Agr: Cultivating Connections Between Language and Agriculture
Discover the root "agr," derived from Latin, meaning "field." Words like agriculture and agrarian reflect its historical and modern significance in shaping civilizations. Explore how "agr" connects language, history, and science to our collective heritage of working the land.
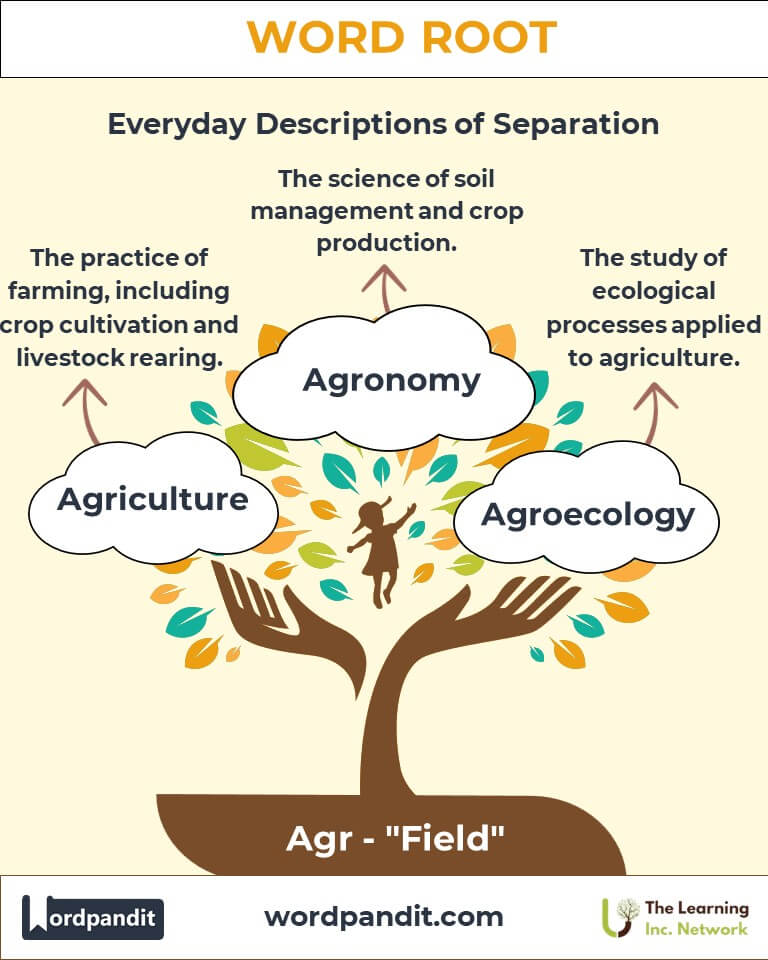
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Roots of "Agr"
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Agr"
- Common Agr-Related Terms
- "Agr" Through Time
- "Agr" in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: "Agr" in Action
- Cultural Significance of "Agr"
- The "Agr" Family Tree
- FAQs About the agr Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: agr Word Root Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Agr"
Introduction: The Roots of "Agr"
Picture a vast field, golden with ripe grain, embodying the essence of cultivation and sustenance. The root "agr" (pronounced ay-gr), meaning "field," represents humanity's enduring relationship with the land. Originating from Latin, it forms the backbone of terms central to farming, rural life, and land use. Words like agriculture and agrarian highlight its pivotal role in our lexicon and livelihoods.

Etymology and Historical Journey
"Agr" derives from the Latin word ager, meaning "field" or "land." In ancient Rome, the ager publicus referred to public lands, vital for agriculture and governance. As Latin evolved into Romance languages, "agr" persisted, influencing terms in science and society. In English, its legacy shines in words like agriculture (field cultivation) and agrarian (relating to rural life).
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of "Agr"
To remember "agr," visualize a farmer plowing a field, sowing seeds that symbolize the root's enduring connection to cultivation and growth.
Mnemonic Device: "AGR is where it all begins—fields of growth for food and words!"
Common Agr-Related Terms
- Agriculture (ag-rih-kuhl-chur): The practice of farming, including crop cultivation and livestock rearing.
Example: "Agriculture sustains billions by providing food and raw materials." - Agrarian (uh-gray-ree-uhn): Relating to rural or agricultural societies.
Example: "The agrarian lifestyle emphasizes a close connection to the land." - Agroecology (ag-roh-ee-kol-uh-jee): The study of ecological processes applied to agriculture.
Example: "Agroecology promotes sustainable farming practices." - Agronomy (ag-rah-nuh-mee): The science of soil management and crop production.
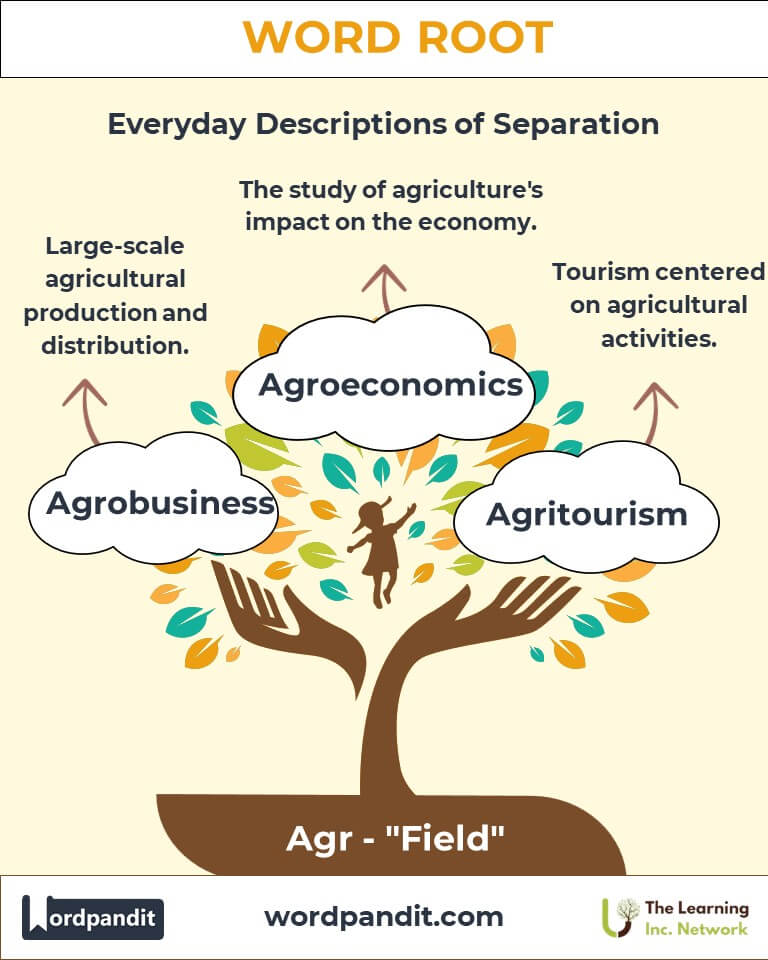
Example: "Advances in agronomy have revolutionized food production." - Agrobusiness (ag-roh-biz-nes): Large-scale agricultural production and distribution.
Example: "Agrobusiness dominates the global food industry."
"Agr" Through Time
- Ancient Roots: The Romans used "agr" in legal and administrative terms like ager publicus, reflecting land ownership and agricultural practices.
- Modern Growth: Terms like agrobusiness emerged in the 20th century, blending traditional farming with industrial-scale practices.
"Agr" in Specialized Fields
- Ecology:
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural systems for sustainability.
Example: "Agroforestry improves soil health and biodiversity."
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural systems for sustainability.
- Economics:
- Agroeconomics: The study of agriculture's impact on the economy.
Example: "Agroeconomics helps balance food security and market dynamics."
- Agroeconomics: The study of agriculture's impact on the economy.
- Education:
- Agricultural Science: Academic programs dedicated to farming innovations.
Example: "Agricultural science degrees prepare students for sustainable farming careers."
- Agricultural Science: Academic programs dedicated to farming innovations.
Illustrative Story: "Agr" in Action
In the fertile valley of Evergreen, a young agronomist named Clara worked tirelessly to improve soil fertility. Inspired by agroecology, she introduced crop rotation techniques that doubled yields while preserving the land. Her efforts not only boosted local agriculture but also united the agrarian community, demonstrating the enduring impact of "agr."
Cultural Significance of "Agr"
The root "agr" symbolizes humanity's bond with the land. From ancient myths celebrating harvests to modern movements advocating sustainable farming, "agr" reflects cultural values tied to the earth. Festivals like Thanksgiving and harvest celebrations honor this connection, underscoring its timeless relevance.

The "Agr" Family Tree
- Agri- (Latin, "field"):
- Agribusiness: Large-scale farming enterprises.
- Agritourism: Tourism centered on agricultural activities.
- Geo- (Greek, "earth"):
- Geography: Study of Earth's features.
- Geology: Study of Earth's physical structure.
- Rural- (Latin, "countryside"):
- Rural: Relating to the countryside.
- Rustic: Characteristic of rural life.
FAQs About the Ac and Acr Word Roots
Q: What do "ac" and "acr" mean?
A: "Ac" and "acr" are derived from the Latin root "acer," which means sharp, bitter, or pointed. These roots are used to describe intensity or sharpness, whether in physical sensations, smells, tastes, or intellectual qualities. For instance, "acrid" refers to a sharp or bitter smell, while "acumen" describes sharpness of intellect.
Q: What is the origin of "acrimonious"?
A: The word "acrimonious" comes from the Latin term "acrimonia," which refers to sharpness or severity. It entered English to describe bitterness in speech or behavior. Acrimonious exchanges often convey hostility or sharp criticism, commonly seen in heated debates or arguments.
Q: How is "acute" used in medicine?
A: In medical terminology, "acute" describes conditions or diseases that arise suddenly and with significant intensity or severity. For example, "acute appendicitis" refers to a rapid onset of severe symptoms requiring immediate attention. It contrasts with "chronic," which refers to long-lasting conditions.
Q: Are "acrid" and "acerbic" synonyms?
A: While both words share the root meaning sharp or bitter, they differ in usage: "Acrid" typically refers to unpleasant smells or tastes, like the acrid odor of smoke. "Acerbic" describes sharpness or harshness in tone or behavior, such as acerbic remarks in a conversation.
Q: What does "acumen" mean, and how is it used?
A: "Acumen" refers to sharpness of insight, judgment, or understanding. It’s commonly used in professional contexts to praise someone's ability to make quick, effective decisions. For example, "Her financial acumen helped the company navigate a challenging market."
Q: What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
A: Acute describes something intense or severe that occurs suddenly, like an acute illness or acute pain. Chronic refers to conditions that develop over time and persist for a long duration, such as chronic back pain.
Q: How does "acrimonious" relate to interpersonal dynamics?
A: "Acrimonious" describes bitterness or hostility in interactions. Acrimonious disputes often arise in legal battles, political debates, or personal conflicts, characterized by sharp criticism and harsh tones.
Q: Can "acerbic" be positive?
A: While "acerbic" typically has a negative connotation, describing harsh or biting remarks, it can be positive in specific contexts. For example, an acerbic wit might be appreciated for its sharp humor or cleverness, especially in satire.
Test Your Knowledge: Ac and Acr Mastery Quiz
1. What does "acute" mean?
2. Which word describes a sharp smell?
3. What is "acrimony"?
4. What is the difference between "acute" and "chronic"?
5. Which word best describes sharpness in tone?
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of "Agr"
The root "agr" encapsulates humanity's agricultural heritage and evolving connection with the land. From ancient fields to modern sustainability movements, its impact spans language, culture, and science. As we strive for a balanced relationship with nature, "agr" reminds us of the fertile ground that sustains life and civilization.














