Technology in Business: Essential Concepts for Reading Comprehension
Technology has revolutionized the business landscape, driving efficiency, innovation, and global connectivity. From automating manufacturing processes to enhancing customer engagement through AI, businesses leverage technology to adapt to a rapidly evolving marketplace. RC passages on this topic often explore the strategic use of tools, trends, and innovations. Understanding these concepts equips readers to analyze how technology transforms operations, decision-making, and sustainability in modern business.
🔑 Key Concepts
This guide explores the following essential concepts in technology in business:
- E-Commerce
- Cloud Computing in Business
- AI in Marketing
- Blockchain for Supply Chain
- Automation in Manufacturing
- CRM Tools
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
- FinTech
- Remote Work Technology
- Green Tech for Corporations
🔍 Detailed Explanations
1. E-Commerce
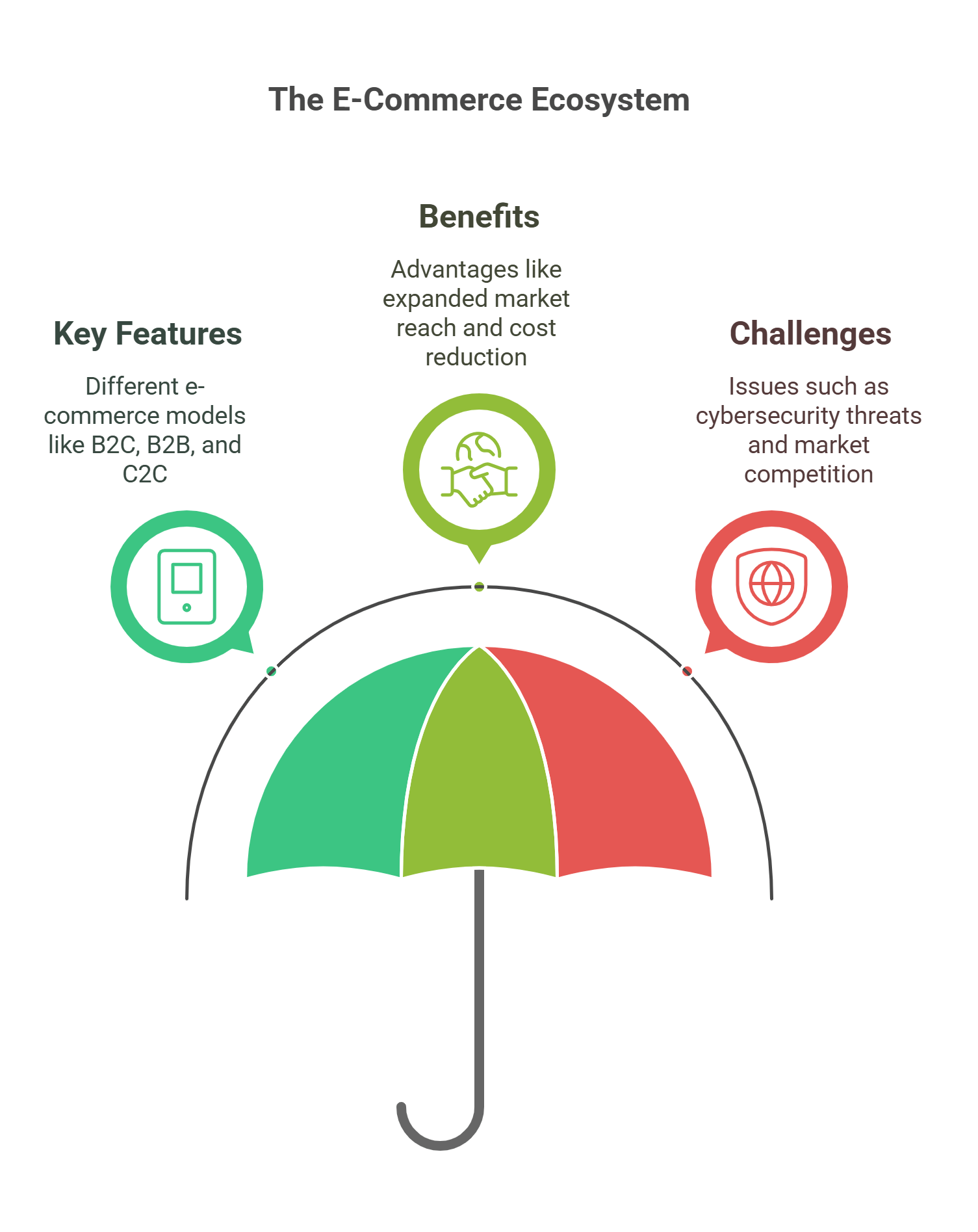
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services online. It has transformed retail by enabling businesses to reach global markets and offering consumers convenience and choice.
- Key Features:
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Direct sales to customers (e.g., Amazon, eBay).
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses (e.g., Alibaba).
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Platforms like Etsy and Depop facilitate peer-to-peer transactions.
- Benefits:
- Expands market reach and reduces overhead costs.
- Provides data analytics for personalized marketing.
- Challenges:
- Cybersecurity threats like fraud and data breaches.
- Competition in an oversaturated market.
Example: Shopify enables small businesses to set up online stores, democratizing access to e-commerce.
Explained Simply: E-commerce is like opening a shop that’s always online and accessible from anywhere.
2. Cloud Computing in Business
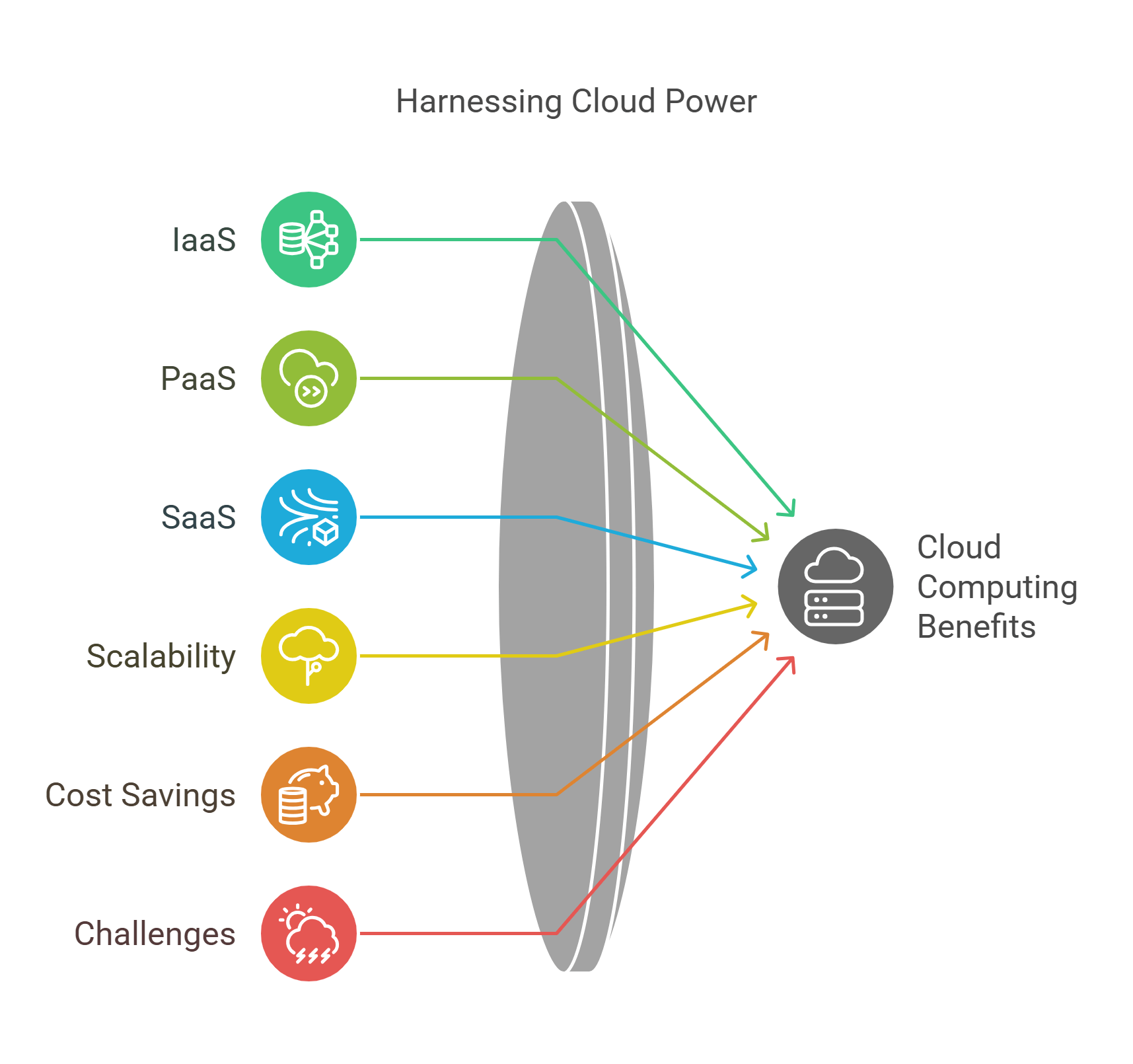
Cloud computing allows businesses to store, process, and manage data on remote servers accessed via the internet, reducing reliance on physical infrastructure.
- Types of Cloud Computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources (e.g., Amazon Web Services).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers tools for developing and managing applications (e.g., Google Cloud Platform).
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft 365).
- Benefits:
- Scalability to match business needs.
- Cost savings on hardware and maintenance.
- Challenges:
- Data security concerns in shared environments.
- Dependence on reliable internet connectivity.
Example: Netflix uses cloud computing to stream content globally, scaling its services based on user demand.
Explained Simply: Cloud computing is like renting storage and computing power instead of buying your own hardware.
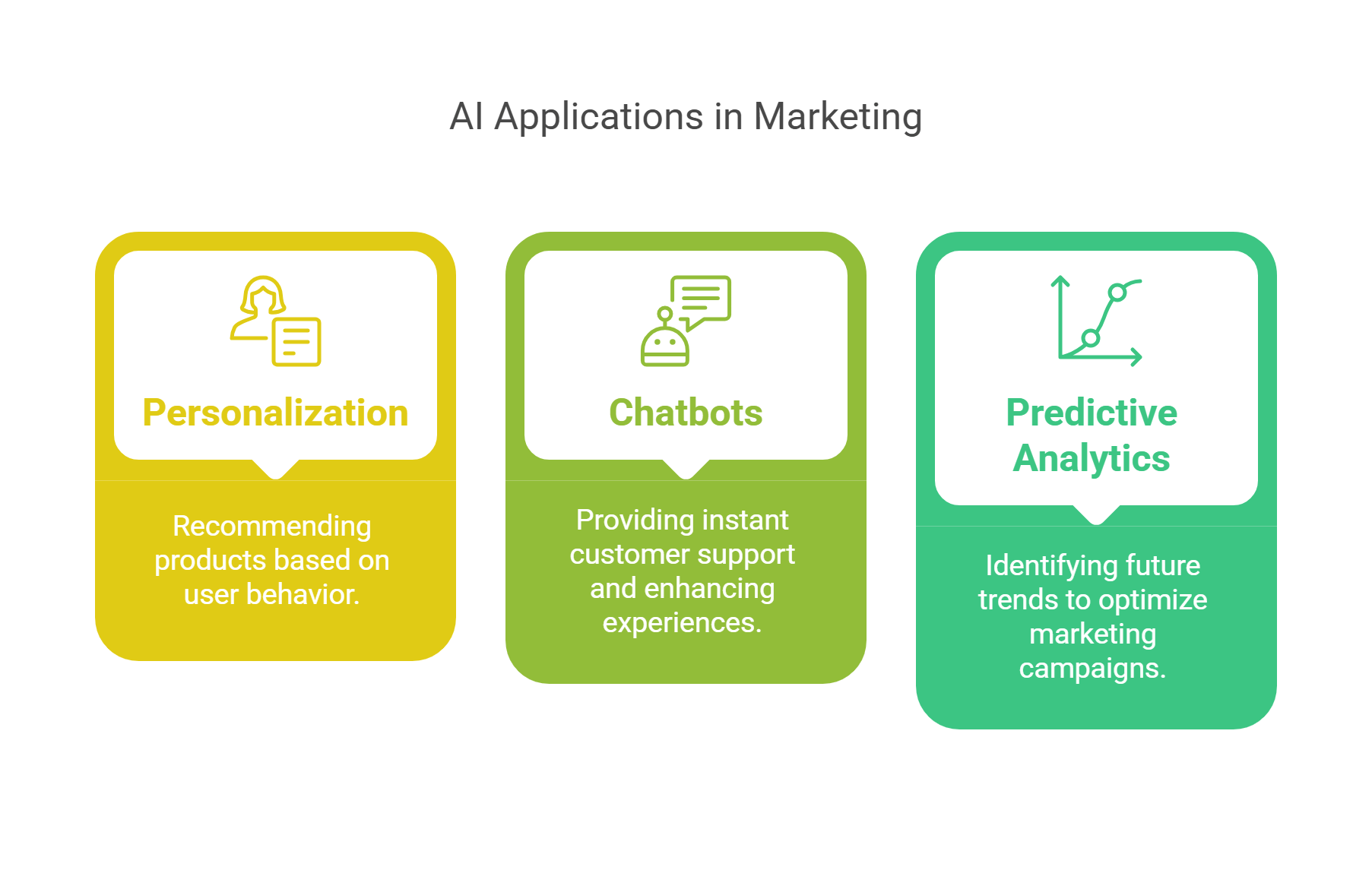
3. AI in Marketing
Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances marketing strategies by analyzing data, predicting trends, and automating customer engagement.
- Key Applications:
- Personalization: Recommending products or content based on user behavior.
- Chatbots: Providing instant customer support and improving user experiences.
- Predictive Analytics: Identifying future trends to optimize campaigns.
- Benefits:
- Increases efficiency and ROI by targeting the right audience.
- Enhances customer satisfaction through tailored interactions.
Example: Spotify’s recommendation algorithm uses AI to curate personalized playlists based on listening habits.
Explained Simply: AI in marketing is like having a smart assistant that predicts what customers want and helps deliver it.
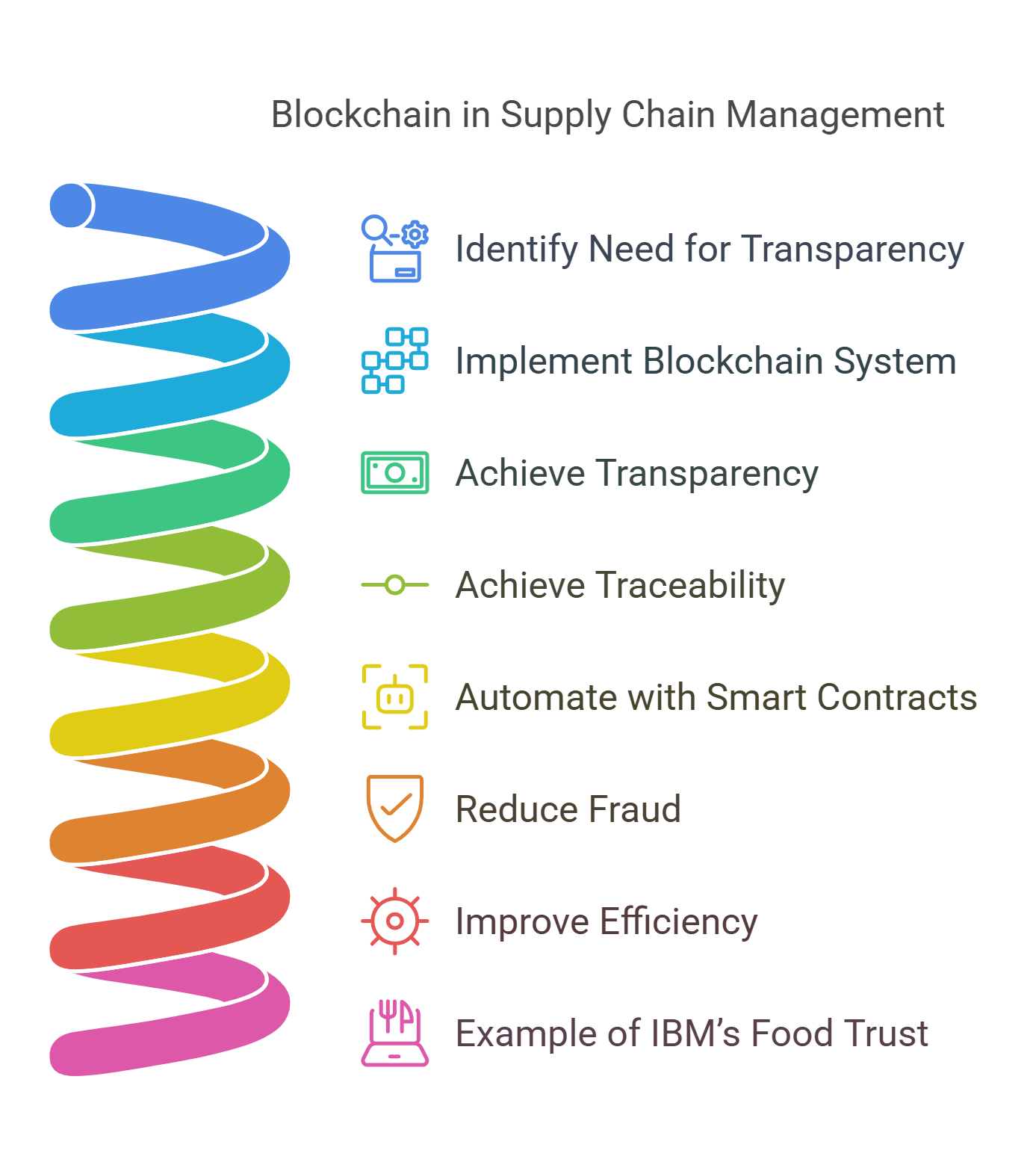
4. Blockchain for Supply Chain
Blockchain technology offers a secure, transparent, and decentralized system for tracking goods and verifying transactions in supply chains.
- Key Features:
- Transparency: Immutable records accessible to all stakeholders.
- Traceability: Tracks every step in the supply chain, from raw materials to delivery.
- Smart Contracts: Automates processes like payments upon delivery verification.
- Benefits:
- Reduces fraud and counterfeiting in industries like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods.
- Improves efficiency by eliminating intermediaries.
Example: IBM’s Food Trust blockchain ensures the traceability of food items, enhancing safety and trust.
Explained Simply: Blockchain in supply chains is like a digital ledger that keeps everyone honest and informed.
5. Automation in Manufacturing
Automation in manufacturing uses robotics, AI, and IoT to perform repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce human error.
- Key Technologies:
- Industrial Robots: Perform assembly, welding, and packaging tasks.
- IoT Sensors: Monitor equipment performance and prevent downtime.
- 3D Printing: Enables rapid prototyping and on-demand production.
- Benefits:
- Increases productivity and consistency.
- Reduces costs by optimizing resource use.
- Challenges:
- Potential job displacement in manual roles.
- High initial investment in automation technologies.
Example: Tesla’s Gigafactories use advanced robotics to streamline electric vehicle production.
Explained Simply: Automation is like having tireless workers who deliver precision and speed around the clock.
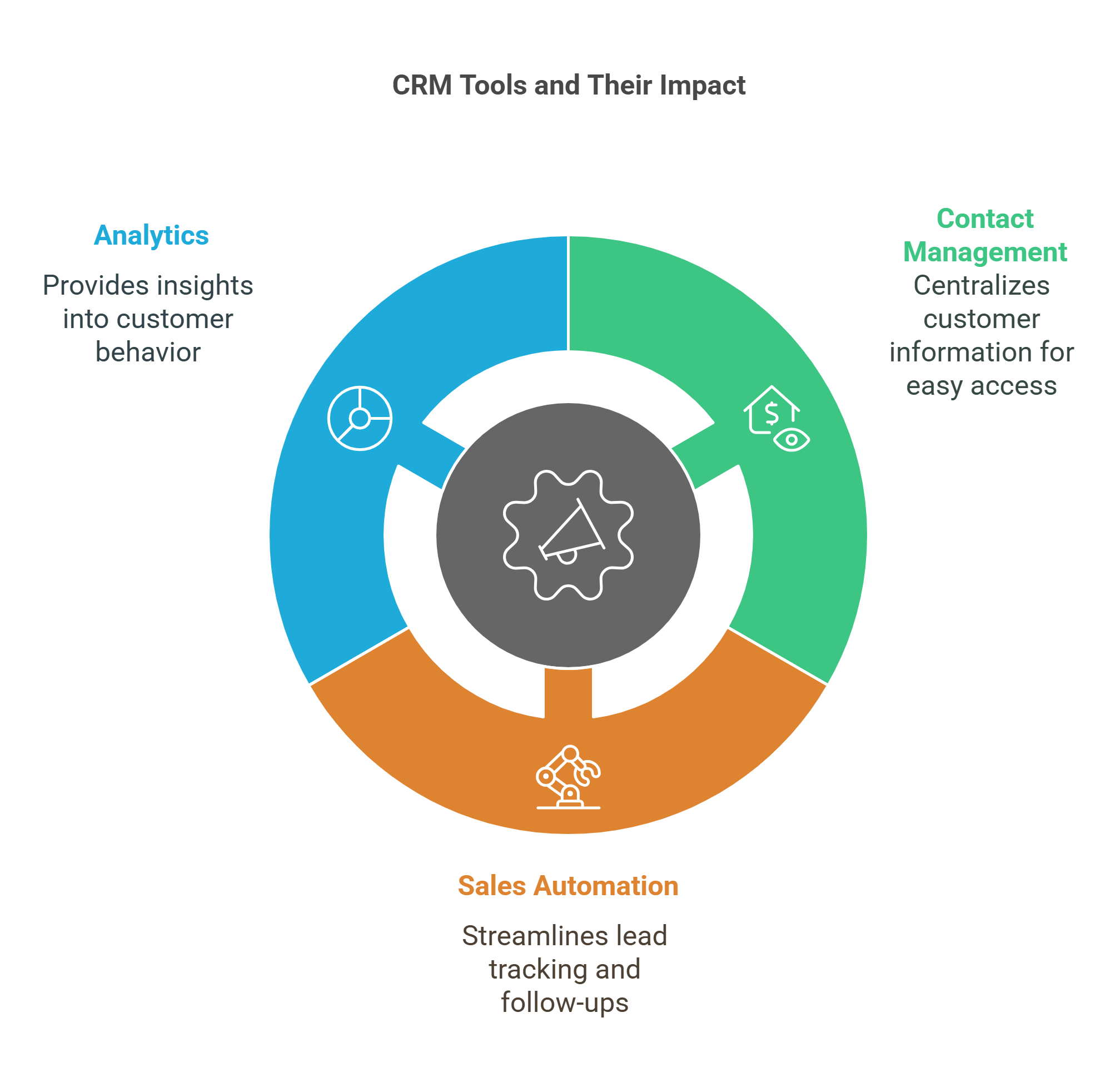
6. CRM Tools
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools are software solutions designed to manage interactions and relationships with customers. They help businesses track customer data, improve sales processes, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Key Features:
- Contact Management: Centralized databases for storing customer information.
- Sales Automation: Streamlining tasks like lead tracking and follow-ups.
- Analytics: Insights into customer behavior and preferences for better decision-making.
- Benefits:
- Improves customer retention through personalized engagement.
- Boosts productivity by automating routine tasks.
Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM are widely used tools in diverse industries.
Explained Simply: CRM tools are like digital diaries for businesses, helping them remember every customer and optimize their experience.
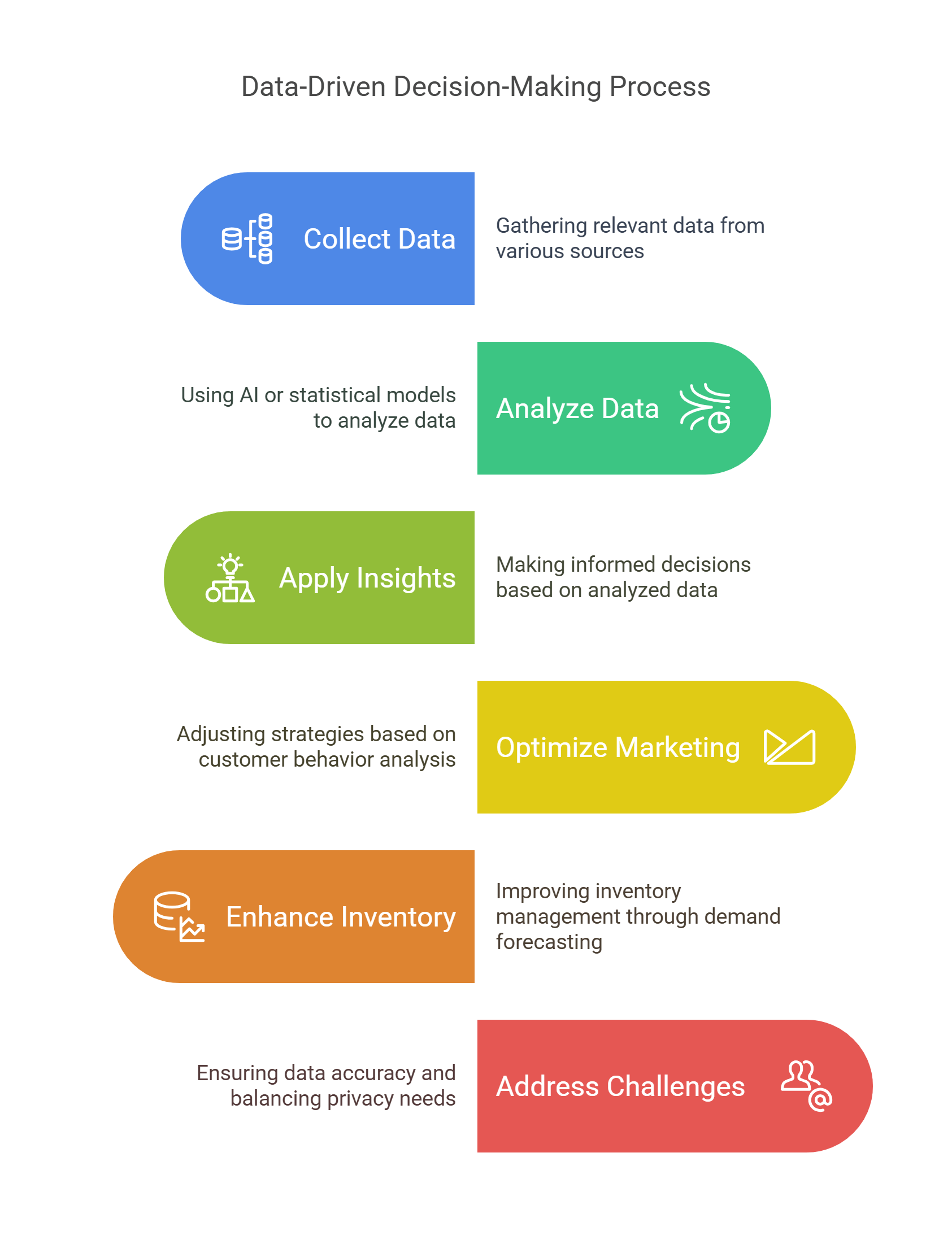
7. Data-Driven Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making (DDDM) involves using data analytics to guide business strategies and operations. It prioritizes evidence-based approaches over intuition or guesswork.
- Steps in DDDM:
- Collect relevant data from various sources.
- Analyze data using tools like AI or statistical models.
- Apply insights to make informed decisions.
- Applications:
- Optimizing marketing campaigns based on customer behavior.
- Enhancing inventory management through demand forecasting.
- Challenges:
- Ensuring data accuracy and avoiding biases in analysis.
- Balancing data privacy with operational needs.
Example: Amazon’s recommendation engine uses customer data to suggest products, driving higher sales and engagement.
Explained Simply: Data-driven decision-making is like having a crystal ball powered by facts and figures.
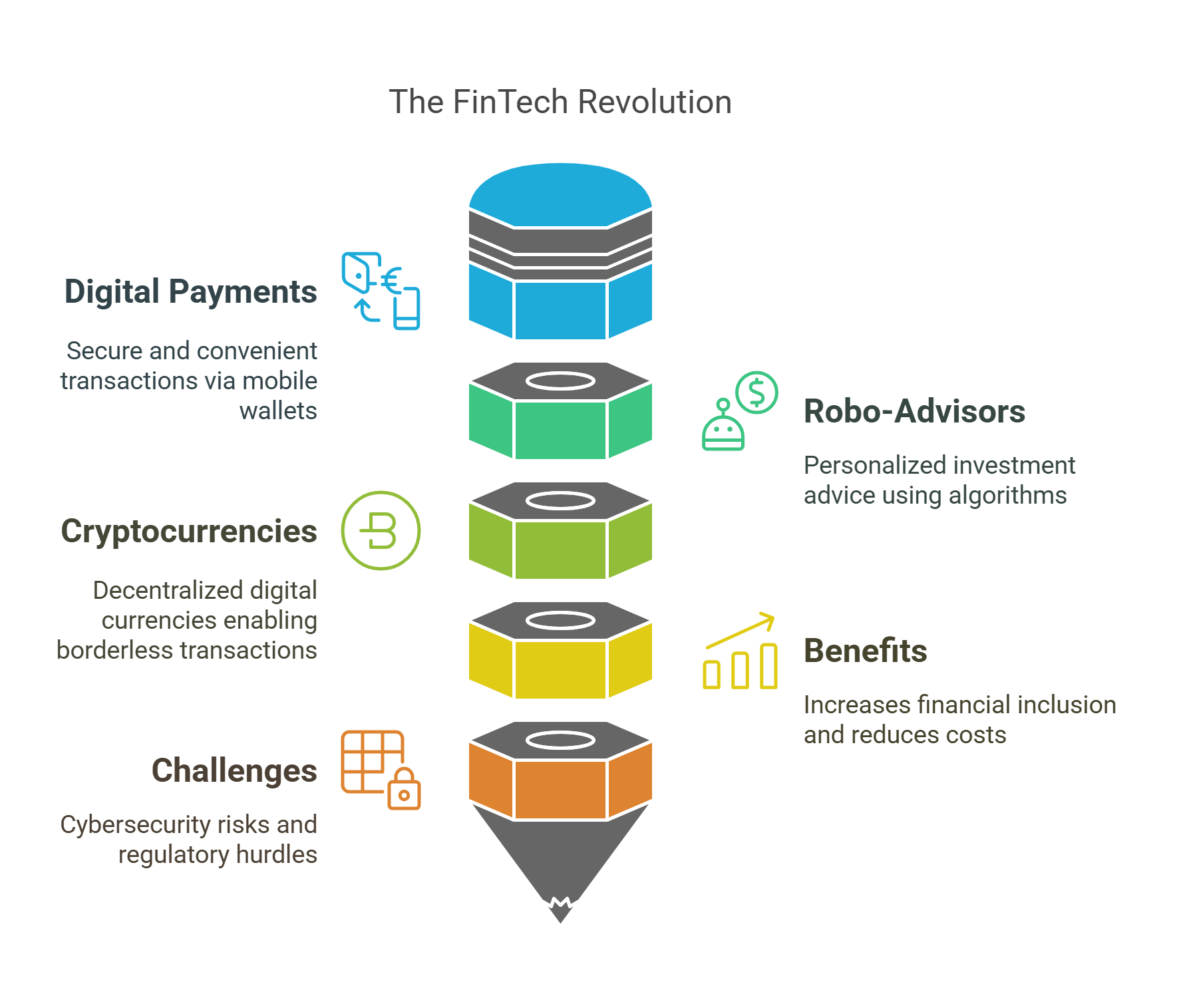
8. FinTech
Financial Technology (FinTech) encompasses innovations that improve and automate financial services, revolutionizing banking, investing, and payment systems.
- Key Innovations:
- Digital Payments: Mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, PayPal) offer secure and convenient transactions.
- Robo-Advisors: Use algorithms to provide personalized investment advice.
- Cryptocurrencies: Decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin enable borderless transactions.
- Benefits:
- Increases financial inclusion by offering accessible services.
- Reduces costs and enhances efficiency for businesses and consumers.
- Challenges:
- Cybersecurity risks and regulatory hurdles.
- Volatility in emerging technologies like cryptocurrencies.
Example: Stripe streamlines online payment processing for businesses globally.
Explained Simply: FinTech is like modernizing your wallet, making financial services smarter and faster.
9. Remote Work Technology
Remote work technology enables employees to collaborate and perform tasks outside traditional office settings. It has become integral to business continuity, especially after the global shift during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Key Tools:
- Video Conferencing: Platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams facilitate virtual meetings.
- Collaboration Software: Tools like Slack and Trello improve communication and task management.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox allow access to files from anywhere.
- Benefits:
- Increases flexibility and work-life balance for employees.
- Reduces overhead costs by minimizing the need for physical office spaces.
- Challenges:
- Maintaining team cohesion and productivity in virtual environments.
- Addressing cybersecurity risks in remote setups.
Example: Remote work technologies enabled companies like Twitter to transition to permanent remote work models.
Explained Simply: Remote work technology is like taking your office anywhere, as long as there’s Wi-Fi.
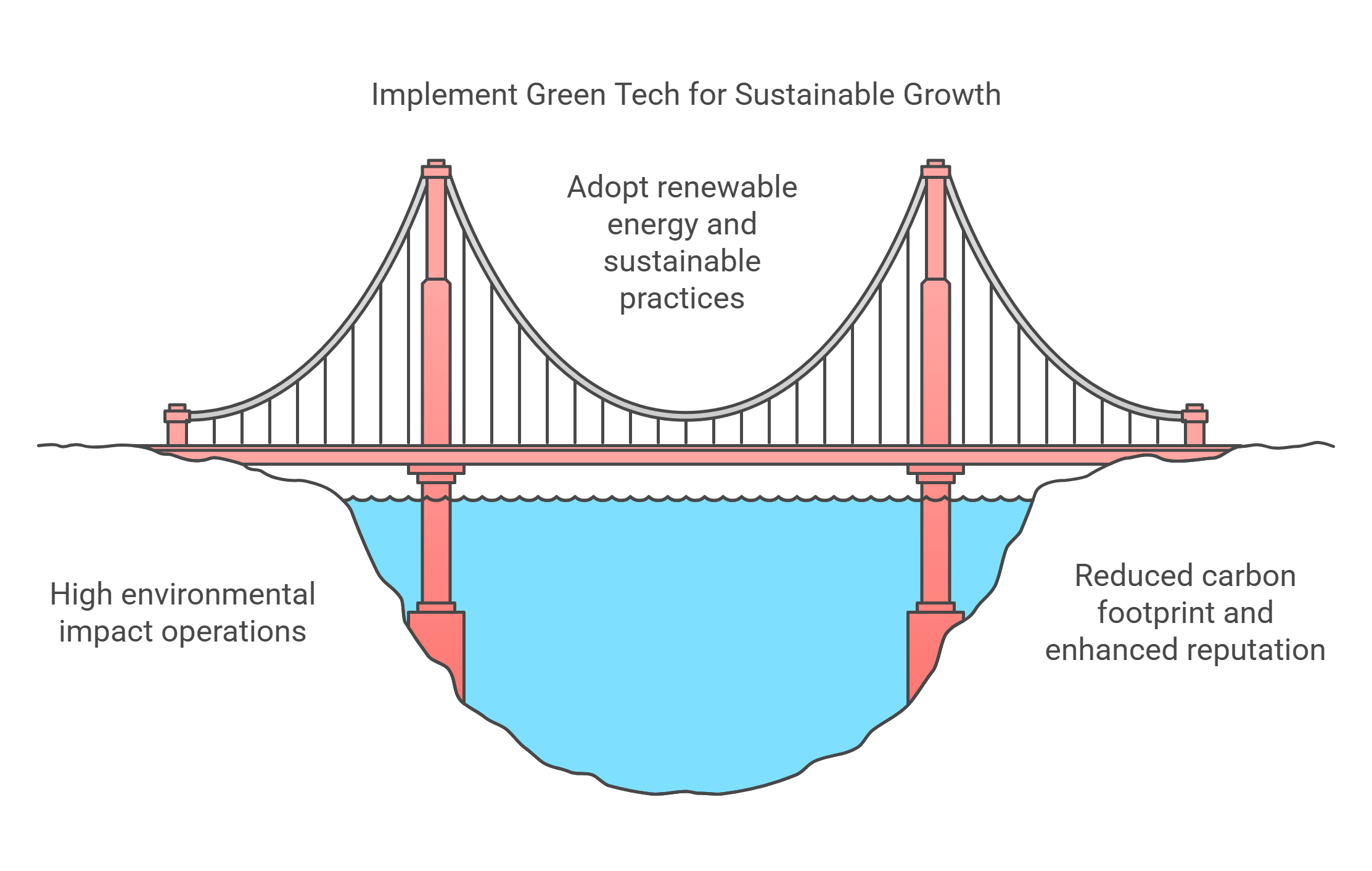
10. Green Tech for Corporations
Green technology focuses on reducing the environmental impact of business operations through sustainable innovations. It is crucial for meeting corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals and addressing climate change.
- Key Applications:
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels and wind turbines power corporate facilities.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart lighting and HVAC systems reduce energy consumption.
- Sustainable Materials: Biodegradable packaging and recycled materials in production.
- Benefits:
- Reduces operational costs and enhances brand reputation.
- Helps corporations comply with environmental regulations.
- Challenges:
- High upfront investment in green technologies.
- Balancing sustainability with profitability in competitive markets.
Example: Google operates carbon-neutral data centers powered by renewable energy.
Explained Simply: Green tech is like running your business on clean energy, ensuring profits and planet coexist.
✨ Conclusion
Technology drives innovation and efficiency across industries, transforming business practices in areas like e-commerce, supply chain management, and sustainability. By exploring concepts such as CRM tools, FinTech, and green tech, readers can critically analyze RC passages and appreciate how technology reshapes the modern business world.












