Ab: The Root of Distancing in Language and Thought
Discover the versatility and significance of the root "ab," meaning "away from," in the development of words that shape our understanding of separation, deviation, and abstraction. Explore how "ab" enriches fields ranging from philosophy to medicine.
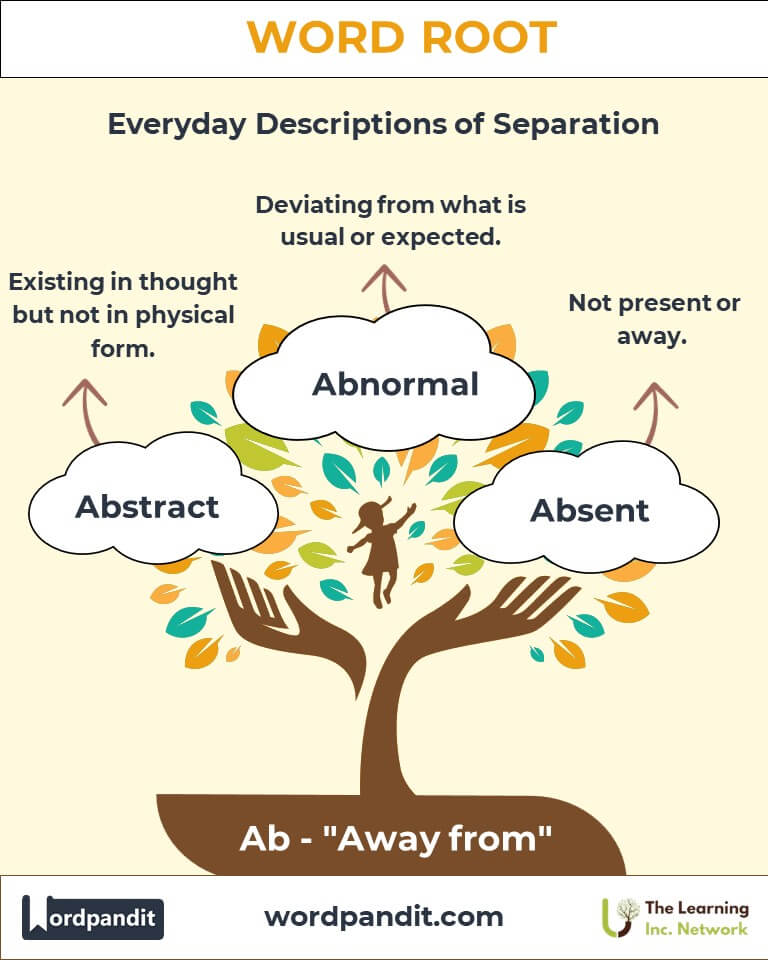
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Role of Ab- in Language
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Ab
- Common Ab-Related Terms
- Ab Through Time
- Ab in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Ab in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Ab Root
- The Ab Family Tree
- FAQs About the Ab Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Ab Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Lingering Legacy of "Ab"
Introduction: The Essence of "Ab"
Have you ever wondered why "abstract" ideas feel distant from reality or why "abnormal" describes deviations from the norm? These concepts stem from the Latin root "ab," meaning "away from." Pronounced simply as "ab," this root serves as the foundation for a rich vocabulary centered on distancing, separation, and divergence. Whether describing a physical departure or a conceptual leap, "ab" bridges language and thought, enriching how we express movement and deviation.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "ab" originates from Latin, where it conveyed the sense of "away from" or "off." In classical times, "ab" prefixed words to denote removal or distance, such as "abstain" (to hold away from) and "abduct" (to lead away). As Latin evolved into modern European languages, "ab" retained its core meaning, branching into English vocabulary through both direct borrowings and adaptations in scientific and philosophical contexts.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Ab"
To remember "ab," think of an arrow pointing away from a central point, symbolizing separation or movement. Here's a vivid mnemonic:
“Ab takes you away—abstract from reality, abnormal from the usual.”
Common "Ab"-Related Terms
- Abstract (ab-strakt)
- Definition: Existing in thought or as an idea but not having a physical or concrete existence.
- Example: "Her abstract painting left viewers to interpret its meaning for themselves."
- Abnormal (ab-nor-mal)
- Definition: Deviating from what is normal or usual.
- Example: "The doctor noted an abnormal growth during the examination."
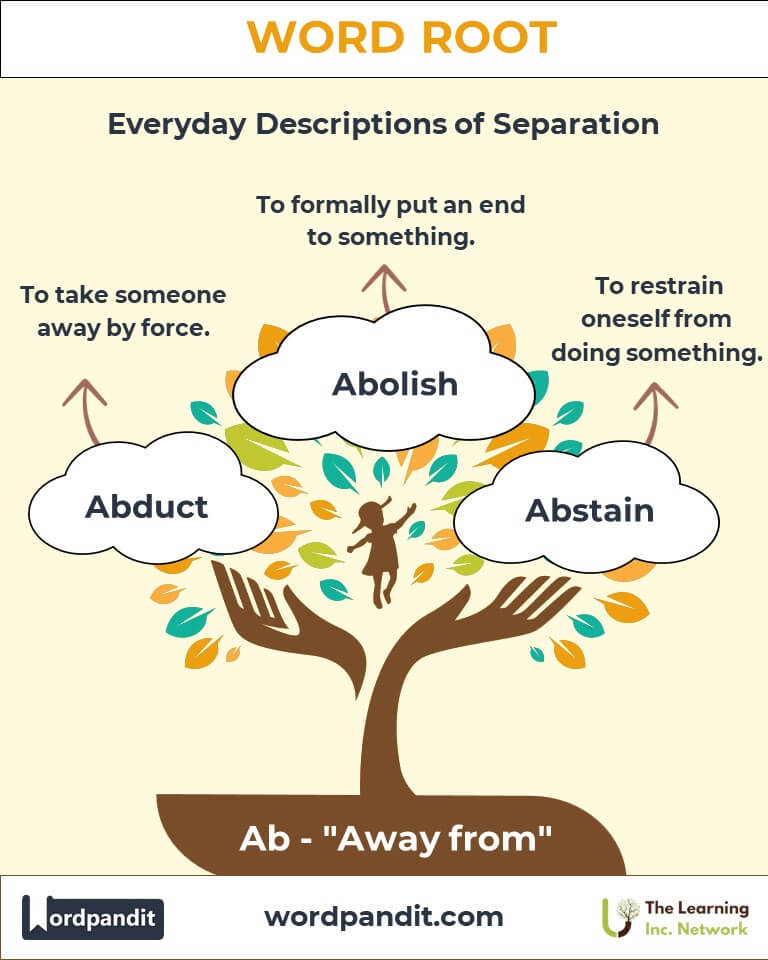
- Abduct (ab-duhkt)
- Definition: To take someone away by force.
- Example: "The novel tells the story of a hero who rescues a child abducted by villains."
- Abolish (ab-uh-lish)
- Definition: To formally put an end to something.
- Example: "The government abolished the outdated law."
- Abstain (ab-stayn)
- Definition: To restrain oneself from doing or enjoying something.
- Example: "He chose to abstain from voting to remain neutral."
- Absent (ab-sent)
- Definition: Not present or away.
- Example: "Many students were absent from school due to the flu outbreak."
"Ab" Through Time
1. Abstraction in Art and Philosophy
Originally meaning "drawn away," abstraction evolved into a cornerstone of modern art and philosophical discourse, signifying ideas detached from physical reality.
Shift: From describing physical removal to conceptual distancing.
2. Abolition Movements
The term "abolish" became a rallying cry for justice during the fight to end slavery and other oppressive systems.
Impact: Reflecting "ab" as a tool for societal change.
"Ab" in Specialized Fields
1. Medicine
Abnormality: Describes conditions deviating from the standard health parameters.
Example: "The scan revealed an abnormality in the patient’s brain structure."
2. Law and Politics
Abolish: Used in legal texts to denote the termination of practices or statutes.
Relevance: Central to legal reform and civil rights advancements.
3. Art and Literature
Abstract: Describes non-representational art and conceptual ideas in literature.
Application: Encourages interpretation and subjective understanding.
Illustrative Story: "Ab" in Action
In a bustling city, a young artist named Mia struggled to translate her emotions onto canvas. Frustrated by traditional methods, she turned to abstraction, letting "abstract" brushstrokes guide her journey. Her breakthrough came when a gallery showcased her "Abnormal Perspectives" series, challenging viewers to see beauty in the unconventional. Meanwhile, across town, a social reformer successfully campaigned to "abolish" outdated laws, proving that moving "away from" the norm often leads to progress.
Cultural Significance of "Ab"
The root "ab" resonates in cultural narratives of distancing and transformation. Whether in the abolition of oppressive systems or the abstract expression of emotions, "ab" symbolizes the courage to deviate and innovate. From the Renaissance to modernity, its presence in art, law, and science underscores the human drive to move away from limitations.

The "Ab" Family Tree
- Ad- (toward):
- Adapt: To adjust toward new conditions.
- Example: "She adapted quickly to her new environment."
- De- (down, away):
- Descend: To move down.
- Example: "The balloon slowly descended to the ground."
- Ex- (out):
- Exclude: To shut out.
- Example: "The policy excluded anyone without proper identification."
FAQs About the "Ab" Word Root
Q: What does "ab" mean?
A: The root "ab" comes from Latin, meaning "away from" or "off." It conveys the idea of separation, distancing, or deviation. This core meaning applies across various fields, from abstract ideas (separated from reality) to abnormal conditions (deviating from the norm).
Q: Is "ab" always a prefix?
A: Yes, "ab" functions primarily as a prefix in English. It attaches to other word parts to form terms that emphasize separation or movement away. Examples include "abstain" (to hold oneself away) and "absent" (being away).
Q: What does "abstract" mean, and how does it relate to "ab"?
A: "Abstract" combines "ab" (away from) with "tract" (drawn or pulled). It refers to concepts or ideas that are removed from physical or concrete reality. For instance, abstract art does not depict realistic scenes but instead focuses on shapes and emotions.
Q: What is the difference between "abnormal" and "aberrant"?
A: Both terms describe deviations, but "abnormal" refers to anything that differs from the standard, often implying undesirability (e.g., an abnormal heartbeat). "Aberrant" has a similar meaning but is more specific, often used in scientific or behavioral contexts to describe deviations from expected norms (e.g., aberrant behavior in biology).
Q: Can "ab" have positive connotations?
A: While "ab" often suggests separation or deviation, it can have positive meanings. For instance, "abolish" uses "ab" to signify the removal of something undesirable, such as oppressive laws or outdated practices.
Q: How is "ab" used in medical terminology?
A: In medicine, "ab" appears in terms like "abnormality" (deviation from healthy norms) and "ablation" (removal of tissue or parts of an organ). It signifies physical or functional separation.
Q: What does "abstain" mean in a legal or ethical context?
A: "Abstain" means to voluntarily refrain or hold oneself back from an action. In legal or ethical contexts, it often refers to choosing not to participate in a vote or decision to avoid conflicts of interest or maintain neutrality.
Test Your Knowledge: "Ab" Mastery Quiz
1. What does "ab" mean?
2. Which term means "not normal"?
3. What is an example of "ab" in law?
4. What does "abstract" mean in art?
5. Which "ab" word describes someone who refrains from something?
Conclusion: The Lingering Legacy of "Ab"
The root "ab" weaves a rich narrative of movement and deviation in language, symbolizing humanity’s quest to break free from constraints. Whether in abstract art, abnormal science, or the abolition of injustice, "ab" continues to shape how we express distance and transformation. Embrace the root "ab" as a reminder of the power of stepping away from the ordinary.














