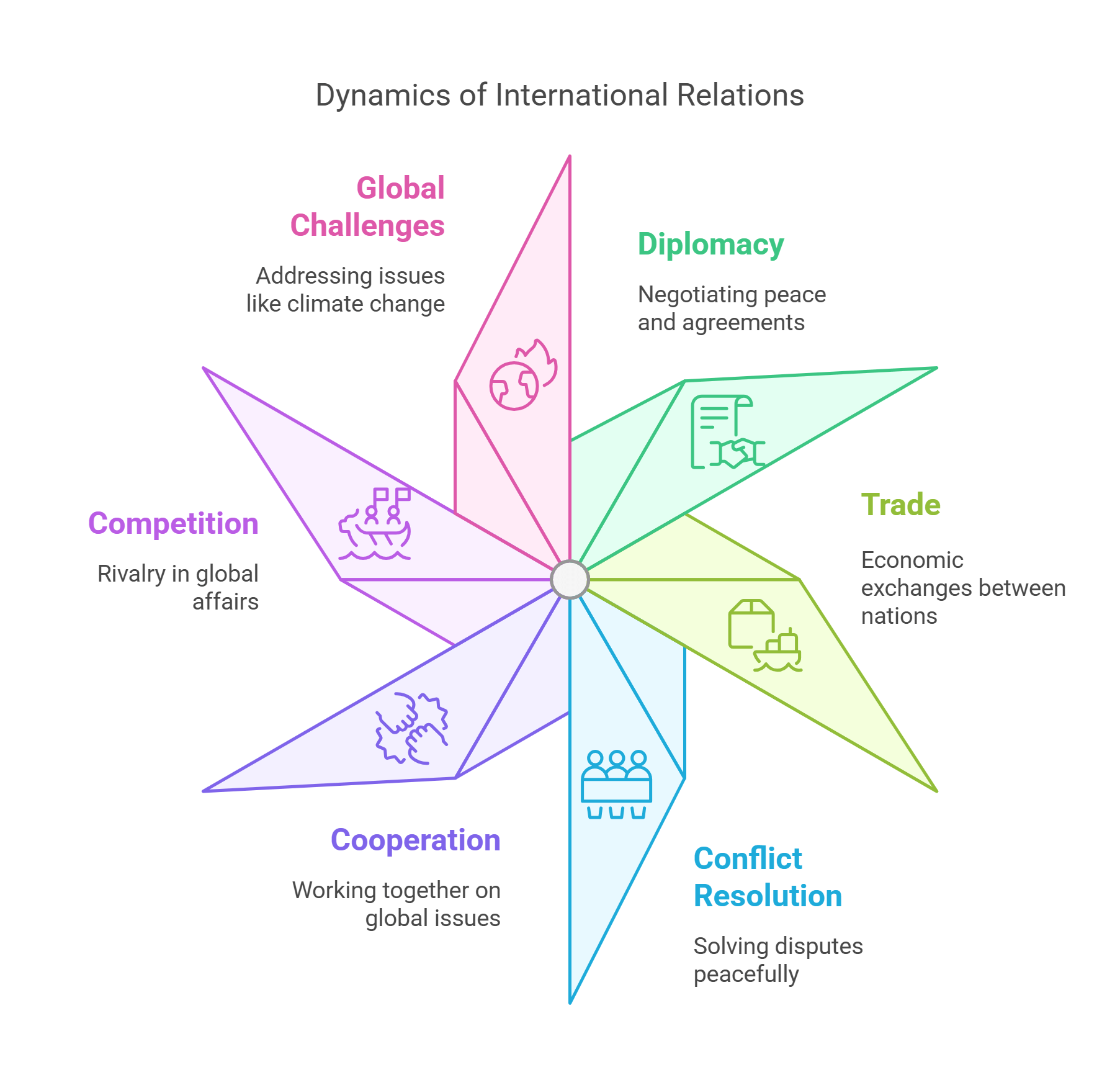
International relations explore how countries interact and cooperate on global issues like trade, security, and climate change. This field analyzes power dynamics, alliances, and conflicts.
- Examines global interactions between nations.
- Includes diplomacy, trade, and conflict resolution.
- Focuses on cooperation and competition.
- Addresses global challenges like climate change.
- Key to analyzing geopolitical arguments in RC passages.
How Would You Explain This to a 10-Year-Old?
It’s like when kids from different classrooms work together to share a playground. They need to agree on rules and solve fights, but sometimes they argue about who gets the biggest slide.
Conclusion
Political science concepts provide a rich lens for analyzing reading comprehension passages. These ideas help uncover the deeper meaning behind arguments about power, governance, and societal structures. By mastering these concepts, you’ll not only excel in RC passages but also develop a clearer understanding of how the world operates.













