Ad Word Root: The Root of Direction and Purpose in Language
Discover the dynamic root "Ad," derived from Latin, meaning "to" or "toward." From its use in everyday terms like "adhere" to specialized fields such as law and medicine, this root guides us toward understanding the flow and purpose embedded in language.
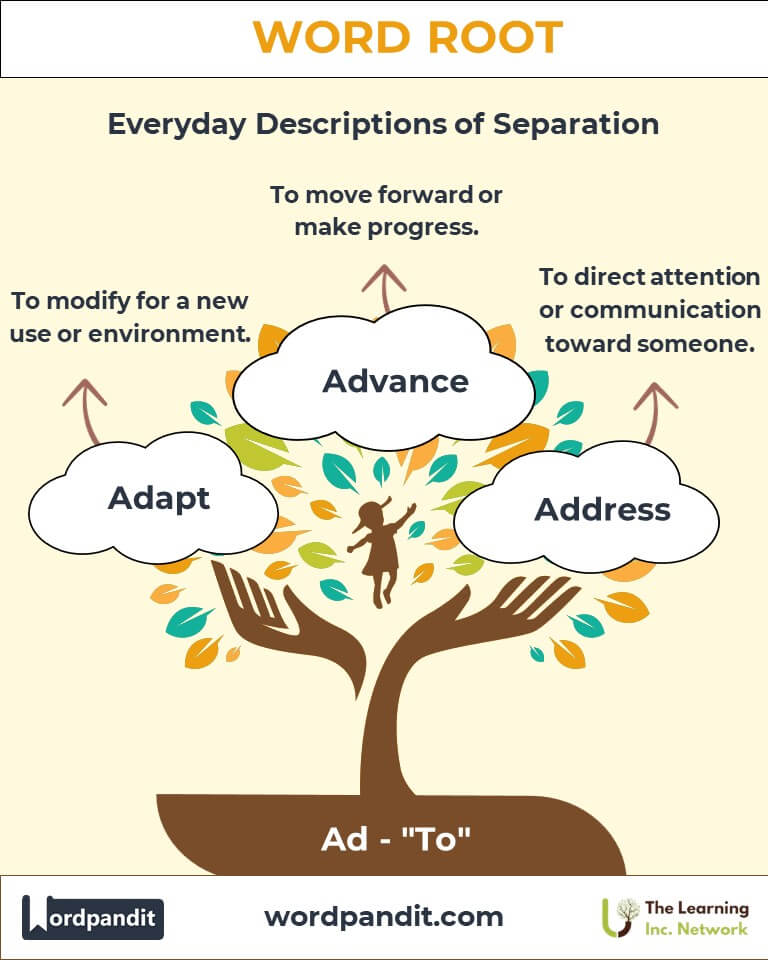
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Essence of "Ad"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Ad"
- Common "Ad"-Related Terms
- "Ad" Through Time
- "Ad" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Ad" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Ad"
- The "Ad" Family Tree
- FAQs About the Ad Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Ad Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Ad"
Introduction: The Essence of "Ad"
Imagine standing at a crossroads and deciding to move toward a destination. The root "Ad" encapsulates this act of purposeful movement, meaning "to" or "toward." Pronounced simply as "ad," it originates from Latin and has given rise to a plethora of words that signify motion, adherence, or proximity. From terms like "adjacent" (next to) to "adhere" (to stick to), this root bridges gaps, unites ideas, and directs actions.

Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "Ad" stems from Latin, where it denoted directionality—physically or metaphorically—toward a target. Over centuries, it became a versatile prefix, integrating into English through Middle French and Middle English. In ancient Rome, phrases like "ad astra" (to the stars) symbolized ambition and aspiration, a legacy that continues in expressions and technical terms today.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Ad"
Picture an arrow pointing toward a goal, with the word "Ad" written boldly on it. This image embodies movement and purpose.
Mnemonic Device: "Ad" advances action—always toward something!
Common "Ad"-Related Terms
- Adjacent (uh-jay-sent): Next to or adjoining something else.
- Example: "The two adjacent houses shared a backyard."
- Adhere (ad-heer): To stick firmly to a surface or a principle.
- Example: "She adhered to her values, even under pressure."
- Adapt (uh-dapt): To modify for a new use or environment.
- Example: "Animals adapt to their surroundings for survival."
- Advance (ad-vans): To move forward or make progress.
- Example: "The troops advanced toward the enemy lines."
- Address (uh-dres): To direct attention or communication toward someone.
- Example: "The CEO addressed the employees at the meeting."
"Ad" Through Time
The root "Ad" has evolved through its integration into English, often combining with other roots to form new meanings:
- Advert (Historic): Initially meant "to turn toward," now refers to drawing attention, especially in marketing.
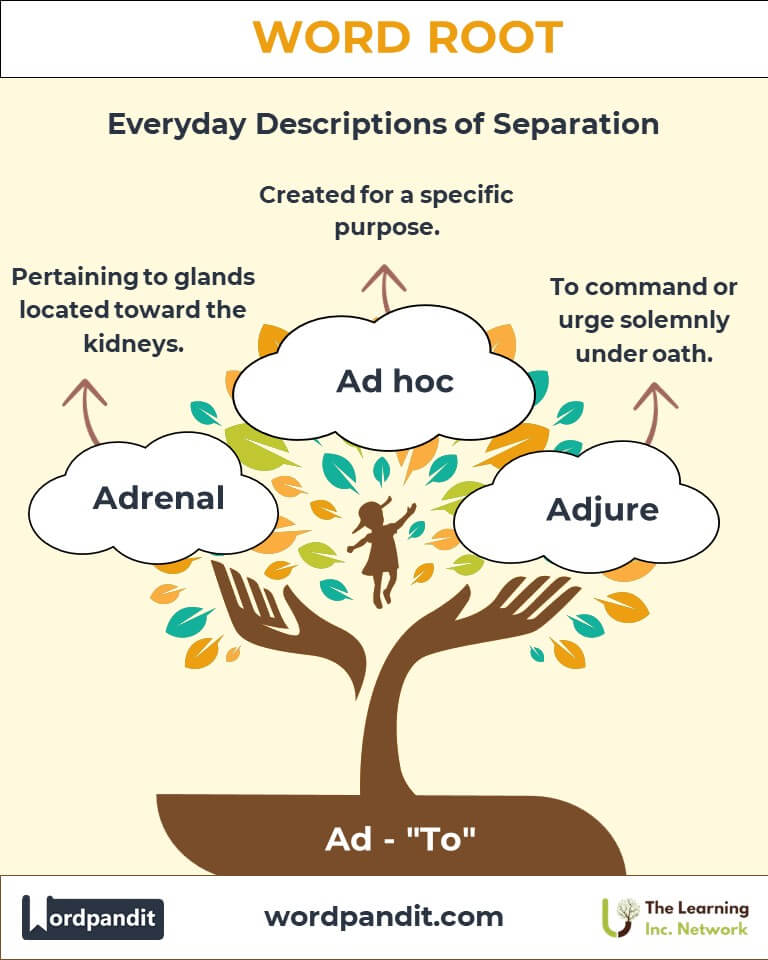
- Adjure (Legal): Used in formal oaths, illustrating how "Ad" signifies focused directionality in speech.
"Ad" in Specialized Fields
The root "Ad" finds applications across numerous disciplines:
- Medicine:
- Adrenal: Pertaining to glands located toward the kidneys.
- Example: "The adrenal glands play a critical role in hormone production."
- Adrenal: Pertaining to glands located toward the kidneys.
- Law:
- Ad hoc: Created for a specific purpose.
- Example: "The committee was formed ad hoc to address the emergency."
- Ad hoc: Created for a specific purpose.
- Education:
- Adaptation: The process of adjusting teaching methods to meet student needs.
- Example: "Curriculum adaptation ensures inclusivity."
- Adaptation: The process of adjusting teaching methods to meet student needs.
- Technology:
- Address: Refers to the location of data or a destination in computing.
- Example: "Ensure the correct IP address is entered for access."
- Address: Refers to the location of data or a destination in computing.
Illustrative Story: "Ad" in Action
Amira, a budding architect, was tasked with designing a city block. She adhered to environmental principles, ensuring every building was adjacent to green spaces. As her plans advanced, she adapted new techniques to make the project sustainable. On the project's completion, her dedication was addressed in an awards ceremony, showcasing how "Ad" words propelled her journey forward.
Cultural Significance of "Ad"
The root "Ad" has transcended its linguistic origins to become a symbol of connection and direction. Latin phrases like "Ad infinitum" (to infinity) permeate literature, philosophy, and even pop culture. The concept of moving "toward" a goal resonates universally, making "Ad" a bridge between languages, disciplines, and ideologies.

The "Ad" Family Tree
Exploring related roots expands the understanding of "Ad":
- Ac- (Latin variant of "Ad"):
- Accede: To agree or approach.
- Accumulate: To gather toward a mass.
- Ag- (Latin variant):
- Aggregate: To collect together.
- Aggrandize: To increase in power or influence.
- Ap- (Latin variant):
- Appoint: To assign to a position.
- Apply: To put effort toward a purpose.
FAQs About the Ac and Acr Word Roots
Q: What do "ac" and "acr" mean?
A: "Ac" and "acr" are derived from the Latin root "acer," which means sharp, bitter, or pointed. These roots are used to describe intensity or sharpness, whether in physical sensations, smells, tastes, or intellectual qualities. For instance, "acrid" refers to a sharp or bitter smell, while "acumen" describes sharpness of intellect.
Q: What is the origin of "acrimonious"?
A: The word "acrimonious" comes from the Latin term "acrimonia," which refers to sharpness or severity. It entered English to describe bitterness in speech or behavior. Acrimonious exchanges often convey hostility or sharp criticism, commonly seen in heated debates or arguments.
Q: How is "acute" used in medicine?
A: In medical terminology, "acute" describes conditions or diseases that arise suddenly and with significant intensity or severity. For example, "acute appendicitis" refers to a rapid onset of severe symptoms requiring immediate attention. It contrasts with "chronic," which refers to long-lasting conditions.
Q: Are "acrid" and "acerbic" synonyms?
A: While both words share the root meaning sharp or bitter, they differ in usage: "Acrid" typically refers to unpleasant smells or tastes, like the acrid odor of smoke. "Acerbic" describes sharpness or harshness in tone or behavior, such as acerbic remarks in a conversation.
Q: What does "acumen" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Acumen" refers to sharpness of insight, judgment, or understanding. It’s commonly used in professional contexts to praise someone's ability to make quick, effective decisions. For example, "Her financial acumen helped the company navigate a challenging market."
Q: What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
A: Acute describes something intense or severe that occurs suddenly, like an acute illness or acute pain. Chronic refers to conditions that develop over time and persist for a long duration, such as chronic back pain.
Q: How does "acrimonious" relate to interpersonal dynamics?
A: "Acrimonious" describes bitterness or hostility in interactions. Acrimonious disputes often arise in legal battles, political debates, or personal conflicts, characterized by sharp criticism and harsh tones.
Q: Can "acerbic" be positive?
A: While "acerbic" typically has a negative connotation, describing harsh or biting remarks, it can be positive in specific contexts. For example, an acerbic wit might be appreciated for its sharp humor or cleverness, especially in satire.
Test Your Knowledge: Ac and Acr Mastery Quiz
1. What does "acute" mean?
2. Which word describes a sharp smell?
3. What is "acrimony"?
4. What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
5. Which word best describes sharpness in tone?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Ad"
The root "Ad" continues to guide and inspire language, symbolizing motion and purpose across disciplines. Whether directing actions, adhering to values, or advancing goals, "Ad" unites us in our journey toward achievement. Explore its depths, and let it propel your understanding forward!














